Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(2):64-70
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005115
To determine the prevalence of toxoplasmosis and to identify the main factors associated with seroreactivity in pregnant women cared for at two reference centers in a city in Northeast Brazil.
A cross-sectional study was conducted on 561 pregnant women at two high-risk prenatal reference centers in a city in Northeast Brazil. All women were interviewed using an epidemiological questionnaire and had their blood samples collected for the following serological tests: anti-Toxoplasma gondii IgG and IgM (ELISA), IgG avidity test, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS version 18.0 for Windows, calculating odds ratio, confidence interval of 95% and with the level of significance set at 5%.
Seroreactivity for toxoplasmosis was detected in 437 women (77.0%), susceptibility in 124 (22.1%) and active infection in 5 (0.9%). There was no significant association between seroreactivity for toxoplasmosis and age, location, income, education, availability of sewage, number of pregnancies or gestational age. The variables significantly associated (p≤0.05) with seroreactivity were multiparity (p=0.03) and living with stray dogs (p=0.01).
This study identified high seroreactivity for toxoplasmosis among patients seen during prenatal care, as well as factors associated with seroreactivity. Appropriate guidelines about primary preventive measures should be emphasized and quarterly serological monitoring is recommended for pregnant women in this city and elsewhere in the Northeast of Brazil.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(12):535-540
DOI 10.1590/So100-720320140005086
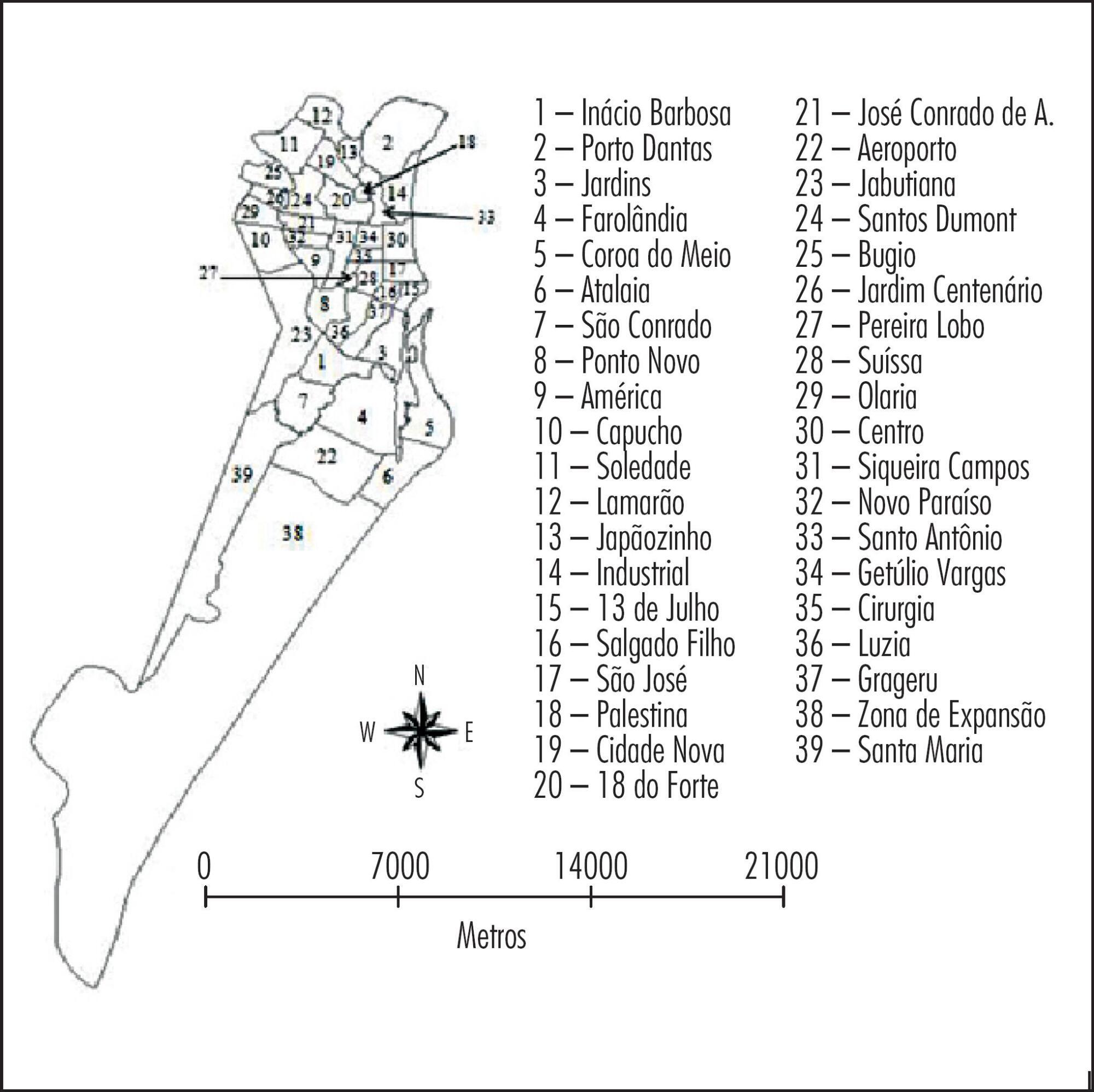
To analyze the spatial distribution of the prevalence of anti-toxoplasma gondii antibodies in pregnant women from a Brazilian Northeast city, and to correlate such prevalence with average maternal age and place of residence.
A descriptive, analytical and ecological study was conducted from January 1st to December 31st 2012. Data were obtained retrospectively from the Medical Specialties Center database and processed with the Epi info statistical package (Epi 7, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, USA) and with Microsoft Excel 2010. The X2 test was applied to assess the association between the prevalence of antibodies to toxoplasma gondii and the average age. Spatial analysis of infection prevalence was performed using the TerraView software, version 4.2.2, with Kerneldensity estimation, which estimates the quantity of events through maps in order to identify areas with the highest concentration of cases in the city.
