-
Original Article
Assessing Endoscopic Suture Performance of Gynecology and Obstetrics Residents Following Methodic Training
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(10):603-608
12-11-2023
Summary
Original ArticleAssessing Endoscopic Suture Performance of Gynecology and Obstetrics Residents Following Methodic Training
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(10):603-608
12-11-2023Views174See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the performance of residents in gynecology and obstetrics before and after practicing laparoscopic sutures, to establish when the training shows the best results, in addition to comparing whether being in different years of residency influences this progression.
Methods
A prospective cohort study involving 32 medical residents evaluated with a pretest to establish their previous knowledge in laparoscopic suture. This test consisted of knotting two wires, one made of polypropylene and the other of polyglactin, with a blocking sequence of five semi-knots. We set a 30-minute limit to complete the task. Then, the residents held four training meetings, focusing on suture, Gladiator rule, knot, and symmetries, in addition to executing blocking sequences. A second test to establish progress was performed.
Results
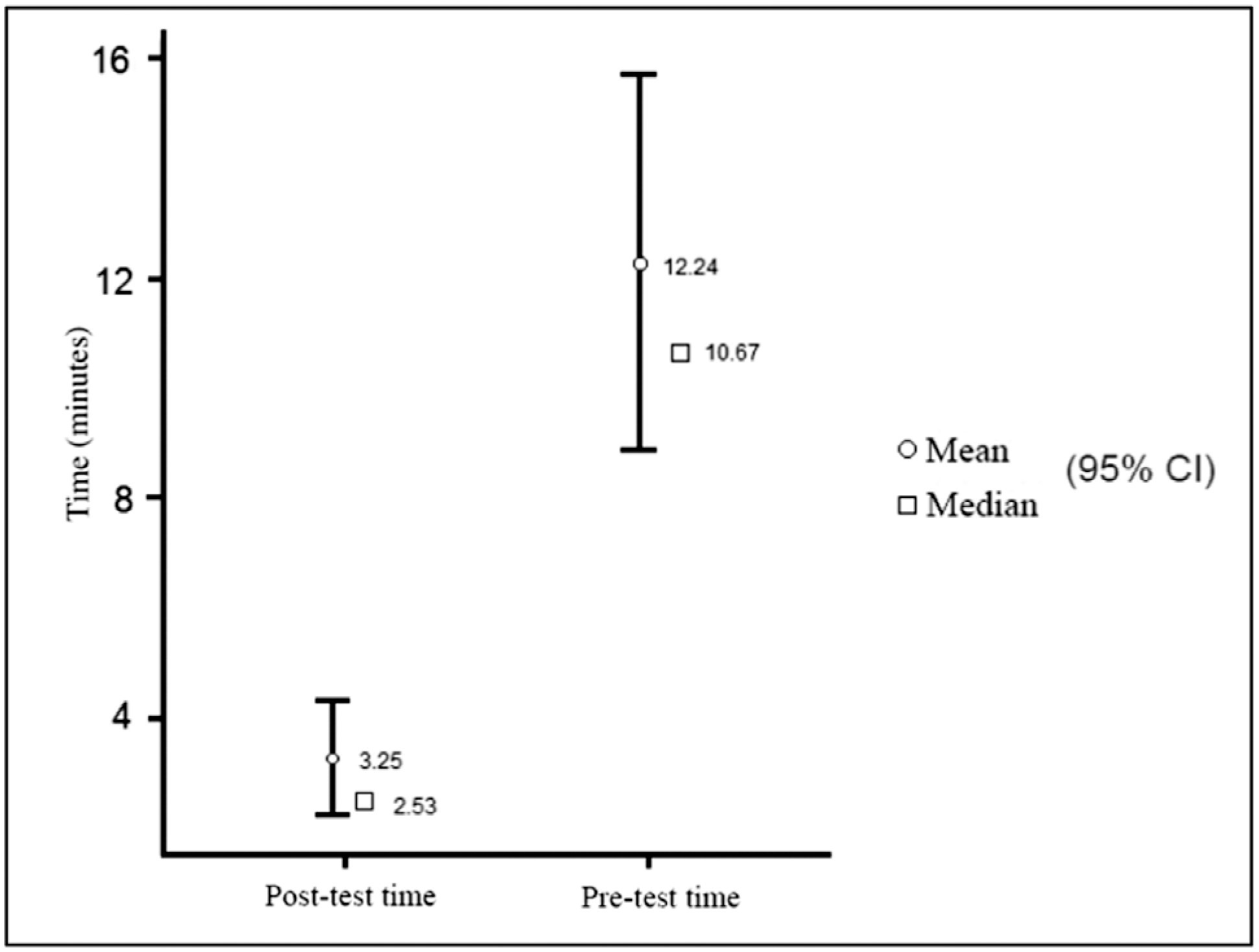
Regarding the time spent to make the stiches using polyglactin wire, a statistically significant time improvement (p< 0.01) was observed, with a 10.67-minute pretraining median (mean 12.24 minutes) and a 2.53-minute posttraining median (mean 3.25 minutes). Regarding the stitches with polypropylene wire, a statistically significant time improvement (p< 0.05) was also observed, with a 9.38-minute pretraining median (mean 15.43 minutes) and a 3.65-minute posttraining median (mean 4.54 minutes). A total of 64.2% of the residents had been able to make the knot with polypropylene previously. One hundred percent were able to complete the task in the posttest.
Conclusion
Model training using the Gladiator rule for laparoscopic suture improves the knotting time with statistically similar performance, regardless of the year of residency, after systematic training.
