Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 07-26-2024;46:e-rbgo49
The purpose of this study was to analyze the available evidence regarding the efficacy of iPDE5 in the treatment of female sexual dysfunction (FSD).
A comprehensive literature search was conducted in March 2023 through the main scientific databases.
A total of 53 articles were identified, out of which, 6 met the predefined inclusion criteria. All of these were randomized controlled trials. Among the included studies, 4 demonstrated the effectiveness of sildenafil in improving sexual response and addressing FSD, while 2 studies failed to establish its efficacy in this context.
Overall, the efficacy of sildenafil in the treatment of FSD remains controversial and inconclusive based on the available evidence. Further research is necessary to clarify the therapeutic potential of iPDE5 in addressing FSD and to better understand the factors that influence treatment outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 07-27-2021;43(6):467-473
To assess the sexual function of women with spina bifida (SB), and to verify the factors that influence their sexual function.
A cross-sectional study in which a validated female-specific questionnaire was applied to 140 SB female patients from four different cities (Porto Alegre, Brazil; and Barcelona, Madrid, and Málaga, Spain) between 2019 and 2020. The questionnaires collected data on the clinical characteristics of SB, and female sexual function was assessed using the 6-item version of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI-6) validated to Portuguese and Spanish.
Half of the patients had had sexual activity at least once in the life, but most (57.1%) did not use any contraception method. Sexual dysfunction was present in most (84.3%) patients, and all sexual function domains were impaired compared those of non-neurogenic women. The presence of urinary and fecal incontinence significantly affected the quality of their sexual activity based on the FSFI-6.
The specific clinical aspects of the SB patients, such as urinary and fecal incontinence, should be properly addressed by their doctors, since they are associated with reduced sexual activity and lower FSFI-6 scores in the overall or specific domains. There is also a need to improve gynecological care among sexually-active SB patients, since most do not use any contraceptive methods and are at risk of inadvertent pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 08-26-2020;42(7):427-435
We performed a systematic review to assess the effectiveness and safety of Tribulus terrestris to treat female sexual dysfunction (FSD).
We performed unrestricted electronic searches in the MEDLINE, CENTRAL, EMBASE, LILACS, CINAHL, PsycINFO,WHO-ICTR, Clinicaltrials.gov and OpenGrey databases. Selection of studies We included any randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared T. terrestris versus inactive/active interventions. After the selection process, conducted by two reviewers, 5 RCTs (n = 279 participants) were included.
Data extraction was performed by two reviewers with a preestablished data collection formulary.
Due to lack of data and clinical heterogeneity, we could not perform meta-analyses. The risk of bias was assessed by the Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) tool, and the certainty of evidence was assessed with Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE).
After 1 to 3 months of treatment, premenopausal and postmenopausal women randomized to T. terrestris had a significant increase in sexual function scores. Three months of treatment with T. terrestris showed a significant increase in the serum testosterone levels of premenopausal women. There was no report of serious adverse events, and none of the studies assessed health-related quality of life. The certainty of the evidence was very low, whichmeans that we have very little confidence in the effect estimates, and future studies are likely to change these estimates.
MoreRCTs are needed to supportor refute the use of T. terrestris. The decision to use this intervention should be shared with the patients, and the uncertainties around its effects should be discussed in the clinical decision-making process. Number of Protocol registration in PROSPERO database: CRD42019121130
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 09-30-2019;41(9):555-563
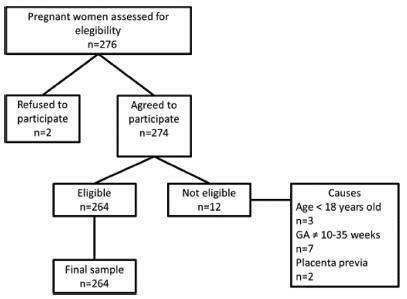
To determine the prevalence of sexual dysfunction and its associated factors in pregnant women.
A descriptive, cross-sectional study including 262 pregnant women aged 18 years or older with gestational age between 10 and 35 weeks. Women with urinary tract infections and conditions of gestational risk were excluded. The Pregnancy Sexual Response Inventory (PSRI) questionnaire was used. We performed a univariate descriptive analysis, and comparisons between the mean values of the sexual function domains were made using the Student t-test. The chi-squared test was used to determine the association between the independent and dependent variables. The prevalence ratios, with their respective 95% confidence intervals, were also estimated, and a multivariate analysis was performed.
A total of 64.9% of women reported a decrease in the frequency of sexual activity during pregnancy. Slightly more than half of the women (50.8%) were satisfied, and arousal was reported as excellent/good by 30.5% of them. The frequency of sexual difficulties/dysfunctions increased with pregnancy, rising from 5.7% to 58.8%, and pain during sexual intercourse was reported by 45.8% of them. Having higher education degree decreased the chance of being sexually dissatisfied by 50%. The total PSRI score showed a significant decrease from the prepregnancy period (mean score = 89.8, “excellent”) to the pregnancy period (mean score = 59.2, “good”).
The mean sexual function score during pregnancy was classified as good, although most pregnant women reported at least one type of alteration in the sexual function domains, and the report of dissatisfaction was more frequent in women with lower schooling.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 11-01-2018;40(11):693-698
The aim of the present study is to identify the association between personality traits of postmenopausal women and the occurrence of sexual dysfunction.
A total of 43 postmenopausal women were evaluated according to their self-perception of the quality of their sexual life. They answered the following questionnaires: Sociodemographic Profile Questionnaire, Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) and Factorial Personality Inventory (FPI-II).
Women with poorer sexual self-perception showed low affective need (p< 0.01) and low need for organization (p< 0.01). Based on the need for control and opposition, there was no difference between the groups. Groups separated by the scores obtained on the FSFI showed no significant differences.