The seroprevalence of IgG was 68.5% (95%CI 67.2-69.8) and the prevalence of IgM was 0.36% (95%CI 0.23-0.6). A higher IgG prevalence was associated with increased age in the oldest neighborhoods of the state capital, whereas a higher IgG prevalence among younger women was detected in suburban neighborhoods. The spatial concentration of IgM antibodies was higher in suburban neighborhoods, with no significant correlation between seroprevalence and age.
Geoprocessing allowed the identification of areas with the highest prevalence, as well as the most susceptible average age and it was also useful as an instrument for the evaluation and implementation of appropriate preventive measures for this municipality and for other regions of Brazil.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):467-472
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800005
PURPOSE: to assess human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) seroprevalence among pregnant women attended at Public Health Units in Goiânia-Goiás and some epidemiologic characteristics of the studied group. METHODS: from September/2003 to December/2004, 15,485 pregnant women were submitted to enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assays (ELISA), to screen HTLV-I, using filter paper - dried blood in, and to confirm the infection, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of whole blood was performed. The epidemiologic factors evaluated were: average age, age of 30 years and above, schooling less than nine years, marital status and number of pregnancies. The factors average age, age of 30 years and above, and schooling less than nine years were compared between the infected and non-infected pregnant group. Statistical analysis used Fisher's exact test and Student's t test. RESULTS: the found prevalence was 0.1%. The average age among the infected pregnant group was 26.4 years, 43.7% of them being 30 years old and above, and 62.5% with schooling less than nine years. The non-infected group showed an average age of 24.4 years, 15.4% of them being ³ 30 years old and above, and only 41.5% with schooling less than nine years. Significant statistical difference was noticed only regarding age of 30 years and above and schooling less than nine years. CONCLUSION: the study shows that HTLV-I seroprevalence among pregnant women in Goiânia during the studied period was 0.1%. It occurred more among pregnant women who were 30 years old and above and those with schooling of less than nine years.