-
Original Article
Gene Polymorphisms in FAS (Rs3740286 and Rs4064) Are Involved in Endometriosis Development in Brazilian Women, but not those in CASP8 (rs13416436 and rs2037815)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):450-457
08-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleGene Polymorphisms in FAS (Rs3740286 and Rs4064) Are Involved in Endometriosis Development in Brazilian Women, but not those in CASP8 (rs13416436 and rs2037815)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):450-457
08-01-2018Views119Abstract
Objective
The present study aims to investigate the association between caspase-8 (CASP8) (rs13416436 and rs2037815) and Fas cell surface death receptor (FAS) (rs3740286 and rs4064) polymorphisms with endometriosis in Brazilian women.
Methods
In the present case-control study, 45 women with a diagnosis of endometriosis and 78 normal healthy women as a control group were included. The genotyping was determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with Taqman hydrolysis probes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Darmstadt, Germany). Genotypic and allelic frequencies were analyzed using Chi-squared (χ2) test. In order to determine the inheritance models and haplotypes ,SNPStats (Institut Català d’Oncologia, Barcelona, Spain) was used. Levels of 5% (p = 0.05) were considered statistically significant.
Results
No significant difference was observed in genotypic or allelic frequencies between control and endometriosis groups for rs13416436 and rs2037815 (CASP8 gene). On the other hand, a significant difference between rs3740286 and rs4064 (FAS gene) was found. Regarding polymorphisms in the FAS gene, a statistically significant differencewas found in co-dominant and dominantmodels. Only the haplotype containing the rs3740286A and rs4064G alleles in the FAS gene were statistically significant.
Conclusion
The polymorphisms in the CASP8 gene were not associated with endometriosis. The results indicate an association between FAS gene polymorphisms and the risk of developing endometriosis.
Key-words ApoptosisEndometriosisGenetic polymorphismGenetic predisposition to diseaseReal-time polymerase chain reactionSee more -
Systematic Review
Zika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and Microcephaly
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):235-248
05-01-2017
Summary
Systematic ReviewZika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and Microcephaly
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):235-248
05-01-2017Views322Abstract
From the discovery of the Zika virus (ZIKV) in 1947 in Uganda (Africa), until its arrival in South America, it was not known that it would affect human reproductive life so severely. Today, damagetothe central nervous system is known to be multiple, and microcephaly is considered the tip of the iceberg. Microcephaly actually represents the epilogue of this infection’s devastating process on the central nervous system of embryos and fetuses. As a result of central nervous system aggression by the ZIKV, this infection brings the possibility of arthrogryposis, dysphagia, deafness and visual impairment. All of these changes of varying severity directly or indirectly compromise the future life of these children, and are already considered a congenital syndrome linked to the ZIKV. Diagnosis is one of the main difficulties in the approach of this infection. Considering the clinical part, it has manifestations common to infections by the dengue virus and the chikungunya fever, varying only in subjective intensities. The most frequent clinical variables are rash, febrile state, non-purulent conjunctivitis and arthralgia, among others. In terms of laboratory resources, there are also limitations to the subsidiary diagnosis. Molecular biology tests are based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR)with reverse transcriptase (RT) action, since the ZIKV is a ribonucleic acid (RNA) virus. The RT-PCR shows serum or plasma positivity for a short period of time, no more than five days after the onset of the signs and symptoms. The ZIKVurine test is positive for a longer period, up to 14 days. There are still no reliable techniques for the serological diagnosis of this infection. If there are no complications (meningoencephalitis or Guillain-Barré syndrome), further examination is unnecessary to assess systemic impairment. However, evidence is needed to rule out other infections that also cause rashes, such as dengue, chikungunya, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, rubella, and herpes. There is no specific antiviral therapy against ZIKV, and the therapeutic approach to infected pregnant women is limited to the use of antipyretics and analgesics. Anti-inflammatory drugs should be avoided until the diagnosis of dengue is discarded. There is no need to modify the schedule of prenatal visits for pregnant women infected by ZIKV, but it is necessary to guarantee three ultrasound examinations during pregnancy for low-risk pregnancies, and monthly for pregnant women with confirmed ZIKV infection. Vaginal delivery and natural breastfeeding are advised.
Key-words arbovirus infectionsblindness/ etiologydeafness/ etiologymicrocephaly/ ultrasonographyPregnancy complicationsReal-time polymerase chain reactionZika virusSee more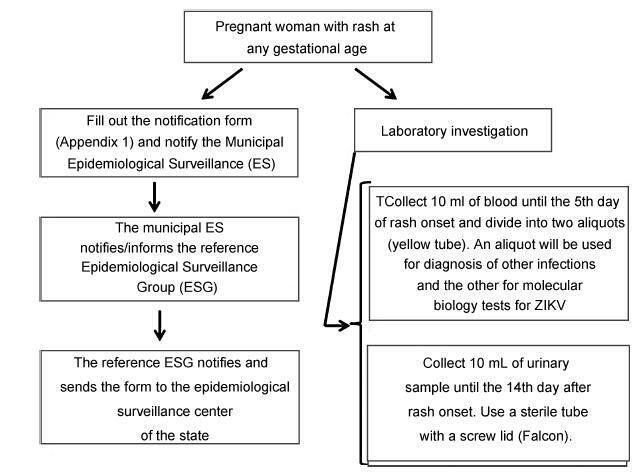
-
Artigos Originais
Detection of Human Cytomegalovirus and Herpes Simplex Virus type 2 in cervical sample
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(11):499-504
12-20-2012
Summary
Artigos OriginaisDetection of Human Cytomegalovirus and Herpes Simplex Virus type 2 in cervical sample
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(11):499-504
12-20-2012DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001100004
Views80PURPOSE: To detect the presence of Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and Herpes Simplex Virus type 2 (HSV-2) DNA in cervical samples from women assisted in a primary health care clinic in the city of Coari, Amazonas, Brazil. METHODS: Participated in this study 361 sexually active women between 18 and 78 years. They were been assisted in a Basic Health Care Clinic for routine gynecological exam. The cervical samples were collected using endocervical brush. The viruses were detected using real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) technique. RESULTS: Mean age was 36.4 years (standard deviation (SD)=13.4). HCMV DNA was found in cervical samples from 30 women (8.3%; IC95% 5.8 - 11.8) and HSV 2 DNA in 2 women (0.6%; IC95% 0.1 - 2.2). Two women related being HIV positive, one of them infected with HCMV. There were no statistically significant associations between infections by the pathogens studied and socioeconomic, clinical or behavioral variables. CONCLUSIONS: The prevalence of the HCMV infection found in the sample points to the need for screening of the virus during pregnancy and surveillance in immunocompromised patients. The low prevalence of HSV-2 found is probably due to the fact that cervical sampling is not appropriate for this type of study because of the characteristics of viral biology related to neurovirulence.
Key-words AmazonasBrazilCytomegalovirus infectionsHerpesvirus 2 humanMolecular diagnosisReal-time polymerase chain reactionSee more


