-
Original Article04-30-2025
Clinical and epidemiological profile of pregnant and postpartum women affected by COVID-19 who required respiratory support
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo14
Abstract
Original ArticleClinical and epidemiological profile of pregnant and postpartum women affected by COVID-19 who required respiratory support
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo14
Views109Abstract
Objective:
This study described the clinical and epidemiological profile and the management provided to pregnant and postpartum women with COVID-19 who required respiratory support.
Methods:
A descriptive study was conducted with pregnant and postpartum women with confirmed COVID-19 who received care between April 2020 and December 2021 in eight referral centers in northeastern Brazil. Statistical analysis was conducted using Epi-Info 7.2.5 and Medcalc, version 20.112.
Results:
Of the 720 patients admitted, 208 (32.7%) required respiratory support. Mean age of the participants was 28.9±7.1 years. Most (52.8%) were brown-skinned; 31.3% had little formal schooling; 41.1% had a personal income and 23.1% were married. Around half were referred from another hospital. Overall, 36.8% were obese and 36.9% were hypertensive. Criteria for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) were present in 80.7% of cases. Overall, 151 patients (74.7%) required corticoids, and 150 (76.1%) were admitted to an intensive care unit. Non-invasive ventilation was needed in 89.4% of cases, with nasal catheters being the most common type (55.3% of cases). Invasive mechanical ventilation was necessary in 35.5% of cases and 91.6% had a cesarean section. Maternal near miss and death occurred in 24% and 12.9% of cases, respectively.
Conclusion:
Pregnant and postpartum women with COVID-19 who required respiratory support were predominantly brown-skinned, in the third trimester of pregnancy and had been referred from another hospital. The cesarean section rate was high; the presence of criteria for SARS was common and the rates of COVID-19-related maternal near miss and death were high.
Clinical Trials registry:
NCT04462367
Key-words Cesarian sectionCOVID-19Intensive care unitsNear miss, healthcareNoninvasive ventilationObesityPostpartum periodPregnancyPregnancy trimester, thirdRespiration, artificialSARS-CoV-2severe acute respiratory syndromeSee more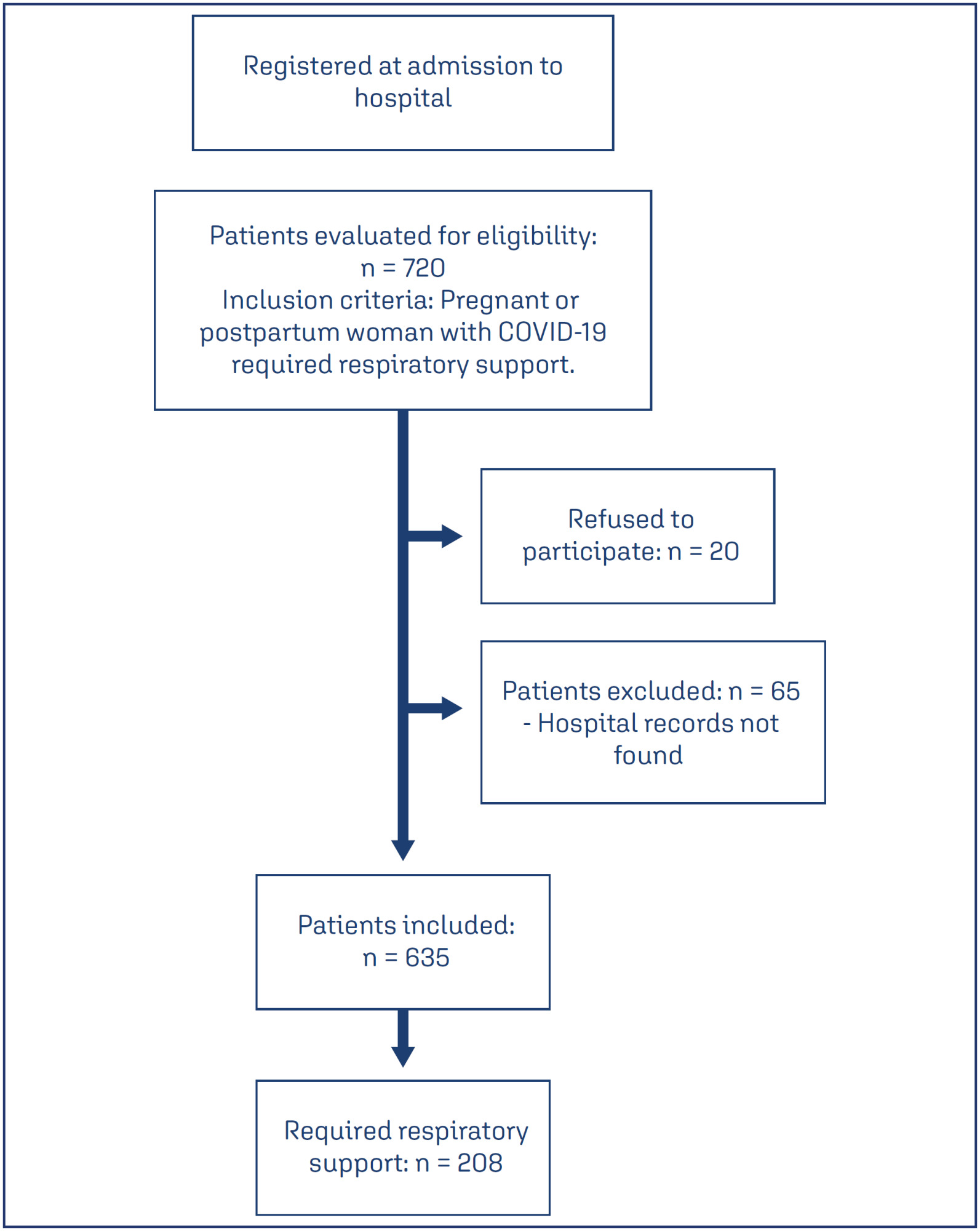
