Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):089-095
We evaluated internal consistency, test-retest reliability, and criterion validity of the Brazilian Portuguese version of the Female Sexual Function Index 6-item Version (FSFI-6) for postpartum women.
Therefore, questionnaires were applied to 100 sexually active women in the postpartum period. The Cronbach α coefficient was used to evaluate the internal consistency. Test-retest reliability was analyzed by Kappa for each item of the questionnaire and by the Wilcoxon parametric test, comparing the total scores of each evaluation. For the assessment of criterion validity, the FSFI was used as the gold standard and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was constructed. Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). It was found that the internal consistency of the FSFI-6 questionnaire was considerably high (0.839).
The test-retest reliability results were satisfactory. It can also be stated that the FSFI-6 questionnaire presented excellent discriminant validity (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.926). Women may be considered as having sexual dysfunction if the overall FSFI-6 score is < 21, with 85.5% sensitivity, 82.2% specificity, positive likelihood ratio of 4.81 and negative likelihood ratio of 0.18.
We conclude that the Brazilian Portuguese version of FSFI-6 is valid for use in postpartum women.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):497-502
Construction and validation of the WhatsApp Stress Scale (WASS), a questionnaire designed for physicians that measures how the use of smartphones and related software communication applications affects the quality of life of gynecologists who use this tool to communicate with patients.
The present cross-sectional observational study analyzed 60 gynecologists according to weekly WhatsApp usage time for communication with patients and compared the data with the perception of the doctor on the use of this virtual interaction as a stressor. Physicians were equally divided into three groups:<2hours, 2 to 5 hours, and>5 hours. The authors created a questionnaire in Likert scale format. The study proceeded in three phases: development of the questionnaire items, pretesting, constructing, and validity and reliability testing using factor analysis, Cronbach α coefficient, and paired t-test.
A 9-item instrument using a 5-point Likert scale was created and administered to the participants in 3 different times: T0, T1 (15minutes after the end of T0), and T2 (15 days later). All questionnaire items possessed adequate content validity indices and the internal consistency of the instrument was satisfactory (Cronbach α 0.935; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.744-0.989; p=0.0001). No statistically significant differences were observed in the responses between the rounds of testing, indicating good test-retest reliability. A positive association between the high frequency of WhatsApp usage for communication with patients and the stress perceived by the doctor was shown.
The WASS is a valid and reliable instrument for assessing the use of messaging applications to communicate with patients as a stressor perceived by gynecologists.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):20-25
To validate the premenstrual symptoms screening tool (PSST) in relation to the daily record of severity of problems (DRSP) for premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) diagnoses.
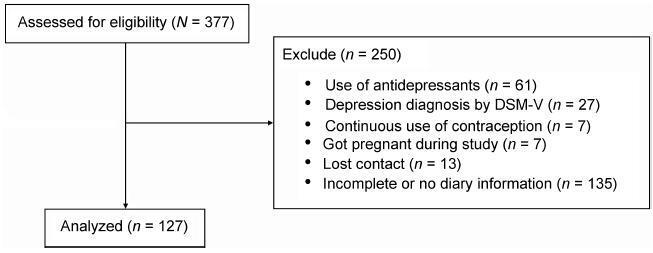
A cross-sectional study with 127 women (20 45 years) with PMS complaints. The women were evaluated in terms of weight, height and body mass index (BMI). After using the primary care evaluation of mental disorders (PRIME-MD) questionnaire to exclude the diagnosis of depression, the PSST was completed and the women were instructed to fill out the DRSP for two consecutive menstrual cycles. The agreement between the two questionnaires was assessed by the Kappa (k) and the prevalence-adjusted, bias-adjusted kappa (PABAK) values.
Two-hundred and eighty-two women met the eligibility criteria and answered the PSST. The DRSP was completed for two cycles by 127 women. The percentages of women with PMS and PMDD diagnoses by the DRSP were 74.8% and 3.9% respectively; by PSST, the percentages were41.7% and 34.6% respectively. The number of patients considered "normal" (with symptoms below the threshold for the diagnosis of PMS) was similar in both questionnaires. There was no agreement (Kappa = 0.12) in the results of PMS/ PMDD diagnosis (the PABAK coefficient confirmed this result = 0.39). The PSST had a high sensitivity (79%) and a low specificity (33.3%) for PMS/PMDD diagnosis.
The PSST should be considered a diagnostic screening tool. Positive PMS/PMDD cases by PSST should be further evaluated by DRSP to confirm the diagnosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(10):518-523
To translate into Portuguese, culturally adapt and validate the Uterine Fibroid Symptom - Quality of Life (UFS-QoL) questionnaire for Brazilian women with uterine leiomyoma.
Initially, the UFS-QoL questionnaire was translated into Brazilian Portuguese in accordance with international standards, with subsequent cultural, structural, conceptual and semantic adaptations, so that patients were able to properly answer the questionnaire. Fifty patients with uterine leiomyoma and 19 patients without the disease, confirmed by abdominal pelvic examination and/or transvaginal ultrasound, were selected at the outpatient clinics of the Department of Gynecology of the Universidade Federal de São Paulo (Unifesp). The UFS-QoL questionnaire was administered to all women twice on the same day, with two different interviewers, with an interval of 15 minutes between interviews. After 15 days, the questionnaire was readministered by the first interviewer. Reliability (internal consistency and test-retest), construct and discriminative validity were tested to ratify the questionnaire.
The reliability of the instrument was assessed by Cronbach’s α coefficient with an overall result of 0.97, indicating high reliability. The survey results showed a high correlation (p= 0.94; p 0.001).
The UFS-QoL questionnaire was successfully adapted to the Brazilian Portuguese language and Brazilian culture, showing reliability and validity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(6):293-299
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000600005
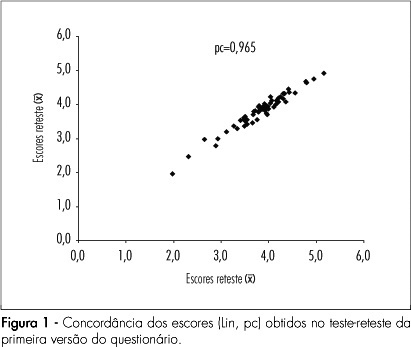
PURPOSE: to generate and validate a proper questionnaire to evaluate the sexual function in post-menopause women. METHODS: 251 women, within 2 to 15 years postmenopause, were included in the study. Questionnaire's reproductibility/reliability was evaluated by Pearson, intraclass and Lin's correlation coefficients. The internal consistance was examined by the Cronbach's alpha coefficient. Classical item theory guidelines were used for face, content and construct validation. RESULTS: an instrument with 57 items and nine domains was generated. Fourteen questions (24.5%) were eliminated by either poor correlation with the scale or low discriminative power. The final version with 43 items has shown good reproductibility (r=0.719, 95%CI=0.690-0.750; pc=0.887; 95%CI=0.850-0.930; p<0.001). Internal consistance was also adequate (α=0.951). About 60% of the reviewers have confirmed face and content validation. The construct validation was assessed by the Cronbach alpha 0.951. CONCLUSIONS: it was concluded that the new instrument is appropriate for evaluating the sexual function in post-menopause women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(5):248-252
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000500005
PURPOSE: to analyze the isoflavone and estrogen effects on the postmenopausal quality of life. METHODS: this is a randomized and double-blind study with 79 postmenopausal patients, 12 months of amenorrhea, 40 years old or more and body mass index (BMI) above 30 kg/m². The participants were randomly divided into two treatment groups: GECP received orally two capsules, every 12 hours, one contained 0.625 mg conjugated equine estrogen and another placebo (n=33); GECS received two capsules of 150 mg extract of soy, with 60 mg isoflavone (n=32). Both treatments were administered for six months. The Quality Menopause Specific Questionnaire of Life was applied before and after one, three and six months of treatment. The parameters of gynecological cancer risk were evaluated. ANOVA and the Tukey test were used for data analysis. RESULTS: there was a reduction in the values of the vasomotor parameters after six months of treatment, 1.6±0.8 and 2.4±1.6, compared to before therapy, 4.0±2.2 and 4.2±2.3 in GECP and GECS, respectively. The psychological aspects showed reduction in values after six months of therapy, 2.5±1.2 and 2.9±1.4, compared to before treatment, 3.6±1.6 and 4.1±1.9 in GECP and GECS, respectively. Similar results were obtained on the physical aspects and in the sexual symptoms. CONCLUSIONS: isoflavones may positively act on life quality of postmenopausal women. This effect was similar to conjugated equine estrogen.