-
Adolescent Female Victims of Sexual Violence: Analysis of Loss of Follow-up after Emergency Care and Outpatient Follow-up
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):661-675
Abstract
Original Article/Sexual Violence/Pediatric and Adolescent GynecologyAdolescent Female Victims of Sexual Violence: Analysis of Loss of Follow-up after Emergency Care and Outpatient Follow-up
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):661-675
Views111See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the loss to follow-up after emergency care and during 6-months of outpatient follow-up, and the associated variables, among adolescent sexual violence survivors.
Methods
This is a retrospective study with review of the medical records of 521 females, aged 10 to 18 years, who received emergency care in a referral service in São Paulo, Brazil. The variables were sociodemographic; personal history; characteristics of abuse, disclosure, and reactions triggered after abuse (physical and mental disorders as well as social changes), psychotropic prescription needs, and moment of abandonment: after emergency care and before completing 6 months of outpatient follow-up. To compare groups of patients lost to follow-up at each time point, we used the Chi-square and Fisher exact tests followed by multiple logistic regression with stepwise criterion for selection of associated variables. We calculated the odds ratio with confidence interval (OR, CI 95%). The level of significance adopted was 5%.
Results
A total of 249/521 (47.7%) adolescents discontinued follow-up, 184 (35.3%) after emergency care and 65 (12.4%) before completing outpatient follow-up. The variables of living with a partner (OR = 5.94 [CI 95%; 2.49–14.20]); not having a religion (OR = 2.38 [CI 95%;1.29–4.38)]), having a Catholic religion [OR = 2.11 (CI 95%; 1.17–3.78)]; and not disclosing the abuse [OR = 2.07 (CI 95%; 1.25–3.44)] were associated with loss to follow-up after emergency care. Not needing mental disorder care (OR = 2.72 [CI 95%; 1.36–5.46]) or social support (OR = 2.33 [CI 95%; 1.09–4.99]) were directly associated with loss to outpatient follow-up.
Conclusion
Measures to improve adherence to follow-up should be aimed at adolescents who live with a partner and those who do not tell anyone about the violence.
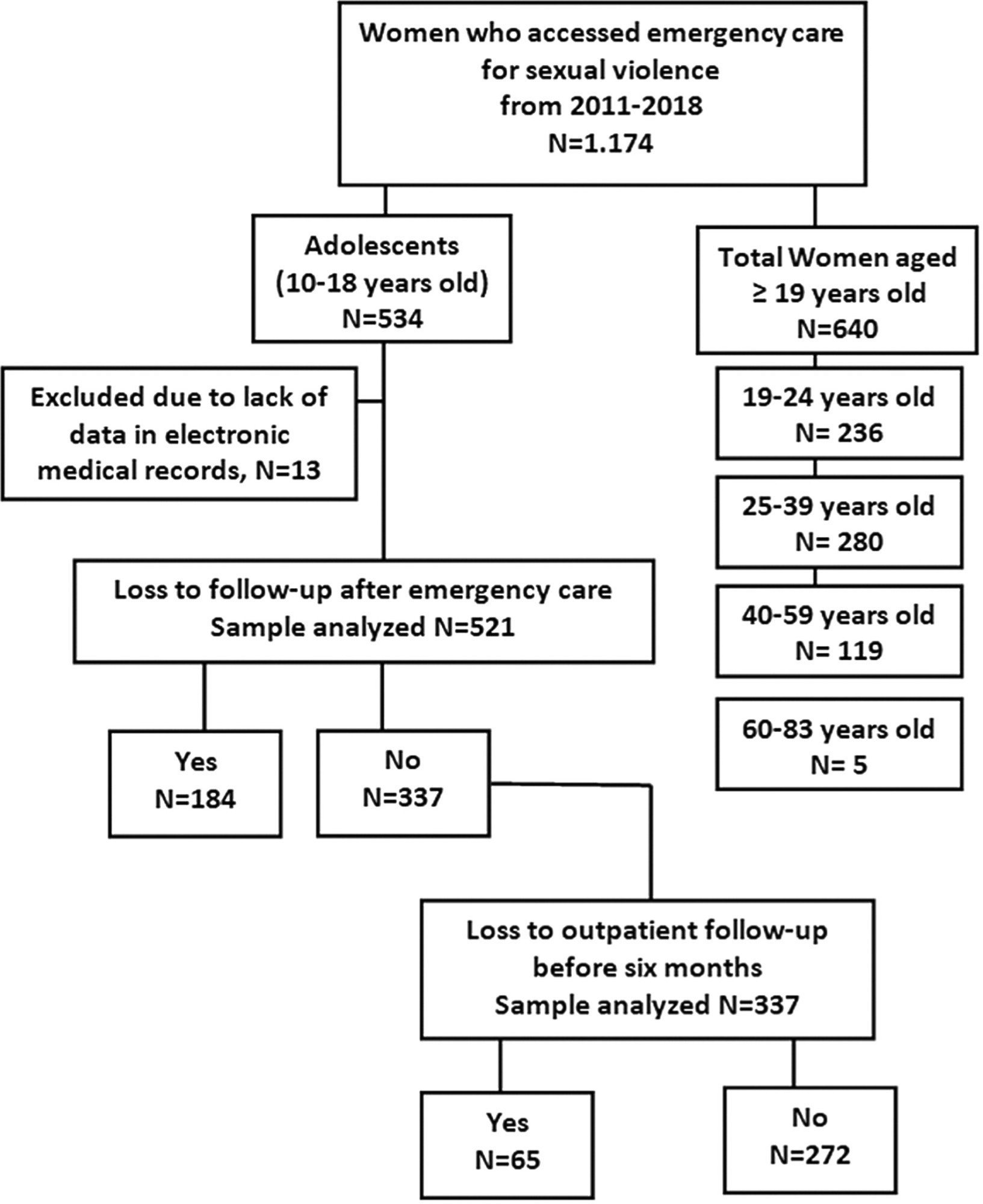
-
Original Article02-28-2022
Assistance to Victims of Sexual Violence in a Referral Service: A 10-Year Experience
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):47-54
Abstract
Original ArticleAssistance to Victims of Sexual Violence in a Referral Service: A 10-Year Experience
