Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):729-744
To review the current state of knowledge on the impact of the surgical treatment on the sexual function and dyspareunia of deep endometriosis patients.
A systematic review was conducted in accordance with the Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. We conducted systematic searches in the PubMed, EMBASE, LILACS, and Web of Science databases from inception until December 2022. The eligibility criteria were studies including: preoperative and postoperative comparative analyses; patients with a diagnosis of deep endometriosis; and questionnaires to measure sexual quality of life.
Two reviewers screened and reviewed 1,100 full-text articles to analyze sexual function after the surgical treatment for deep endometriosis. The risk of bias was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for observational studies and the Cochrane Collaboration's tool for randomized controlled trials. The present study was registered at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; registration CRD42021289742).
General variables about the studies, the surgical technique, complementary treatments, and questionnaires were inserted in an Microsoft Excel 2010 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, United States) spreadsheet.
We included 20 studies in which the videolaparoscopy technique was used for the excision of deep infiltrating endometriosis. A meta-analysis could not be performed due to the substantial heterogeneity among the studies. Classes III and IV of the revised American Fertility Society classification were predominant and multiple surgical techniques for the treatment of endometriosis were performed. Standardized and validated questionnaires were applied to evaluate sexual function.
Laparoscopic surgery is a complex procedure that involves multiple organs, and it has been proved to be effective in improving sexual function and dyspareunia in women with deep infiltrating endometriosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(6):319-324
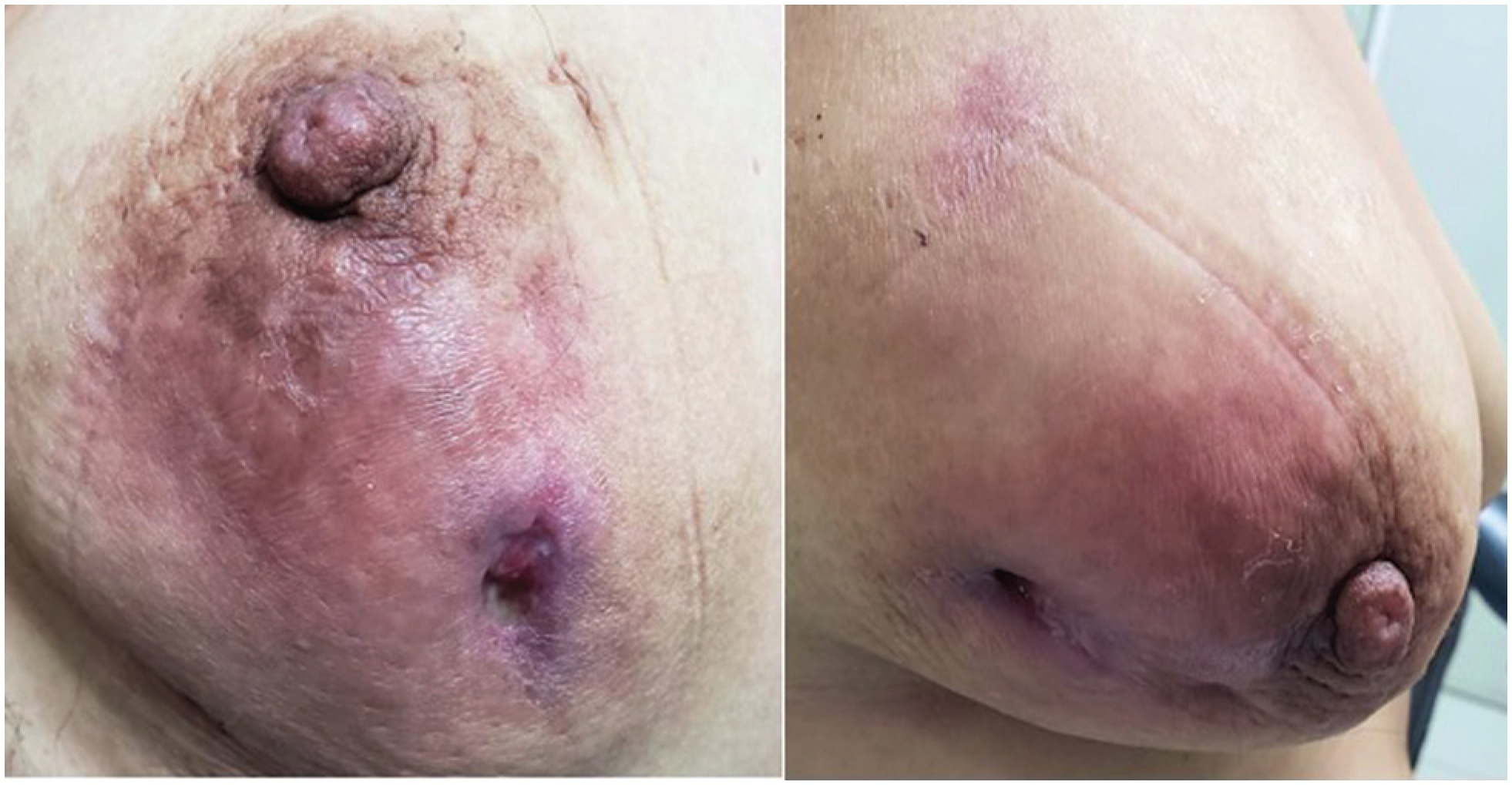
Reporting our experience of the management and treatment of Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM) in a low-income country by describing patients characteristics and therapy with emphasis on conservative surgical excision and postoperative care as the cornerstone of treatment.
