-
Original Article11-07-2019
Do We Know How to Avoid OASIs in Non-Supine Birth Positions? A Retrospective Cohort Analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):581-587
Abstract
Original ArticleDo We Know How to Avoid OASIs in Non-Supine Birth Positions? A Retrospective Cohort Analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):581-587
Views180See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the association between the upright and supine maternal positions for birth and the incidence of obstetric anal sphincter injuries (OASIs).
Methods
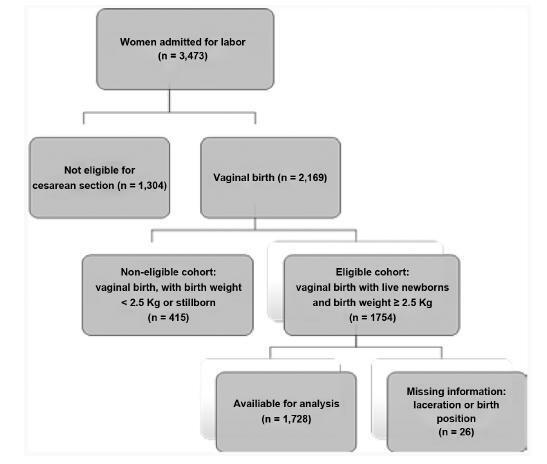
Retrospective cohort study analyzed the data of 1,728 pregnant women who vaginally delivered live single cephalic newborns with a birth weight of 2,500 g. Multiple regression analyses were used to investigate the effect of the supine and upright positions on the incidence of OASIs after adjusting for risk factors and obstetric interventions.
Results
In total, 239 (13.8%) births occurred in upright positions, and 1,489 (86.2%) in supine positions. Grade-III lacerations occurred in 43 (2.5%) patients, and grade-IV lacerations occurred in 3 (0.2%) women. Supine positions had a significant protective effect against severe lacerations, odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 0,47 [0.22- 0.99], adjusted for the use of forceps 4.80 [2.15-10.70], nulliparity 2.86 [1.44-5.69], and birth weight 3.30 [1.56-7.00]. Anesthesia (p<0.070), oxytocin augmentation (p<0.228), shoulder dystocia (p<0.670), and episiotomy (p<0.559) were not associated with the incidence of severe lacerations.
Conclusion
Upright birth positions were not associated with a lower rate of perineal tears. The interpretation of the findings regarding these positions raised doubts about perineal protection that are still unanswered.
-
Original Article05-16-2019
Postpartum Depression: Epidemiological Clinical Profile of Patients Attended In a Reference Public Maternity in Salvador-BA
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):155-163
Abstract
Original ArticlePostpartum Depression: Epidemiological Clinical Profile of Patients Attended In a Reference Public Maternity in Salvador-BA
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):155-163
Views186See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the clinical epidemiological state of women with suspected post partum depression (PPD) in a public maternity hospital in Salvador, state of Bahia, Brazil.
Methods
A cross-sectional research was performed with puerperal patients attended at a public maternity hospital in Salvador, Bahia. Data collection was performed from June to September 2017. The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale was used as a screening instrument, and, subsequently, women with positive scores answered a questionnaire to identify their clinical and epidemiological status.
Results
Out of 151 postpartum women from the research, 30 (19.8%) presented suspicion of PPD. There was a prevalence of single mothers 13 (43.3%), women with complete fundamental education 15 (50.0%), women with black skin color 14 (46.7%), and those with a monthly family income of up to one minimum wage 18 (40.0%).
Conclusion
Although PPD is an underdiagnosed disease, a high prevalence of the condition was found in our research. It is, then, considered that these results reinforce its significance as a public health problem, requiring prevention strategies, early diagnosis and effective treatment.
-
Original Article08-01-2018
Maternal Factors Associated with Low Birth Weight in Term Neonates: A Case-controlled Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):444-449
Abstract
Original ArticleMaternal Factors Associated with Low Birth Weight in Term Neonates: A Case-controlled Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):444-449
Views138See moreAbstract
Objective
To identify maternal factors associated with the presence of low birth weight in term neonates.
