Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):454-459
Streptococcus agalactiae is an important pathogen in neonates and pregnant women. Neonatal invasive infections due to S. agalactiae are life-threatening and preventive strategies for this challenge of human have become a concern. The aim of the present study was to determine the prevalence of rectovaginal colonization, related risk factors and antibiotic resistance pattern of S. agalactiae among pregnant women in Iran.
The present study was performed on 240 pregnant women. Vaginal and rectal swabs were obtained from all of the women and then were transferred to the laboratory. The isolation and identification of S. agalactiae was performed by standard microbiological tests and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay. The antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of the isolates were determined by the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion. Polymerase chain reaction was used to detect ermB and mefA genes in erythromycin-nonsusceptible isolates.
Out of 240 pregnant women, 16 cases (6.7%) were colonized by S. agalactiae. There is no significant association between demographic-obstetric factors and maternal S. agalactiae colonization in the pregnant women. Linezolid, vancomycin and ampicillin were the most effective antibiotics against S. agalactiae. The ermB gene was present in 6 (35.29%) S. agalactiae isolates. However, the mefA gene was not detected in any of the isolates.
Given the relatively significant prevalence of S. agalactiae colonization in the pregnant women in the present study and the risk of serious neonatal infections, the screening of pregnant mothers for the bacteria seems necessary. Our findings highlight the importance of appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis during pregnancy for the prevention of early onset S. agalactiae-neonatal infection and comorbidity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(12):544-549
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001200003
PURPOSE: To describe the epidemiological cases and microbiological profile of Streptococcus agalactiae serotypes isolated from infected newborns of a Women's Health Reference Centre of Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil. METHODS: Cross-sectional laboratory survey conducted from January 2007 to December 2011. The newborns' strains, isolated from blood and cerebrospinal fluid samples, were screened by hemolysis on blood ágar plates, Gram stain, catalase test, CAMP test, hippurate hydrolysis or by microbiological automation: Vitek 2 BioMerieux®. They were typed by PCR, successively using specific primers for species and nine serotypes of S. agalactiae. RESULTS: Seven blood samples, one cerebrospinal fluid sample and an ocular sample, were isolated from nine newborns with infections caused by S. agalactiae, including seven cases of early onset and two of late onset. Only one of these cases was positive for paired mother-child samples. Considering that 13,749 deliveries were performed during the study period, the incidence was 0.5 cases of GBS infections of early onset per 1 thousand live births (or 0.6 per 1 thousand, including two cases of late onset) with 1, 3, 2, zero and 3 cases (one early and two late onset cases), respectively, for the years from 2007 to 2011. It was possible to apply PCR to seven of nine samples, two each of serotypes Ia and V and three of serotype III, one from a newborn and the other two from a paired mother-child sample. CONCLUSIONS: Although the sample was limited, the serotypes found are the most prevalent in the literature, but different from the other few Brazilian studies available, except for type Ia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(12):395-400
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001200004
PURPOSE: To assess the prevalence of Streptococcus agalactiae, a Group B streptococcus, in pregnant women, and their possible risk factors, as well as the impact of perinatal colonization and antimicrobial susceptibility. METHODS: We evaluated 213 pregnant women from 20 weeks of gestation, regardless of risk factors, attending a tertiary teaching hospital. The technique used was a single sterile swab to collect secretions from the vaginal and perianal regions. The newly obtained samples were stored in Stuart transport medium and taken to the laboratory, where they were inoculated in Todd-Hewitt selective medium supplemented with Gentamicin (8 ug/mL) and nalidixic acid (15 ug/mL), with subsequent cultivation on blood agar plates. The materials were tested with Gram, catalase with hydrogen peroxide and CAMP (Christie, Atkins, Munch-Petersen), and results were serologically confirmed with the Streptococcal Grouping Kit, Oxoid®. The positive samples were tested for antimicrobial susceptibility. We also assessed socioeconomic, reproductive, clinical, and obstetric variables, and newborn care. Statistical analysis was performed with Epi-Info 6.04. RESULTS: The prevalence of colonization obtained by field tests was 9.8% by CAMP test, but only 4.2% by serology. The only protective factor was white skin color (p=0.01, 0.45>OR>0.94, 95%CI). There was no difference in prevalence of Group B streptococcus regarding other reproductive and obstetric variables. Infection occurred in only one of the newborns from colonized mothers; although it was revealed infection with Pseudomonas spp. High resistance to ampicillin (4/9), cephalothin (4/9), penicillin (4/9), erythromycin (3/9), clindamycin (7/9), and cloramphenicol (1/9) was detected. CONCLUSIONS: The infection rate was lower than that found in other studies, although a high rate of resistance to antibiotics commonly used for treatment was detected. Since there are no studies on the prevalence of Group B streptococcus in Ceará, we cannot perform a comparative analysis of the population, and further studies are needed with geographically similar groups to validate these results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(8):397-403