A retrospective cohort of women with histopathological diagnosis of IGM from 2014 to 2018 at Instituto Nacional Materno Perinatal in Lima, Peru. Patients' characteristics, clinical presentation, treatment, management, postoperative care, and follow-up were analyzed.
Thirty-eight patients with histopathological diagnosis of IGM were identified. Their average age was 35.9 years and 23 (60.5%) reported previous use of hormonal contraceptives. Nine (23.7%) patients had chronic mastitis with previous treatment. The time from the onset of symptoms to the first clinic consult was 5.1 months on average. Twenty-one (55.3%) patients had the lesion in the right breast, with a mean size of 6.9 cm. Conservative surgical excision was performed in all patients. Additionally, 86.8% required corticosteroids and 78.9% were treated with antibiotics. Complete remission was obtained at 141 days on average (range 44 to 292 days). Six (15.8%) women reported ipsilateral recurrence and 5 (13.2%), contralateral. The latency time was 25.5 months on average.
The conservative surgical treatment demonstrated and close follow-up made for a high cure rate, but with recurrence similar to that reported in the literature. Use of gloves is an alternative to manage post operative wounds in a low-income country. The most frequent adverse effect was breast surgical scar.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1117-1121
Although obesity can result in high morbidity and mortality in surgical outcomes because of multiple comorbidities, determinants of outcome in obese patients who underwent endometrial cancer surgery remain unclear. The aim of this study is to assess the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and surgical outcomes in obese patients with endometrial cancer.
An institutional retrospective review of the demographic details, clinical characteristics, and follow-up data of 142 patients with endometrial cancer who underwent surgery during a 72-month period was performed. The patients were divided into three groups based on their BMI; patients with BMI < 25 were identified as normal weight, patients with BMI between 25 and 30 were accepted as overweight, and those with BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 were identified as obese. The groups' demographic and clinical variables were compared.
Of the 142 patients, 42 were in the normal weight group, 55 in the overweight group, and 45 in the obese group. Age, surgical procedures, blood loss, preoperative health status, and metastatic lymph nodes did not show a significant difference between groups. However, surgery time and total lymph nodes were higher in the obese group. (p = 0.02, p = 0.00, and p = 0.00, respectively). Common complications were anemia, fever, intestinal injury, deep vein thrombosis, fascial dehiscence and urinary infection. There was no significant difference according to the complications.
Our results indicated that higher BMI was significantly associated with a longer duration of endometrial cancer surgery. Minimally invasive surgeries and conventional laparotomy could be performed safely in obese patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1014-1020
Cervical pregnancy is challenging for the medical community, as it is potentially fatal. The treatment can be medical or surgical; however, there are no protocols that establish the best option for each case. The objective of the present study was to describe the cases of cervical pregnancy admitted to a tertiary university hospital over a period of 18 years.
A retrospective study based on a review of the medical records of all cervical pregnancies admitted to the Women's Hospital at Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Southeastern Brazil, from 2000 to 2018.
We identified 13 cases of cervical pregnancy out of a total of 673 ectopic pregnancies; only 1 case was initially treated with surgery because of hemodynamic instability. Of the 12 cases treated conservatively, 7 were treated with single-dose intramuscular methotrexate, 1, with intravenous and intramuscular methotrexate, 1, with intravenous methotrexate, 1, with 2 doses of intramuscular methotrexate, and 2, with intra-amniotic methotrexate. Of these cases, one had a therapeutic failure that required a hysterectomy. Two women received blood transfusions. Four women required cervical tamponade with a Foley catheter balloon for hemostasis. There was no fatal outcome.
Cervical pregnancy is a rare and challenging condition from diagnosis to treatment. Conservative treatment was the primary method of therapy used, with satisfactory results. In cases of increased bleeding, cervical curettage was the initial treatment, and it was associated with the use of a cervical balloon for hemostasis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):511-518
The Burch procedure (1961) was considered the gold standard treatment for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) before the midurethral slings (MUSs) were introduced, in 2001.
