Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):676-682
12-05-2023
Recurrent miscarriage has been linked to hormonal disturbance due to dysregulation of its receptors rather than to the availability of the hormone. We aimed to investigate endometrial expression of progesterone and estrogen receptors in relation to serum and endometrial hormonal levels in unexplained recurrent miscarriage.
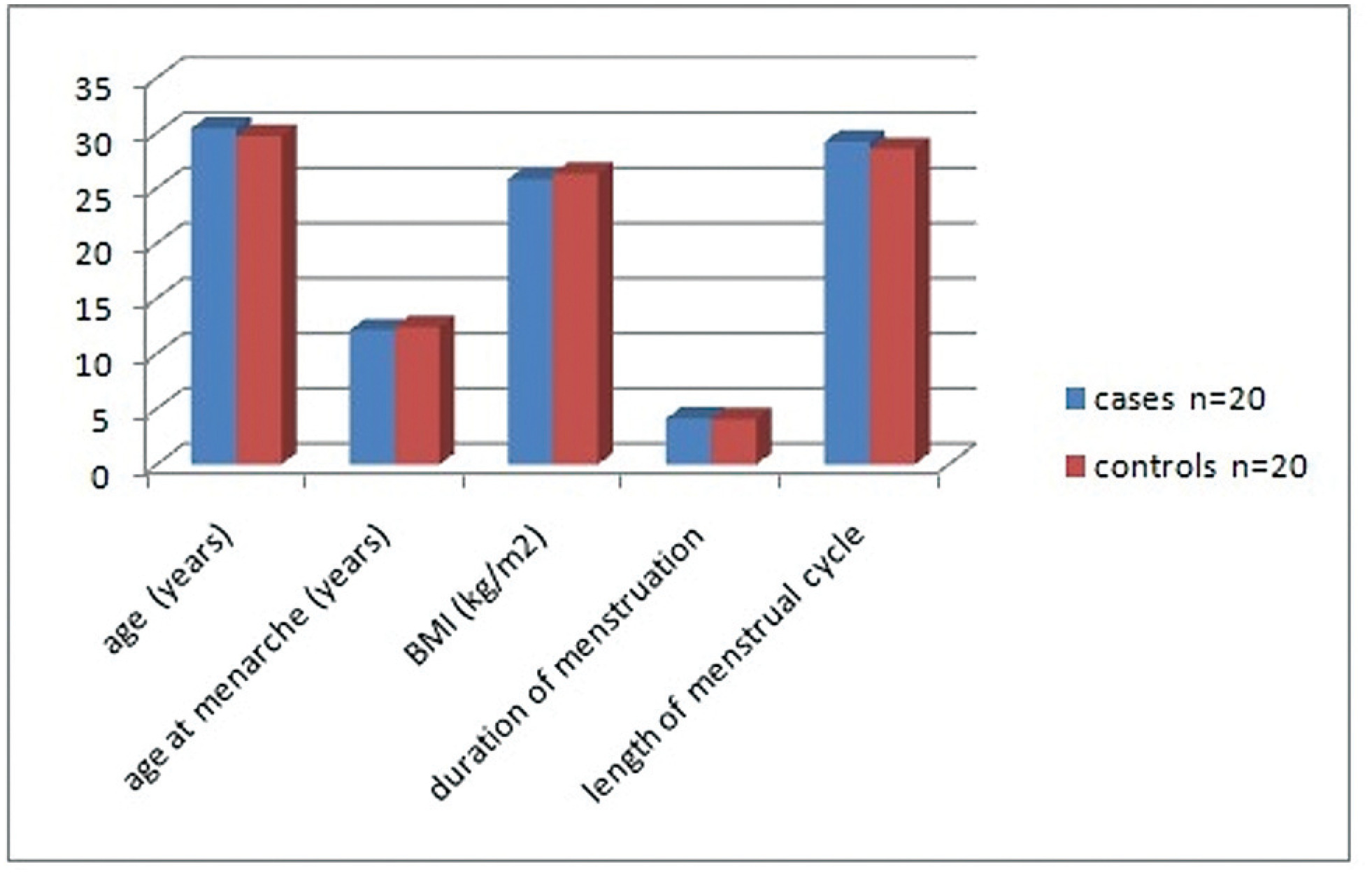
The present case control study included 20 cases with unexplained recurrent miscarriage and 20 parous women as controls. Ovulation was confirmed using an ovulation kit and 10 to 12 days after detecting the urinary luteinizing hormone surge, all women were subjected to a blood sample and to an endometrial biopsy. Progesterone and estrogen levels were measured in serum and in endometrial tissue and receptor concentrations were in the endometrial sample.
Women with recurrent miscarriage showed significantly lower concentration of receptors in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus of endometrial tissue compared with controls. The nuclear/cytoplasm ratio of progesterone receptor was significantly higher in cases compared with controls, implicating that recurrent miscarriage is probably linked to nongenomic activity of the hormone; this was also significant for estrogen receptor. Serum progesterone and estrogen hormonal levels were comparable between groups while both hormones were significantly reduced in the endometrium of recurrent miscarriage cases. Receptors significantly correlated with endometrial hormonal level but not to serum level.
Recurrent miscarriage might be linked to reduced endometrial progesterone and estrogen receptors and appears to be more related to nongenomic activity of progesterone. Endometrial receptors expression correlates to tissue hormonal level rather than to serum hormonal level.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(7):527-533
10-14-2004
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000700004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of hysterosalpingography (HSG) and transvaginal sonography (TVS) in terms of detecting uterovaginal anomalies in women with a history of recurrent miscarriage. METHODS: eighty patients who presented two or more consecutive miscarriages were submitted to HSG, TVS and hysteroscopy (HSC). The following diagnoses were considered separately: uterine malformations, intrauterine adhesions and polypoid lesions. Hysteroscopy was the gold standard. The matching among the different methods was evaluated by the kappa coefficient and its significance was tested. The significance level was 0.05 (alpha=5%). Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, with 95% of statistical confidence interval, were calculated. RESULTS: uterovaginal anomalies were detected in 29 (36.3%) patients: 11 (13.7%) were uterine malformations, 17 (21.3%) intrauterine adhesions and one (1.3%) a polypoid lesion. The global matching between HSG and HSC was 85.5%, while between TVS and HSC it was only 78.7%. The best accuracy of HSG appeared to be for the diagnosis of uterine malformations and intrauterine adhesions (diagnostic accuracy of 97.5 and 95%, respectively). For the diagnosis of polypoid lesions, HSG had a diagnostic accuracy of only 92.5%, due to the low rate of positive predictive value (14.3%). TVS had a worse accuracy for all diagnoses, 93.7% for the diagnosis of uterine malformations and 85% for intrauterine adhesions, due to low sensitivity. CONCLUSIONS: histerosalpingography showed a good diagnostic accuracy for the diagnosis of uterine cavity diseases. TVS had good specificity, but with low sensitivity.