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Assessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo17
Abstract
Original ArticleAssessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo17
Views144Abstract
Objective:
This retrospective study aimed to investigate blood-based immune-inflammatory biomarkers (IIBs) in predicting neonatal outcomes in pregnancies with pregestational diabetes mellitus (PGDM).PIV[(neutrophil×platelet×monocyte)/lymphocyte)], SII (neutrophil×platelet/lymphocyte), and NLR neutrophil/lymphocyte) values were evaluated in all three trimesters, and their correlation with neonatal outcomes was examined.
Methods:
We included 82 cases of PGDM pregnancies delivered after 32 weeks. Maternal age, gravidity, parity, types of diabetes, and route of delivery were noted. For neonatal outcomes, we recorded gestational age at birth, birth weight percentile, existence of fetal growth restriction, LGA, neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) requirement, Apgar Score <7 at 1, 5, or 10 minutes, need for positive pressure ventilation (PPV), need for mechanical ventilation, hypoglycaemia, hyperbilirubinemia and the need for phototherapy. PIV, SII and NLR values were calculated in each trimester and their association with adverse neonatal outcomes was analyzed.
Results:
We could not detect any consistent and significant correlation between SII and PIV values and adverse neonatal outcomes for each trimester. There was a correlation between 3rd trimester NLR and adverse neonatal outcomes, including APGAR <7, the requirement for PPV and mechanical ventilation (p=0.056, 0.013 and 0.060, respectively).
Conclusion:
While SII and PIV values did not consistently correlate with adverse neonatal outcomes throughout each trimester in PGDM pregnancies, 3rd-trimester NLR showed a notable association with the requirement for PPV with statistical significance and with Apgar Score <7 and the requirement for mechanical ventilation without statistical significance. NLR in the third trimester may hold potential as a predictive marker for specific adverse neonatal outcomes in PGDM pregnancies, warranting further investigation.
Key-words biomarkersDiabetes mellitusGestational ageHypoglycemiaInfant, newbornIntensive care units, neonatalLymphocytesMaternal ageMonocytesNeuthrophilsPregancyPregnancy in diabetesRespiration, artificialSee more