Methods
Matched hospital-based case-controlled study performed in a high complexity institution located in the city of Neiva, Colombia. The study included women with term gestation and singleton live fetuses. Patients with prior diseases, coming from other regions, with pregnancy resulting from assisted reproduction, or with a diagnosis of fetal abnormality or aneuploidy were excluded. Low birth weight was the dependent variable, and the independent variables that were analyzed were maternal sociodemographic and clinical characteristics. Adjusted and non-adjusted odds ratios (aOR and OR) together with the 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were reported.
Results
The study included 270 participants (90 cases and 180 controls). Controlling for maternal age, educational level, socioeconomic and civil status, social security and the presence of maternal disease during gestation, it was found that weight gain (aOR 0.77, 95% CI 0.70-0.85) and the absence of prenatal care (aOR 8.20, 95% CI 3.22-20.87) were among the factors associated with low birth weight.
Conclusions
The absence of weight gain and of prenatal care are factors associated with the presence of low birth weight in term neonates and should be considered in clinical practice.
-
Original Article02-01-2017
Predictors of cesarean delivery in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):60-65
Abstract
Original ArticlePredictors of cesarean delivery in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):60-65
Views233See moreAbstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate which risk factors may lead patients with gestational diabetes mellitus to cesarean delivery.
Methods
This was a retrospective, descriptive study. The subjects of the study were pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus attending a public maternity hospital in the south of Brazil. The primary outcomes assessed were based on maternal and fetal characteristics. The data were correlated using an odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (95%CI), calculated using multinomial logistic regression.
Results
A total of 392 patients with gestational diabetes mellitus were analyzed, and 57.4% of them had cesarean deliveries. Among the maternal characteristics, the mean age of the patients and the pregestational body mass index were greater when a cesarean delivery was performed (p = 0.029 and p < 0.01 respectively). Gestational age at birth, newborn weight, weight class according to gestational age, and Apgar score were not significant. The analysis of the OR showed that the chance of cesarean delivery was 2.25 times (95%CI = 1.49-2.39) greater if the pregnant woman was obese, 4.6 times (95%CI = 3.017-7.150) greater if she was a primigravida, and 5.2 times (95% CI = 2.702-10.003) greater if she had a previous cesarean delivery. The other parameters analyzed showed no differences.
Conclusion
The factors that led to an increase in the occurrence of cesarean deliveries included history of a prior cesarean section, first pregnancy, and obesity.
-
Original Article10-01-2016
Factors Associated with Infant Mortality in a Northeastern Brazilian Capital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(10):482-491
Abstract
Original ArticleFactors Associated with Infant Mortality in a Northeastern Brazilian Capital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(10):482-491
Views161See moreAbstract
Purpose
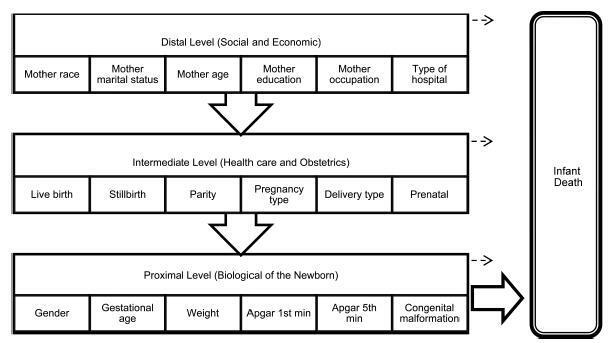
Identify factors associated with infant mortality by a hierarchical model based on socioeconomic, health care, obstetric and biological determinants in a northeastern Brazilian capital.
Methods
Observational, retrospective cohort study based on secondary data of births and deaths of infants of mothers living in the city of Teresina.
Results
Based on the distal level of determination of infant mortality, the characteristics that remained statistically significant were maternal age, maternal education and maternal occupation (p< 0.001). In the intermediate level, all variables were statistically significant, particularly the type of pregnancy and delivery (p< 0.001). The gender of the baby was the proximal level feature that had no significant association with the outcome, while the other variables of this level had association (p< 0.001).
Conclusions
This study evidenced that, in addition to biological factors, socioeconomic status and maternal and child health care are important to determine infant mortality.