This historical perspective of the Burch’s timeline can encourage urogynecological surgeons to master the Burch technique as one of the options for surgical treatment of SUI.
Criteria A bibliographic search was performed in the PubMed and National Library of Medicine (NIH) databases with the terms Burch colposuspension AND history AND stress urinary incontinence in the last 20 years. The original article by Burch (1961) was included. The references were read by three authors. The exclusion criterion was studies in non-English languages. Biomedical Library Special Collections were included as historical relevant search.
Some modifications of the technique have been made since the Burch procedure was first described. The interest in this technique has been increasing due to the negative publicity associated with vaginal synthetic mesh products. Twenty-nine relevant articles were included in the present review article, and numerous trials have compared Burch colposuspension with MUS.
This historical perspective enables the scientific community to review a standardized technique for SUI. Burch colposuspension should be considered an appropriate surgical treatment for women with SUI, and an option in urogynecological training programs worldwide.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):800-804
In recent years, there has been an increase in the incidence of ectopic pregnancies; therefore, it is important for tertiary centers to report their approaches and outcomes to expand and improve treatment modalities. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the general characteristics, treatment and outcomes of cases diagnosed with ectopic pregnancy.
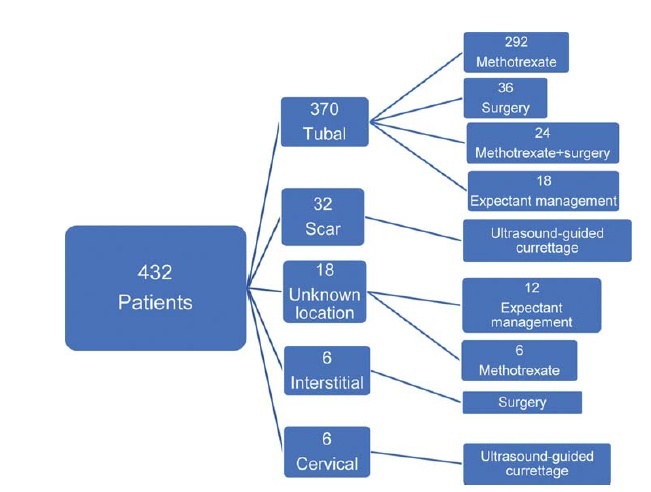
In total, 432 patients treated for ectopic pregnancy between February 2016 and June 2019 were retrospectively evaluated.
Overall, 370 patients had tubal pregnancy, 32 had cesarean scar pregnancy, 18 had pregnancy of unknown location, 6 had cervical pregnancy, and 6 had interstitial pregnancy. The most important risk factors were advanced age (> 35 years; prevalence: 31.2%) and smoking (prevalence: 27.1%). Thirty patients who did not have any symptoms of rupture and whose human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) levels were ≤ 200 mIU/ml were followed-up with expectant management, while 316 patients whose β-hCG levels were between 1,500 mIU/ml and 5,000 mIU/ml did not have an intrauterine gestational sac on the transvaginal or abdominal ultrasound, did not demonstrate findings of rupture, and were treated with a systemic multi-dose methotrexate treatment protocol. In total, 24 patients who did not respond to the medical treatment, 20 patients whose β-hCG levels were > 5,000 mIU/ml, 16 patients who had shown symptoms of rupture at the initial presentation, and 6 patients diagnosed with interstitial pregnancy underwent surgery. Patients with cervical and scar pregnancies underwent ultrasound-guided curettage, and no additional treatment was needed.
The fertility status of the patients, the clinical and laboratory findings, and the levels of β-hCG are the factors that must be considered in planning the appropriate treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(8):428-434
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000800008
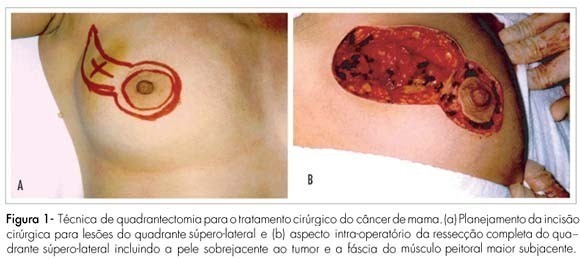
The surgical strategy for breast cancer treatment has changed considerably over the last decade. The breast conserving surgery (BCS) is the standard treatment for early stage breast cancer nowadays. With the current population breast cancer screening programs and the emerging use of systemic neoadjuvant therapy, an increasing number of patients have been eligible to BCS. However, several specific factors must be considered for the therapeutic planning for these patients. This review provides a surgical methodology overview for the BCS in breast carcinoma.