-
Original Articles
Assessment of the Effects of Tribulus Terrestris on Sexual Function of Menopausal Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(3):140-146
03-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticlesAssessment of the Effects of Tribulus Terrestris on Sexual Function of Menopausal Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(3):140-146
03-01-2016Views185See moreObjective
The aim of this study was to study the effects of Tribulus terrestris on sexual function in menopausal women.
Methods
This was a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial that included 60 postmenopausal women with sexual dysfunction. The women were divided into two groups, placebo group and Tribulus group, and evaluated by using the Sexual Quotient-female version (SQ-F) and Female Intervention Efficacy Index (FIEI) questionnaires.
Results
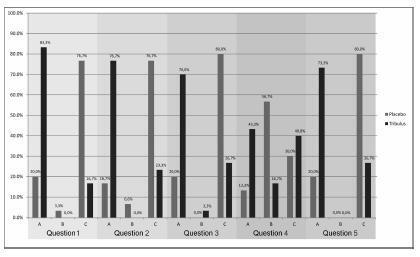
There was no significant difference between the groups in age, age at menopause, civil status, race, and religion. In the evaluation with the SQ-F questionnaire, there were significant differences between the placebo (7.6±3.2) and Tribulus (10.2±3.2) groups in the domains of desire and sexual interest (p d" 0.001), foreplay (3.3±1.5 versus 4.2±1.0) (p d" 0.01), arousal and harmonious interaction with the partner (5.7±2.1 versus 7.2±2.6) (p d" 0.01), and comfort in sexual intercourse (6.5±2.4 versus 8.0±1.9) (p d" 0.01). There was no significant difference between the placebo and Tribulus groups in the domains of orgasm and sexual satisfaction (p = 0.28). In the FIEI questionnaire, there was a significant improvement (p < 0.001) in the domains of vaginal lubrication during coitus and/or foreplay (20 versus 83.3%), sensation in the genitalia during sexual intercourse or other stimuli (16.7 versus 76.7%), sensation in the genital region (20 versus 70%), sexual intercourse and/or other sexual stimulations (13.3 versus 43.3%), and the ability to reach orgasm (20% versus 73.3%). There was no significant difference in adverse effects between the two groups.
Conclusions
After 90 days of treatment, at the doses used, we found Tribulus terrestris to be effective in treating sexual problems among menopausal women.
-
Artigos Originais
Sexual function in women undergoing assisted reproduction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(11):484-488
10-24-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisSexual function in women undergoing assisted reproduction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(11):484-488
10-24-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004952
Views63PURPOSE:
To evaluate sexual function in women undergoing assisted reproductive techniques.
METHODS:
This is a case-control study including 278 women assisted in Human Reproduction services and at the Gynecology Clinic of the University Hospital, Federal University of Goiás, Brazil. The women were divided into a study group (168 infertile women) and a control group (110 fertile women), and they answered the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) questionnaire used the assess the sexual function. We calculated the odds ratio (OR) for the chance of sexual dysfunction in infertile women (p<0.05).
RESULTS:
Out of the analyzed women, 33.09% reported sexual dysfunction, with no difference in the FSFI score between groups (p=0.29). The prevalence of sexual dysfunction was of 36.30% among infertile women and 28.18% among fertile women; however, there was no difference between FSFI scores (p=0.36). The desire and arousal domains were significantly different among infertile women (p=0.01). Infertile women had the same chances of having sexual dysfunction as fertile women (OR=1.4, 95%CI 0.8–2.4; p=0.2).
CONCLUSION:
There were no differences between infertile and fertile women. Infertile women undergoing assisted reproduction techniques require professional approach to sexual health regarding desire and arousal.
Key-words InfertilityReproductive health servicesReproductive techniquesSexual and reproductive healthSexual dysfunction, physiologicSexualitySee more -
Artigos Originais
Sexuality and depression among pregnant women with recurrent spontaneous abortion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):152-156
04-14-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisSexuality and depression among pregnant women with recurrent spontaneous abortion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):152-156
04-14-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140050.0004
Views72See morePURPOSE:
It was to compare pregnant women who experienced recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA) and those who did not in terms of the prevalence of depressive symptoms and sexual behavior.
METHODS:
A prospective case-control study was carried out. The first group consisted of women with RSA and the second, of primigravidae. The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) and one more questionnaire, developed by the authors themselves, about emotional aspects resulting from sexual intercourse during pregnancy were applied. The Student t-test was used to compare quantitative variables with normal distribution, and categorical variables were compared by the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test. The level of significance was set at p<0.05.
RESULTS:
The BDI showed (19.9 versus 10.0%) approximately twice the incidence of depression in the RSA group. Regarding sexual function, the average scores of the FSFI were 21.1 and 16.4 (p<0.05) for the study and control groups, respectively, although no significant difference was observed only in the desire domain (average 3.4±1.3 for the RSA group and 3.7±1.1 for control group) (p=0.1). We observed that, regardless the presence or absence of an RSA history among the pregnant women, the higher the depression score, the lower the sexuality score (r=-0,3).