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000800005
PURPOSE: to indentify the prevalence and risk factors of maternal colonization by group B streptococcus (GBS) in pregnant women with premature labor (PL) and/or premature membrane rupture (PMR). METHODS: two anal and two vaginal swabs were collected from 203 pregnant women with diagnosis of PL or PMR assisted at the practice along one year. Pregnant women with imminent labor at admission were excluded. One swab of each source was placed in a transfer milieu and sent for culture in blood-agar plates; the two remaining swabs were incubated for 24 hours in Todd-Hewitt milieu for further sowing in blood-agar plates. Risk factors were analyzed by the chi-square test, Student's t-test (p-value set at 0.05 and 95% confidence interval) and logistic regression. The following variables were analyzed: age, race, parity and mother schooling; culture results by source and type of culture; admission diagnosis; gestational age at admission; asymptomatic bacteriuria; gestational age at delivery; type of delivery; neonatal GBS colonization rate and immediate neonatal condition. RESULTS: prevalence of maternal GBS colonization was 27.6% (56 cases). The colonization rates according to gestational complications were 30% for PMR, 25.2% for PL and 17.8% for PL + PMR. Univariate analysis has shown that the variables Caucasian race, low level of schooling and bacteriuria were associated with higher colonization rates. Multivariate analysis showed that the presence of urinary infection was the only variable associated with maternal colonization. The GBS detection rate was significantly higher with the use of a selective milieu and collection from both anal and vaginal sources. The neonatal colonization rate was 3.1%. Two cases of early sepsis by GBS occurred in the sample, with prevalence of 10.8 cases per one thousand live births and 50% mortality rate. CONCLUSION: the studied sample showed high maternal colonization rates by Streptococcus agalactiae. To increase GBS detection rate, it is necessary to use a selective culture milieu and to combine anal-rectal and vaginal cultures. There was a high incidence of early neonatal sepsis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(8):393-399
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000800004
PURPOSE: to study cervical colonization in women with preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes. METHODS: two hundred and twelve pregnant women with preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes were studied. Two cervical samples from each woman were collected and bacterioscopy and culture were performed. Association of cervical microorganisms and urinary tract infection, chorioamnionitis, fetal stress, antibiotic use, prematurity, neonatal infection, and neonatal death were evaluated. RESULTS: the prevalence of endocervical colonization was 14.2% (CI95%=9.5-18.9%), with similar results in preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes. Group B streptococcus was the most prevalent organism (9.4%). Other organisms isolated were Candida sp, Streptococcus sp, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli and Enterococcus sp. The most common findings of bacterioscopy were a reduced number of lactobacilli and a great number of leukocytes. Endocervical colonization was associated with a higher occurrence of urinary tract infection (23.8 versus 5.4%; p<0.01), early-onset neonatal infection (25.0 versus 7.3%; p<0.01) and neonatal mortality (two cases in colonized women; p<0.02) when compared with a negative culture of endocervical mucus. CONCLUSIONS: this study showed high prevalence of endocervical colonization despite the use of a nonselective culture media. The main microorganism isolated was group B streptococcus, but other organisms were present in one third of the studied population. More studies are needed to evaluate the influence of endocervical colonization on obstetrical outcome and on neonatal infection and mortality.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(6):274-280
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000600002
