-
Original Article
Applicability, Safety, and Efficiency of Salpingectomy versus Electrocoagulation and Laparoscopic Tubal Section in Ambulatory
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(9):866-870
08-29-2022
Summary
Original ArticleApplicability, Safety, and Efficiency of Salpingectomy versus Electrocoagulation and Laparoscopic Tubal Section in Ambulatory
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(9):866-870
08-29-2022Views96See moreAbstract
Objective
Female sterilization is a surgical procedure that aims women to permanently stop the use of conception. The benefits, risks and cost-effectiveness are important issues. The purpose of this study was comparing the applicability, complications and efficacy of salpingectomy versus electrocoagulation and tubal occlusion by laparoscopy in the Ambulatory Surgery Unit.
Methods
We performed a retrospective and observational study that included women undergoing laparoscopic sterilization procedures at our Ambulatory Surgery Unit, during three years. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS, applying the Fisher exact test, the Mann-Whitney test, and Linear Regression.
Results
Two hundred and twenty-one laparoscopic surgical procedures were performed, including 79 (35.7%) bilateral total salpingectomies and 142 (64.3%) electrocoagulation and bilateral tubal occlusion procedures. The majority of the procedures were performed by a resident (n = 162; 73.3%), with 40% (n = 33) of salpingectomies. The surgical time, independently the type of surgeon, was significantly shorter in the tubal occlusion (42.2 vs. 52.7 min, p < 0.001). Safety and efficacy endpoints were not significantly different between the two groups, with a case of pregnancy in tubal occlusion group.
Conclusion
Salpingectomy is a safe and effective alternative comparing with electrocoagulation and tubal occlusion.
-
Review Article
Effects of Hydrosalpinx on Endometrial Implantation Failures: Evaluating Salpingectomy in Women Undergoing in vitro fertilization
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):304-310
02-18-2021
Summary
Review ArticleEffects of Hydrosalpinx on Endometrial Implantation Failures: Evaluating Salpingectomy in Women Undergoing in vitro fertilization
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):304-310
02-18-2021Views185See moreAbstract
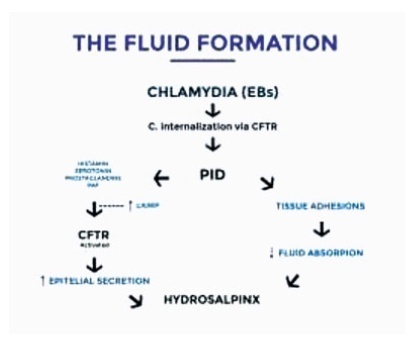
Hydrosalpinx is a disease characterized by the obstruction of the salpinx, with progressive accumulation in the shape of a fluid-filled sac at the distal part of the tuba uterina, and closed to the ovary. Women with hydrosalpinges have lower implantation and pregnancy rates due to a combination of mechanical and chemical factors thought to disrupt the endometrial environment. Evidence suggests that the presence of hydrosalpinx reduces the rate of pregnancy with assisted reproductive technology. The main aim of the present is review to make an overview of the possible effects of hydrosalpinx on in vitro fertilization (IVF).We conducted a literature search on the PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and Google Scholar data bases regarding hydrosalpinx and IVF outcomes. Hydrosalpinx probably has a direct toxic effect on sperm motility and on the embryos. In addition, the increasing liquid inside the salpinges could alter the mechanisms of endometrial receptivity. The window of endometrial receptivity is essential in the implantation of blastocysts, and it triggers multiple reactions arising from the endometrium as well as the blastocysts. Hydrosalpinx could influence the expression of homeobox A10 (HOXA10) gene, which plays an essential role in directing embryonic development and implantation. Salpingectomy restores the endometrial expression of HOXA10; therefore, it may be one mechanism by which tubal
-
Review Article
Is Ovarian Cancer Prevention Currently Still a recommendation of Our Grandparents?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):676-685
12-01-2017
Summary
Review ArticleIs Ovarian Cancer Prevention Currently Still a recommendation of Our Grandparents?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):676-685
12-01-2017Views120See moreAbstract
Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death among gynecologic tumors because in most of the cases (75%), the disease is diagnosed in advanced stages. Screening methods are not available since the disease is rare, and the tested methods, such as ultrasound and CA125, were not able to decrease the mortality rate for this type of cancer. This article discusses the main risk factors for ovarian cancer, and the potential clinical and surgical strategies for the prevention of this disease.


