Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(12):575-580
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005158
To compare the distributions of patients with clinical-pathological subtypes of luminal B-like breast cancer according to the 2011 and 2013 St. Gallen International Breast Cancer Conference Expert Panel.
We studied 142 women with breast cancer who were positive to estrogen receptor and had been treated in São Paulo state, southeast Brazil. The expression of the following receptors was assessed by immunohistochemistry: estrogen, progesterone (PR) and Ki-67. The expression of HER-2 was measured by fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis in tissue microarray.
There were 29 cases of luminal A breast cancers according to the 2011 St. Gallen International Breast Cancer Conference Expert Panel that were classified as luminal B-like in the 2013 version. Among the 65 luminal B-like breast cancer cases, 29 (45%) were previous luminal A tumors, 15 cases (20%) had a Ki-67 >14% and were at least 20% PR positive and 21 cases (35%) had Ki-67 >14% and more than 20% were PR positive.
The 2013 St. Gallen consensus updated the definition of intrinsic molecular subtypes and increased the number of patients classified as having luminal B-like breast cancer in our series, for whom the use of cytotoxic drugs will probably be proposed with additional treatment cost.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(3):97-102
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000300002
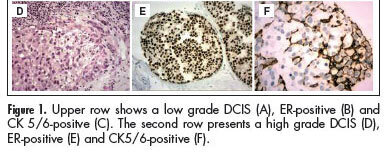
PURPOSE:To compare the prognostic and predictive features between in situ and invasive components of ductal breast carcinomas. METHODS:We selected 146 consecutive breast samples with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) associated with adjacent invasive breast carcinoma (IBC). We evaluated nuclear grade and immunohistochemical expression of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), cytokeratin 5/6 (CK5/6), and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in both components, in situ and invasive, and the Ki-67 percentage of cells in the invasive part. The DCIS and IBC were classified in molecular surrogate types determined by the immunohistochemical profile as luminal (RE/PR-positive/ HER2-negative), triple-positive (RE/RP/HER2-positive), HER2-enriched (ER/PR-negative/HER2-positive), and triple-negative (RE/RP/HER2-negative). Discrimination between luminal A and luminal B was not performed due to statistical purposes. Correlations between the categories in the two groups were made using the Spearman correlation method. RESULTS:There was a significant correlation between nuclear grade (p<0.0001), expression of RE/RP (p<0.0001), overexpression of HER2 (p<0.0001), expression of EGFR (p<0.0001), and molecular profile (p<0.0001) between components in situ and IBC. CK 5/6 showed different distribution in DCIS and IBC, presenting a significant association with the triple-negative phenotype in IBC, but a negative association among DCIS. CONCLUSIONS: Our results suggest that classical prognostic and predictive features of IBC are already determined in the preinvasive stage of the disease. However the role of CK5/6 in invasive carcinoma may be different from the precursor lesions.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(10):581-589
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001000003
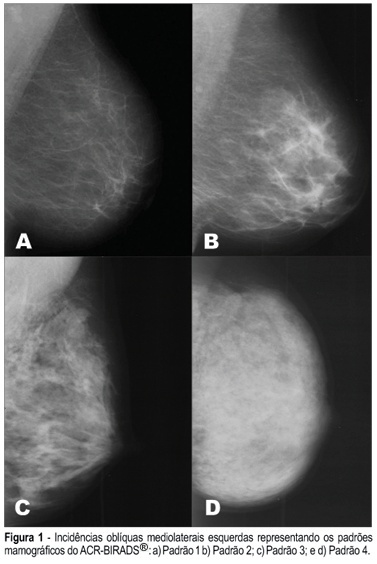
PURPOSE: To assess the presence of estrogen receptor gene polymorphisms HaeIII and MspI as well as clinical factors, and their possible associations with high mammographic density in post-menopausal women. METHODS: One hundred and fifteen post-menopausal women, not in use of hormonal therapy and without clinical or mammographic lesions were evaluated. Three independent observers have determined the mammographic density pattern based on the ACR-BIRADS® 2003 (two subjective and one objective evaluations - Adobe Photoshop 7.0 software). Oral swabs (Cytobrush) were obtained to extract DNA and the polymerase chain reaction - restriction fragment length polymorphism) was performed to assess the presence of polymorphisms in intron 1 and exon 1 from estrogen receptor gene (HaeIII and MspI). RESULTS: The HaeIII polymorphism was found in 43 (37.4%) of the 115 women, while MspI was found in 96 (83.5%) of them. There was a good agreement among determinations of the three observers with regard to mammographic density. Thirty-four (29.6%) women had dense breasts and eighty-one (70.4%) had non-dense breasts. CONCLUSION: The estrogen receptor gene polymorphism Haelll showed no association with mammographic density (Fisher = 0.712), while the association between estrogen receptor gene polymorphism Mspl and mammographic density was near significance (Fisher = 0.098). The associations among age, parity and body mass index revealed statistical significance.