-
Original Article
Clinical Simulation in the Training of Obstetrics and Gynecology Resident from the Perspective of Medical Residency Programs
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):266-272
08-07-2023
Summary
Original ArticleClinical Simulation in the Training of Obstetrics and Gynecology Resident from the Perspective of Medical Residency Programs
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):266-272
08-07-2023Views115Abstract
Objective
This study analyzes the role of clinical simulation in internal medical residency programs (IMRP) in Obstetrics and Gynecology (OB/GYN), attributed by the supervisors, in the training of residents in the city of São Paulo (SP).
Methods
Cross-sectional descriptive, qualitative, and exploratory approach. Semi-structured interviews were performed with ten supervisors of Medical Residency programs in Obstetrics and Gynecology. Interviews were analyzed by means of content analysis under the thematic modality, starting with the core the role of clinical simulation in Obstetrics and Gynecology Medical Residency Programs.
Results
Supervisors view Clinical simulation as: a complementary tool for the teaching and learning process, a possibility of a safe teaching and learning environment, an opportunity to learn from mistakes, a support for professional practice committed to patient safety, a learning scenario for teamwork, a scenario for reflection on the work process in Obstetrics and Gynecology, a scenario for evaluative processes in the medical residency. Still according to supervisors, Clinical Simulation favors decision-making and encourages the resident participation in activities.
Conclusion
Supervisors recognize Clinical Simulation as a powerful pedagogical tool in the learning process of resident doctors in Obstetrics and Gynecology Residency Programs.
Key-words Health human resource traininginternship and residencyobstetrics and gynecology department hospitalpatient safetysimulation trainingSee more -
Original Article
A Simple, Reproducible and Low-cost Simulator for Teaching Surgical Techniques to Repair Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injuries
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):465-470
08-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleA Simple, Reproducible and Low-cost Simulator for Teaching Surgical Techniques to Repair Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injuries
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):465-470
08-01-2018Views159See moreAbstract
Objective
To describe and evaluate the use of a simple, low-cost, and reproducible simulator for teaching the repair of obstetric anal sphincter injuries (OASIS).
Methods
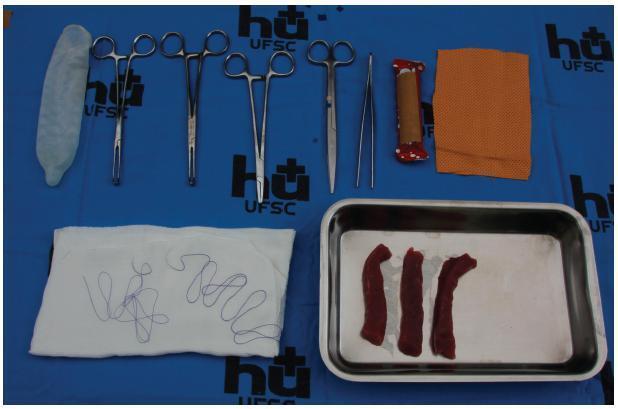
Twenty resident doctors in obstetrics and gynecology and four obstetricians participated in the simulation. A fourth-degree tear model was created using lowcost materials (condom simulating the rectal mucosa, cotton tissue simulating the internal anal sphincter, and bovine meat simulating the external anal sphincter). The simulator was initially assembled with the aid of anatomical photos to study the anatomy and meaning of each component of the model. The laceration was created and repaired, using end-to-end or overlapping application techniques.
Results
The model cost less than R$ 10.00 and was assembled without difficulty, which improved the knowledge of the participants of anatomy and physiology. The sutures of the layers (rectal mucosa, internal sphincter, and external sphincter) were performed in keeping with the surgical technique. All participants were satisfied with the simulation and felt it improved their knowledge and skills. Between 3 and 6 months after the training, 7 participants witnessed severe lacerations in their practice and reported that the simulation was useful for surgical correction.
Conclusion
The use of a simulator for repair training in OASIS is affordable (low-cost and easy to perform). The simulation seems to improve the knowledge and surgical skills necessary to repair severe lacerations. Further systematized studies should be performed for evaluation.
-
Original Article
Breaking Bad News Training Program Based on Video Reviews and SPIKES Strategy: What do Perinatology Residents Think about It?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):552-559
10-01-2017
Summary
Original ArticleBreaking Bad News Training Program Based on Video Reviews and SPIKES Strategy: What do Perinatology Residents Think about It?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):552-559
10-01-2017Views156See moreAbstract
Objective
Resident doctors usually face the task to communicate bad news in perinatology without any formal training. The impact on parents can be disastrous. The objective of this paper is to analyze the perception of residents regarding a training program in communicating bad news in perinatology based on video reviews and setting, perception, invitation, knowledge, emotion, and summary (SPIKES) strategy.
Methods
We performed the analysis of complementary data collected from participants in a randomized controlled intervention study to evaluate the efficacy of a training program on improving residents’ skills to communicate bad news. Data were collected using a Likert scale. Through a thematic content analysis we tried to to apprehend the meanings, feelings and experiences expressed by resident doctors in their comments as a response to an open-ended question. Half of the group received training, consisting of discussions of video reviews of participants’ simulated encounters communicating a perinatal loss to a “mother” based on the SPIKES strategy. We also offered training sessions to the control group after they completed participation. Twenty-eight residents who were randomized to intervention and 16 from the control group received training. Twenty written comments were analyzed.
Results
The majority of the residents evaluated training highly as an education activity to help increase knowledge, ability and understanding about breaking bad news in perinatology. Three big categories emerged fromresidents’ comments: SPIKES training effects; bad news communication in medical training; and doctors’ feelings and relationship with patients.
Conclusions
Residents took SPIKES training as a guide to systematize the communication of bad news and to amplify perceptions of the emotional needs of the patients. They suggested the insertion of a similar training in their residency programs curricula.