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):47-54
Views187See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the assistance provided to women victims of sexual violence and their participation in the follow-up treatment after the traumatic event, presenting a sociodemographic profile, gynecological background, and circumstances of the event, and reporting the results, acceptance, and side effects of prophylaxis for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and pregnancy.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study comprising the period between 2007 and 2016. All women receiving medical care and clinical follow-up after a severe episode of sexual violence were included. Records of domestic violence, male victims, children, and adolescents who reported consensual sexual activity were excluded. The present study included descriptive statistics as frequencies and percentages.
Results
A total of 867medical records were reviewed and 444 cases of sexual violence were included. The age of the victims ranged from10 to 77 years old, most of them selfdeclared white, with between 4 and 8 years of education, and denying having a sexual partner. Sexual violence occurred predominantly at night, on public thoroughfare, being committed by an unknown offender. Most victims were assisted at the referral service center within 72 hours after the violence, enabling the recommended prophylaxis. There was high acceptance of antiretroviral therapy (ART), although half of the users reported side effects. Seroconversion to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or to hepatitis B virus (HBV) was not detected in women undergoing prophylaxis.
Conclusion
In the present cohort, the profile of victims of sexual violence was loweducated, young, white women. The traumatic event occurred predominantly at night, on public thoroughfare, being committed by an unknown offender. Assistance within the first 72 hours after sexual violence enables the healthcare center to provide prophylactic interventions against STIs and unwanted pregnancies.
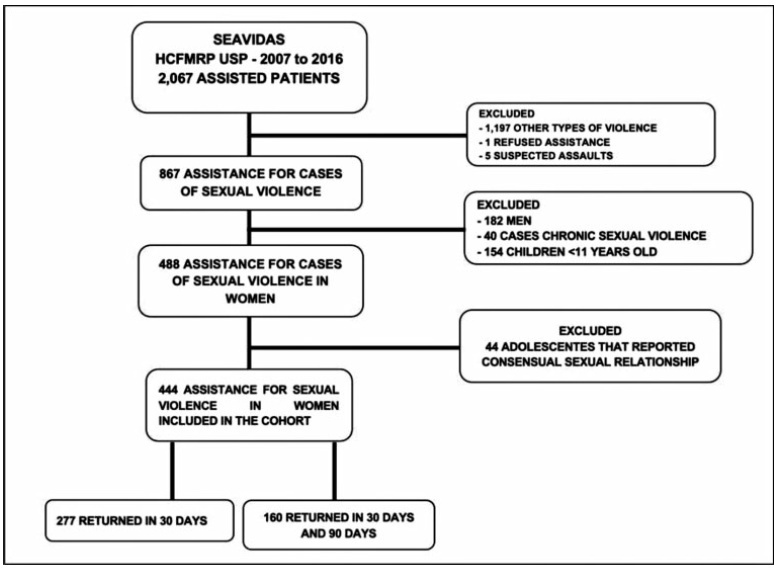
-
Original Article10-23-2020
Epidemiological Profile of the Victims of Sexual Violence Treated at a Referral Center in Southern Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):547-554
Abstract
Original ArticleEpidemiological Profile of the Victims of Sexual Violence Treated at a Referral Center in Southern Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):547-554
Views203See moreAbstract
Objective
To characterize the sociodemographic profile of women victims of sexual violence treated at a university hospital in southern Brazil.