PURPOSE: to assess the prevalence of group B streptococcus colonization (GBS) in pregnant women in prodrome or in labor. METHODS: vaginal and rectal cultures were collected from 201 pregnant women, in the admission sector of a public maternity center in the northeast region of Brazil (São Luís, Maranhão). The samples obtained were inoculated in a Todd-Hewith's selective culture medium and after that they were sub-cultivated in blood-agar plates. The CAMP (Christie, Atkins, Munch-Petersen) test was used to identify GBS, which was then serologically confirmed by the BioMérieux Api 20 Strep kit microtest. GBS positive samples were submitted to an antibiotic sensitivity test. Sociodemographic variables, gynecological-obstetrical antecedents, and perinatal outcomes were studied. The Epi-Info 3.3.2 programs from World Health Organization and Statistical Package for Social Sciences 14.0 version were used for the statistical analysis. The prevalence ratio was used as risk measure, considering p<0.05 as significance level, and accepting 80% power. RESULTS: the prevalence of SGB colonization in the mothers was 20.4%. There was no association between the sociodemographic variables or gynecological-obstetrical antecedents and a larger presence of SGB colonization. There were two cases of infectious outbreak among neonatal babies from colonized mothers, but hemocultures resulted negative. High resistance rates were found for the following antibiotics: clindamycin, 25.4%; erythromycin, 23.4% and ceftriaxone, 12.7%. CONCLUSIONS: the prevalence of SGB colonization was high among the mothers, similar to what had been described in other studies. The elevated rates of antimicrobial resistance, especially to ceftriaxone indicate the need for further studies to determine the serology of this agent and of orientation protocols for rational use of antimicrobials.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(10):575-579
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001000002
PURPOSE: to verify the occurrence of colonization by Streptococcus agalactiae in pregnant women attended at the prenatal outpatient clinic of the Teaching Maternity Hospital of Rio de Janeiro University (UFRJ) and to evaluate the susceptibility of the isolates to antimicrobial agents. METHODS: a total of 167 pregnant women between the 32nd and 41st week of gestation, regardless of risk factors, attended at the antenatal clinic between February 2003 and February 2004, were evaluated. The vaginal/anal material, collected by the same swab, was inoculated in Todd-Hewitt broth to which nalidixic acid (15 µg/mL) and gentamicin (8 µg/mL) were added, with following subcultures onto sheep blood-agar. Identification was carried out observing colony morphology and beta-hemolysis type on blood-agar, catalase, cAMP, and serological tests. The antimicrobial susceptibility testing used agar diffusion and agar dilution methods. Statistical analysis was performed by the chi2 test with the level of significance set at p<0,05. RESULTS: the frequency of colonization was 19.2%, with no significant differences when age, number of gestations, number of abortions and the presence or absence of diabetes mellitus were compared (p>0.05). All 32 isolated strains were susceptible to penicillin, cefotaxime, ofloxacin, chloramphenicol, vancomycin and meropenem. Resistance to erythromycin and clindamycin was detected in 9.4 and 6.2% of the isolates, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: the relatively high incidence (19.2%) of colonization by S. agalactiae among the evaluated pregnant women and the recovery of antimicrobial resistant strains, especially those recommended in cases of penicillin allergy, emphasize the importance, for a correct prevention of neonatal infections, of detecting colonization at the end of pregnancy and evaluating antimicrobial susceptibility.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(4):174-180
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000400003
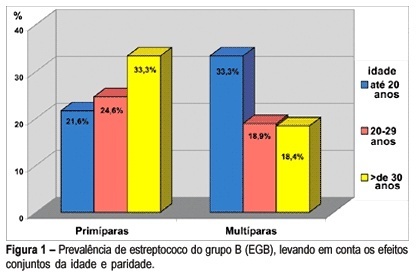
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of group B Streptococcus (GBS) in pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy and explore the factors potentially associated with colonization. METHODS: a sample of 273 pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy, from the prenatal care center in Southern Brasil, was investigated. Vaginal and anorectal samples were collected and innoculated in Todd-Hewitt selective broth supplemented with 10 µg/mL colistin and 15 µg/mL nalidixic acid and afterwards cultured on defibrinated sheep blood agar plates. All suspected colonies were submitted to the agglutination test for detection of the specific group B antigen. The Camp test was used for GBS identification in non-hemolytic varieties. Demographic, socioeconomic, reproductive, and clinico-obstetric data were also analyzed. Prevalence ratio (PR) was used as risk measurement. Confidence interval was considered significant at the level of 95% (alpha=0.05). RESULTS: prevalence of Streptococcus (GBS) colonization amounted to 21.6% (59), 9.9% (27) of pregnant women showing positivity in both sites; vaginal site colonization was found in 6.95% (19) of the women and 4.75% (13) of the samples showed positivity only in the anal site. GBS prevalence was slightly higher in pregnant women under 20 years, in those with less schooling and in primiparae and was twice as high among those who did not reported spontaneous abortion, but with no statistical significance. No difference was found in GBS prevalence according to the history of sexually transmittted diseases and tabagism. When analyzed together, the factors detected as potentially associated with colonization by GBS were: primiparae over 30 years (PR=1.55) and women with more than one sexual partner and increased frequency of sexual activity (p<0.05) (55,6 vs 20.5%; p<0.05). No difference regarding prevalence was found to exist in relation to the history of sexually transmitted diseases, previous spontaneous abortion and tabagism. CONCLUSION: these results confirm the need for routine collection for GBS culture from both sites (vaginal and anal) in all pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy.