Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1021-1031
To develop and validate a protocol for the use of the Dietary Guidelines for the Brazilian Population (DGBP) in the individual dietary advice for pregnant women assisted in primary healthcare (PHC).
Methodological study that involved the elaboration of a protocol in six steps: definition of the format, definition of the instrument to evaluate food consumption, systematization of evidence on food and nutrition needs of pregnant women, extraction of DGBP recommendations, development of messages of dietary guidelines and content, and face validity. The analyses of the validation steps were carried out by calculating the Content Validity Index (CVI) and thematic content analysis.
As products of the steps, the protocol structure was defined and the dietary advice for pregnant women were elaborated, considering physiological changes, food consumption, nutritional and health needs, and socioeconomic conditions of this population. The protocol was well evaluated by experts and health professionals in terms of clarity, relevance (CVI > 0.8), and applicability. In addition, the participants made some suggestions to improve the clarity of the messages and to expand the applicability of the instrument with Brazilian pregnant women.
The instrument developed fills a gap in clinical protocols on dietary advice for pregnant women focused on promoting a healthy diet, contributing to a healthy pregnancy. In addition, it demonstrates potential to contribute to the qualification of PHC professionals and to the implementation of the DGBP recommendations.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):398-408
The present study aimed to evaluate the antenatal care adequacy for women who gave birth at the University Hospital of Santa Catarina in Florianopolis (Brazil) during the COVID-19 pandemic, and to evaluate the association of adequacy with sociodemographic, clinical, and access characteristics.
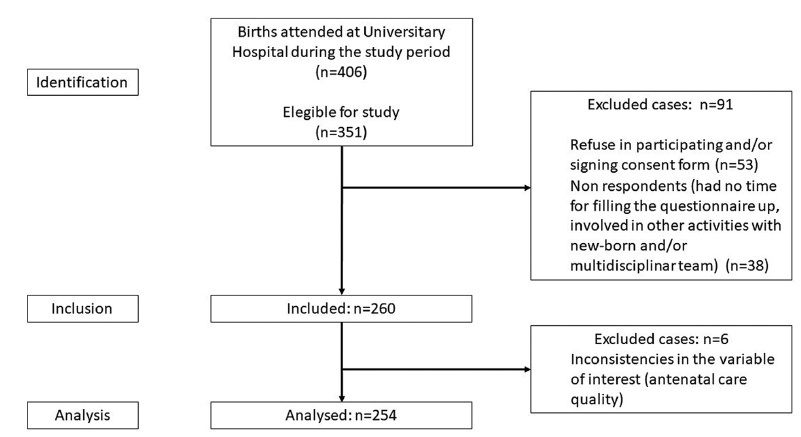
Data were collected between October and December 2020, including 254 patients who delivered in the University Hospital from Federal University of Santa Catarina and answered our questionnaires. Additional data were obtained from patients’ antenatal booklets. Antenatal care was classified as adequate, intermediate, or inadequate according to the number of appointments, gestational age at the beginning of follow-up, and tests results. We carried out a descriptive statistical analysis and a bivariate/with odds ratio analysis onmaternal sociodemographic, clinical and health access variables that were compared with antenatal adequacy.
Antenatal care was considered adequate in 35.8% of cases, intermediate in 46.8%, and inadequate in 17.4%. The followingmaternal variables were associated with inadequate prenatal care (intermediate or inadequate prenatal care): having black or brown skin colour, having two or more children, being of foreign nationality, not being fluent in Portuguese, and using illicit drugs during pregnancy; the clinical variables were more than 6 weeks between appointments, and not attending high-risk antenatal care; as for access, the variables were difficulties in attending or scheduling appointments, and attending virtual appointments only.
In a sample of pregnant women from a teaching hospital in Florianópolis during the COVID-19 pandemic, antenatal care was considered adequate in 35.8%, intermediate in 46.8%, and inadequate in 17.4% of cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):597-606
To evaluate conditions associated with stillbirth (SB), and possible trends related with it, in a maternity hospital school in the North zone of São Paulo.
An observational, cross-sectional study conducted at the Hospital Maternidade- escola de Vila Nova Cachoeirinha with 1,139 SBs in the period of 2003 to 2017. Cases of intermediate SB (ISB) (weight between 500 and 999 g) and late SB (LSB) (weight ≥ 1,000 g) were compared. We evaluated clinical data, laboratory tests, and fetal and placental studies. Data were stored in Windows Excel (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA) worksheets, according to which graphs and tables were constructed. We used the statistical software SPSS for Windows version 18.0 (SPSS In., Chicago, IL, USA), estimating the prevalence ratio (PR) and odds ratio (OR), considering the 95% confidence interval (95% CI).
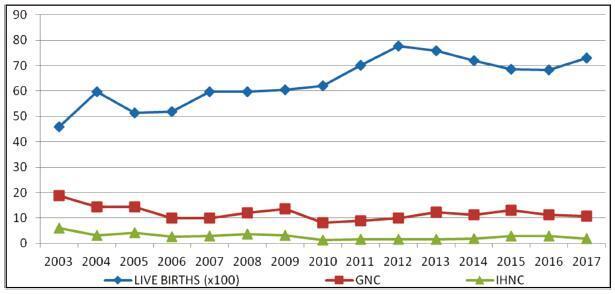
The general SB rate was 11.9%, and the in-hospital SB rate was 2.8%. Pregnant women younger than 16 years of age were more likely to have ISB (OR 0.32, 0.15- 0.76), while patients older than 40 years old had a higher chance of LSB (PR 0.85, 0.72- 0.99). A total of 25.7% of the general population did not have prenatal care, and 77.1% of the cases presented fetal death at admission. The cases of ISB had a statistically significant association with home birth (OR 0.61, 0.46-0.80). Cesarean section was performed in 16.1% of the subjects, and misoprostol was the most used method for induction. Necropsy and placental study of the fetuses were performed, respectively, in 94.2% and 97.3% of the cases. Associated causes were not identified in 22.1% of the cases, and the main causes identified were amniotic sac infections (27.9%), fetal malformations (12.5%), placental abruption (11.2%), hypertensive syndromes (8.5%), and maternal syphilis (3.9%), the latter with an increasing trend.
Among the factors associated to SB were: hypertensive syndromes, amniotic sac infections, fetal malformations, placental abruption and syphilis. There was a growing trend in the number of cases of syphilis, which translates an alert. Diagnostic limitations justify indeterminate causes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(4):185-191
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000400009
PURPOSE: To evaluate the prevalence and factors associated with intimate partner violence (IPV) among women users of Basic Health Units (BHU) in the State of São Paulo. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional descriptive study based on secondary data analysis of women users' interviews at 75 BHU in the State of São Paulo, from August/2008 to May/2009. We used a questionnaire based on the Abuse Assessment Screen and the Conflict Tactics Scales modified by the Violence Against Women Study (VAW), structured and pre-tested. The variables studied were the types of IPV (psychological, physical and sexual) and sociodemographic variables (age, education, race, paid work, religion, marital status and economic class). We interviewed 2,379 women aged 18 to 60 years. RESULTS: The prevalence of lifetime IPV was 55.7%, and the prevalences of psychological, physical and sexual IPV were 53.8, 32.2 and 12.4%, respectively. Women without a partner but previously married, with schooling <8 years and belonging to the lower economic class had a higher risk for all types of IPV, and other factors were also associated with psychological and sexual IPV. CONCLUSIONS: The prevalence of IPV is high. Healthcare professionals in primary care should make an attempt to detect IPV.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(1):10-15
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000100003
PURPOSES: To investigate the effect of an individualized and supervised exercise program for the pelvic floor muscles (PFM) in the postpartum period of multiparous women, and to verify the correlation between two methods used to assess PFM strength. METHODS: An open clinical trial was performed with puerperal, multiparous women aged 18 to 35 years. The sample consisted of 23 puerperal women divided into two groups: Intervention Group (IG, n=11) and Control Group (CG, n=12). The puerperal women in IG participated in an eight-week PFM exercise program, twice a week. The puerperal women in CG did not receive any recommendations regarding exercise. PFM strength was assessed using digital vaginal palpation and a perineometer. The statistical analysis was performed using the following tests: Fisher's exact, c², Student's t, Kolmogorov-Smirnov for two samples, and Pearson's correlation coefficient. Significance was defined as p<0.05. RESULTS: The participants' mean age was 24±4.5 years in IG and 25.3±4 years in CG (p=0.4). After the exercise program, a significant difference was found between the groups in both modalities of muscle strength assessment (p<0.001). The two muscle strength assessment methods showed a significant correlation in both assessments (1st assessment: r=0.889, p<0.001; 2nd assessment: r=0.925, p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: The exercise program promoted a significant improvement in PFM strength. Good correlation was observed between digital vaginal palpation and a perineometer, which indicates that vaginal palpation can be used in clinical practice, since it is an inexpensive method that demonstrated significant correlation with an objective method, i.e. the use of a perioneometer.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(5):293-299
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000500002
Purpose: to study the prenatal care among Public Health Service ("Sistema Único de Saúde") users from Caxias do Sul - RS. Methods: a transversal study of 702 pregnancies attended at the Hospital Geral -Universidade de Caxias do Sul from March 2000 to March 2001 based on the criteria set by the "Programa Nacional de Humanização do Pré-natal e Nascimento (PNHPN)" of the Brazilian Ministry of Health. Results: the observed prenatal coverage was 95.4%, whereas the average of visits was 6.2. The main reported reason for not following prenatal care was the lack of information about its importance (65.6%). In 51.5% of the cases, prenatal care started in the third month of pregnancy, whereas 44.3% of the pregnant women carried out all the proposed complementary tests. Prenatal care was considered inappropriate in 64.8% and appropriate in 35.2% of the cases. The quality of prenatal attention was significantly associated with the mother's education, as well as with the number of previous deliveries. The higher the educational level, the better the quality of observed prenatal care (p=0.0148). In addition, the higher number of previous deliveries showed to be associated with a later beginning of prenatal care and a lower number of visits (p=0.0008). Conclusions: the prenatal care available at Caxias do Sul in spite of its good coverage, should be reviewed in terms of quality. Special attention should be given to education in health along the prenatal assistance.