Method
The present cross-sectional study included all female victims of sexual violence who attended the sexual violence unit at the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA, in the Portuguese acronym) from April 18, 2000 to December 31, 2017.Data were extracted from the electronic record of the patients and stored in a standardized questionnaire database with epidemiological aspects of the victim, the perpetrators and the type of aggression. Statistical analysis was performed using the chi-squared test for trend and descriptive statistics with 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results
During the length of the study, 711 women victims of sexual violence were treated. The mean age of the patients was 24.4 (±10) years old (range from 11 to 69 years old) and most of the victims were white (77.4%), single (75.9%) and sought care at the unit within 72 hours after the occurrence (80.7%). In most cases, violence was exerted by a single perpetrator (87.1%), who was unknown in 67.2% of cases. Victims < 19 years old showed a higher risk of not using contraception (relative risk [RR] = 2.7; 95% CI = 1.9-3.6).
Conclusion
Most victims of sexual violence were treated within 72 hours of the occurrence. The majority of these victims were white and young, and those < 19 years old had a higher risk of not using contraception and to know the sexual perpetrator.
-
Integrative Review04-17-2020
Genital Injuries: Are They Telling us Something about Sexual Violence?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):106-113
Abstract
Integrative ReviewGenital Injuries: Are They Telling us Something about Sexual Violence?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):106-113
Views151See moreAbstract
Genital injury has a forensic relevance after a sexual assault and it has been discussed and investigated among professionals who work in this field. To analyze the studies published in the last decades, the present review examines different factors that may influence this finding, first clarifying terms of the forensic field, such as the peculiarity of the legal medical examination, and the distinction of the terms “legal” and “anatomical” vagina. Finally, it analyses if it is possible that the existence of these injuries in victims explain the lack of consent in sexual contact, and to clarify the meaning of the absence of injuries.
-
Review Article08-16-2006
Sexual violence: recommended procedures and results of emergency care for women victims of rape
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(2):126-135
Abstract
Review ArticleSexual violence: recommended procedures and results of emergency care for women victims of rape
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(2):126-135
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000200009
Views85See moreGender-based violence is related to the power imbalance between men and women that is present, to a greater or lesser degree, in all societies. It was recognized as a human rights problem by the UN relatively recently. It includes emotional, physical and sexual violence. Sexual violence is the extreme form of gender violence, usually accompanied by the other types of violence. Its prevalence is difficult to determine, but it most probably affects at least one third of women some time in their life. It has multiple consequences to women's physical and gynecological health, which depends in great part on the quality of the care the woman received immediately after the assault. Unfortunately, most emergency health services, including those in women's hospitals, are rarely prepared to provide the correct care for these women. Care should be multidisciplinary and involves crisis treatment, meticulous clinical examination with complementary auxiliary methods, treatment of physical lesions, prevention of pregnancy and of sexually transmitted infections and AIDS, and follow-up for at least six months after the aggression.
-
Original Article05-07-2004
Characterization of sexual violence against women in the Maria-Maria project in Teresina, PI
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):111-116
Abstract
Original ArticleCharacterization of sexual violence against women in the Maria-Maria project in Teresina, PI
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):111-116
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200005
Views124See morePURPOSE: to evaluate the characteristics of sexual violence against women, the types of sexual crimes and resulting body lesions. METHODS: descriptive study based on the information obtained from the medical records of 102 victims of sexual violence who were seen at the Maria-Maria project from March 2002 to March 2003 and who fulfilled the eligibility criteria. The characteristics of the violence, the types of crimes and the body injuries are described. For calculation and analysis of the data, the Epi-Info, version 6.04, program, for simple percentages and frequency distribution were used. RESULTS: ages of the victims ranged from 1 to 68 years, 65.7% were younger than 20 years and one in four was younger than 9 years. The majority were single (78.3%) and with a low educational level (74.2%). The crime predominated at night (64.7%), in a secluded area (39.2%), followed by the victim's home (34.3%), and at the location of the attack (67.6%). Among the adolescent victims, the unknown attacker predominated, while among the children the attackers were men known to the victims. In the case of the children younger than 10 years, indecent assault was the most frequent crime (73.8%) while rape was the most frequent crime among the adolescents (66.4%). Body trauma occurred in 76.7% of the cases, mainly hematomas, vulva edema and abrasions. CONCLUSION: sexual violence predominated among children and adolescents, single women and with low educational level. The aggression happened more frequently during the night, by an unknown person, in a secluded area, in the case of adolescents, and by a known person (mainly neighbour), in the victim's home, in the case of children. Rape was the most frequent kind of crime among adolescents and among children it was indecent assault, usually associated with genital and corporeal trauma.