-
Original Article08-01-2016
Postpartum Reclassification of Glycemic Status in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Associated Risk Factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):381-390
Abstract
Original ArticlePostpartum Reclassification of Glycemic Status in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Associated Risk Factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):381-390
Views207See moreAbstract
Objective
The aims of the study were to evaluate, after pregnancy, the glycemic status of women with history of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and to identify clinical variables associated with the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), impaired fasting glucose (IFG), and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT).
Methods
Retrospective cohort of 279 women with GDM who were reevaluated with an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) after pregnancy. Characteristics of the index pregnancy were analyzed as risk factors for the future development of prediabetes (IFG or IGT), and T2DM.
Results:
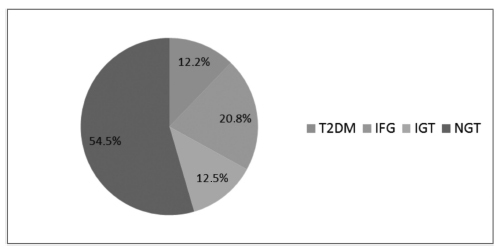
T2DM was diagnosed in 34 (12.2%) patients, IFG in 58 (20.8%), and IGT in 35 (12.5%). Women with postpartum T2DM showed more frequently a family history of T2DM, higher pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI), lower gestational age, higher fasting and 2-hour plasma glucose levels on the OGTT at the diagnosis of GDM, higher levels of hemoglobin A1c, and a more frequent insulin requirement during pregnancy. Paternal history of T2DM (odds ratio [OR] =5.67; 95% confidence interval [95%CI] =1.64-19.59; p =0.006), first trimester fasting glucose value (OR =1.07; 95%CI =1.03-1.11; p =0.001), and insulin treatment during pregnancy (OR =15.92; 95%CI =5.54-45.71; p < 0.001) were significant independent risk factors for the development of T2DM.
Conclusion
A high rate of abnormal glucose tolerance was found in women with previous GDM. Family history of T2DM, higher pre-pregnancy BMI, early onset of GDM, higher glucose levels, and insulin requirement during pregnancy were important risk factors for the early identification of women at high risk of developing T2DM. These findings may be useful for developing preventive strategies.
-
Original Article12-01-2015
The influence of breastfeeding in postpartum oral glucose tolerance test in women with recent gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):565-570
Abstract
Original ArticleThe influence of breastfeeding in postpartum oral glucose tolerance test in women with recent gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):565-570
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005488
Views113See moreAbstract
PURPOSE:
To determine the influence of breastfeeding on the results of a postpartum oral glucose tolerance test in women recently diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus.
METHODS:
The data were obtained from the electronic medical records of the Endocrinopathy Sector during pregnancy, HCMED laboratory system ofHospital das Clínicas of São Paulo , and by telephone. According to the inclusion criteria adopted, 132 patients were eligible for the study. For statistical analysis, the patients were divided into two groups according to whether or not they breastfed. The results were analyzed by the Student t-test and by the Mann-Whitney, Chi-square and Fisher's exact tests, depending on the variable analyzed, with the level of significance set at p<0.05.
RESULTS:
Of the 132 patients included in the study, 114 breastfed and 18 did not. Most of the patients in both groups were overweight or obese. The breastfeeding group had a lower pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index than the non-breastfeeding group (p=0.006). Insulin was introduced earlier in the group that did not breastfeed (23.21±4.33 versus 28.84±6.17; p=0.04). The group that did not breastfeed had a higher mean postpartum fasting glucose value in the oral glucose tolerance test than the group that breastfed (91.3±8.7 versus 86.5±9.3; p=0.01). Breastfeeding acted as a protective factor against the development of glucose intolerance in the postpartum oral glucose tolerance test (OR=0.27; 95%CI 0.09-0.8). By logistic regression, breastfeeding was shown to be an independent protective factor.
CONCLUSION:
There was a statistically significant relationship between breastfeeding and a decreased risk of developing glucose intolerance. Breastfeeding should be encouraged because it is an effective, low cost intervention easily accessible to all patients during the postpartum period.