Postmenopausal women with lower schooling and personality characteristics that demonstrate low affective and organizational needs are more likely to present sexual dysfunction.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 04-01-2017;39(4):184-194
Sexual pleasure is fundamental for the maintenance of health and well-being, but it may be adversely affected by medical and psychosocial conditions. Many patients only feel that their health is fully restored after they resume normal sexual activities. Any discussion of sexuality in a doctor's office is typically limited, mainly because of a lack of models or protocols available to guide the discussion of the topic.
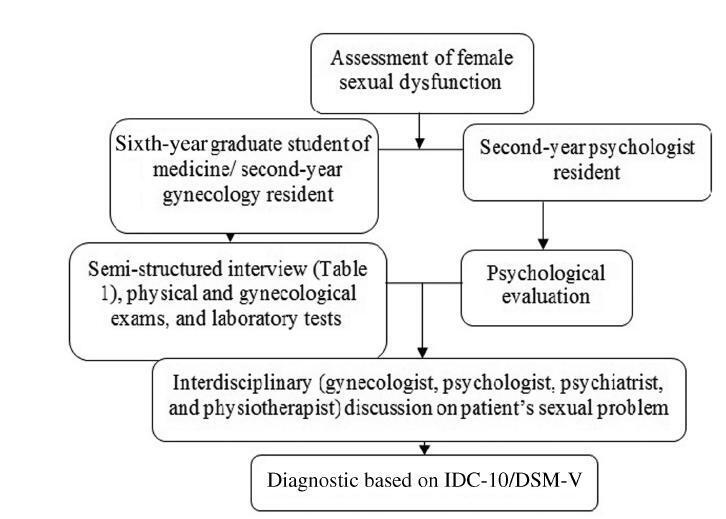
To present a model designed to guide gynecologists in the management of female sexual complaints.
This study presents a protocol used to assess women's sexual problems. A semi-structured interview is used to assess sexual function, and the teaching, orienting and permitting (TOP) intervention model that was designed to guide gynecologists in the management of sexual complaints.
The use of protocols may facilitate the discussion of sexual issues in gynecological settings, and has the potential to provide an effective approach to the complex aspects of sexual dysfunction in women. The TOP model has three phases: teaching the sexual response, in which the gynecologist explains the physiology of the female sexual response, and focuses on the three main phases thereof (desire, excitement and orgasm); orienting a woman toward sexual health, in which sexual education is used to provide information on the concept and healthy experience of sexuality; and permitting and stimulating sexual pleasure, which is based on the assumption that sexual pleasure is an individual right and is important for the physical and emotional well-being.
The use of protocols may provide an effective approach to deal with female sexual dysfunction in gynecological offices.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 02-01-2017;39(2):66-71
To investigate the association between the intensity of climacteric symptoms and sexual dysfunction in women aged 40 to 65 years.
Observational, analytic, cross-sectional study conducted with 63 women aged 40 to 65 treated at the gynecology outpatient clinic of a public hospital in northeastern Brazil. A questionnaire was used to collect identification data, clinical information, gynecological-obstetric data, lifestyle traits and information on chronic diseases. Climacteric symptoms and sexual function were evaluated by means of the Blatt-Kupperman index and the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) respectively. The association between the two indices was investigated using the chi-squared test; the difference in mean scores on the FSFI as a function of menopausal status was evaluated by Student's t-test. The significance level was set to p < 0.05.
The mean value of the Blatt-Kupperman index was 26.42 (standard deviation [SD]: 4.52); 36.51% of the women exhibited severe symptoms. The mean score on the FSFI was 21.84 (SD: 4.11). More than half of the analyzed women (58.73%) exhibited sexual dysfunction (FSFI ≤ 26.5). Regarding the association between the Blatt- Kupperman index and the FSFI, the greater the intensity of the climacteric symptoms (Blatt-Kupperman), the higher the frequency of sexual dysfunction (FSFI). Sexual dysfunction was exhibited by 100% of the participants with severe climacteric symptoms, 70.59% of those with moderate symptoms, and only 9.09% with mild symptoms (p < 0.001).
The application of the Blatt-Kupperman index and of the FSFI allowed the detection of an association between the severity of climacteric symptoms and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 04-01-2016;38(4):164-169
The objective of this study is to associate the results obtained while assessing the pelvic floor muscles (PFM) functionality with the score of sexual satisfaction of young adult women.
This is an observational and cross-sectional study. The inclusion criteria were women aged between 20 and 40 years who have had sexual intercourse, nulliparous, BMI lower than 25 kg/m2, and absence of pelvic floor dysfunction. The evaluation consisted of both the medical history and assessment of the PFM functionality using the Perina pressure biofeedback and Oxford Scale. We measured sexual satisfaction using the Female Sexual Quotient questionnaire and used the KolmogorovSmirnov test to verify the normality of the data. We analyzed non-parametric variables using the Spearman correlation test. The significance level was 5 %.
A total of 80 women with a median age of 26 years and median BMI of 21.64 kg/m2 participated in this study. We divided the subjects into two groups, best and worse PFM functionality, according to median Perina pressure biofeedback and Oxford scale. We found no difference between the groups when comparing the sexual satisfaction scores. There was only a slight significant correlation between the Contraction Voluntary Average obtained using the pressure biofeedback and the primary domain (r = 0.27; p = 0.01).
This study found a slight correlation between PFM functionality and the functionality of the primary domain of the Female Sexual Quotient questionnaire. Therefore, it is not possible to state whether there is an association between the PFM functionality and female sexual satisfaction in young adults.