CONCLUSIONS:
The RSA pregnant group often experiences twice higher depression and more impaired sexual function. There is an inverse association between depression and sexual function.
-
Artigos Originais
Confiability and reliability of an on-line version of the Female Sexual Function Index by test-retest
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(10):469-474
12-09-2013
Summary
Artigos OriginaisConfiability and reliability of an on-line version of the Female Sexual Function Index by test-retest
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(10):469-474
12-09-2013DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001000008
Views45See morePURPOSE: It was to test the validity and reliability of an online version of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI). METHODS: An online version of the FSFI was compared to the pen and paper traditional version. Physiotherapy students in three cities were randomly allocated to two groups - G-pp/ol (n=126) and G-ol/pp (n=147). G-pp/ol women replied to th FSFI using the traditional pen and paper method, while G-ol/pp women answered an online version of the same questionnaire. Data were collected ageing after 15 days, when G-pp/ol women answered the online version while G-ol/pp women answered on paper. All data were transferred to SPSS software. Demographic differences between the test two groups were determined by Student's t-test or Fisher exact (95%CI; p>0.05). Association and correlation between the responses of G-pp/ol and G-ol/pp were assessed for each sample by the t-test and Pearson's coefficient. An identical strategy was used for intragroup comparisons. RESULTS: A total of 273 women participated in the study and 28 (10.2%) giving up the second collection. There were no demographic differences between groups. Fifteen of the 19 FSFI questions were associated and correlated between the two groups in both test and the retest. The intragroup analysis revealed that all FSFI questions and scores were associated and weakly correlated for the same group during both test and retest. CONCLUSION: The online version of the FSFI showed acceptable validity and reliability when compared to the paper version, and can justify the choice of this modality, especially in studies involving private questions.
-
Artigos Originais
Habits and traditions of female college students related to intimate clothing, genital adornments, genital hair removal and sexual practices
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(9):401-406
11-06-2013
Summary
Artigos OriginaisHabits and traditions of female college students related to intimate clothing, genital adornments, genital hair removal and sexual practices
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(9):401-406
11-06-2013DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000900004
Views84See morePURPOSE: To describe the practices and care with the genital area of female college students. METHODS: A descriptive analytical study evaluated the habits and traditions of 364 students from the University of Campinas (Unicamp) regarding the use of underwear, body piercings, tattoos, hair removal and sexual practices. A questionnaire with 42 questions assessed the most current practices among female college students. All questions were self answered and the questionnaires, without any identification, were placed in sealed ballot boxes to ensure the confidentiality of information. The responses were tabulated in Microsoft® Excel 2007 to obtain univariate analysis. RESULTS:The mean age of the college students in the study was 21 years (SD±2.7), and 84% were white. The volunteers who participated in this study were from the biological science area (50%), the exact science area (29%) or the humanity area (21%). It was observed that 61.8% of the respondents wear cotton panties, but at the same time 75.4% wear tight jeans, and only 18.4% wore no panties when sleeping. Only one participant reported having had genital piercing and none of them reported tattooing. Most female college students do genital waxing, and approximately 1/3 of them do so completely. After hair removal, 2/3 apply an anti-inflammatory and/or moisturizer to the region. Only 62% use condoms and 17.6% use a lubricant during intercourse. Half of them receive oral sex, 17.9% practice anal sex and 26.6% of them report feeling pain during sexual intercourse. Vaginal discharge after intercourse was reported in 25.6% of the cases. CONCLUSION:Young female college students from Brazilian public universities have many inadequate care habits related to their genital area. They do not use genital piercing and tattoos, but report having pain during sexual intercourse and vaginal discharge after sex in a large number of cases.
-
Artigos Originais
Impact of pregnancy on female sexual function
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):205-209
07-05-2013
Summary
Artigos OriginaisImpact of pregnancy on female sexual function
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):205-209
07-05-2013DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000500003
Views64See morePURPOSE: To investigate the impact of pregnancy on female sexual function. METHODS: An analytical, cross-sectional study was conducted on 181 non-pregnant and 177 pregnant women aged 18 to 45 years. The study included premenopausal, sexually active women with a steady partner and excluded those taking antidepressants or with a diagnosis of depression. Eleven of these women (6.2%) were in the first trimester, 50 (28.2%), in the second trimester and 116 (65.5%), in the third trimester of pregnancy. The evaluation consisted of an interview in which the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) was applied. The data were analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software, version 16.0. The nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was used to compare the mean FSFI values of pregnant and non-pregnant women. RESULTS: Sexual dysfunction was 40.4% among pregnant women and 23.3% among non-pregnant women, with a significant difference between the scores of the studied groups (p=0.01). The difference in the mean global FSFI values between the groups was also significant (p<0.0001). There were significant differences between pregnant and non-pregnant women regarding desire (p<0.0001), excitation (p=0.003), lubrication (p=0.02), orgasm (p=0.005) and satisfaction (p=0.03). The same was not observed regarding pain. CONCLUSION: We conclude that pregnancy negatively influences female sexual function, particularly the desire and excitement domains, revealing the importance of addressing the issue by professionals dealing with pregnant women.


