-
Original Article
Reproductive Planning and the Choice of Long-acting Reversible Contraceptive Primary to Health: A Cross-Sectional Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(8):456-464
10-09-2023
Summary
Original ArticleReproductive Planning and the Choice of Long-acting Reversible Contraceptive Primary to Health: A Cross-Sectional Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(8):456-464
10-09-2023Views108Abstract
Objective
Evaluate the different perspectives that involve the choice of long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), the issues related to this process and the consequences of deciding one method in the women's in the primary health care (PHC) center in Sousas, a district in Campinas, SP (Brazil).
Methods
This is an analytical cross-sectional study, it was performed at the PHC in Sousas. Data were collected through the analysis of medical records and interviews with women who live in Sousas and had the insertion of the copper intrauterine device (IUD) (D) from April 2021 to April 2022 or the etonogestrel implant (I) from May to December 2022. The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Medical Science School at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP).
Results
Reason for choosing this LARC: medical (D: 52%; I: 100%), easy adhesion (D: 71%; I: 67%), effectiveness (D: 55%; I: 100%). Indication by health professionals (D: 65%; I: 100%). And improvement of clinical characteristics: mood (D: 77%; I: 67%), body mass index (BMI; D: 52%; I: 33%), and libido (D: 84%; I: 67%).
Conclusion
It is suggested that women tend to decide between LARCs when guided by their doctor or PHC health professionals, and they select LARCs because of the ease of use and low failure rates. Therefore, this study highlights how LARCs can positively interfere in the aspects that pervade contraception, such as BMI, libido, and mood.
Key-words clinical parametersHealth educationlong-acting reversible contraceptivePrimary carereproductive planningSee more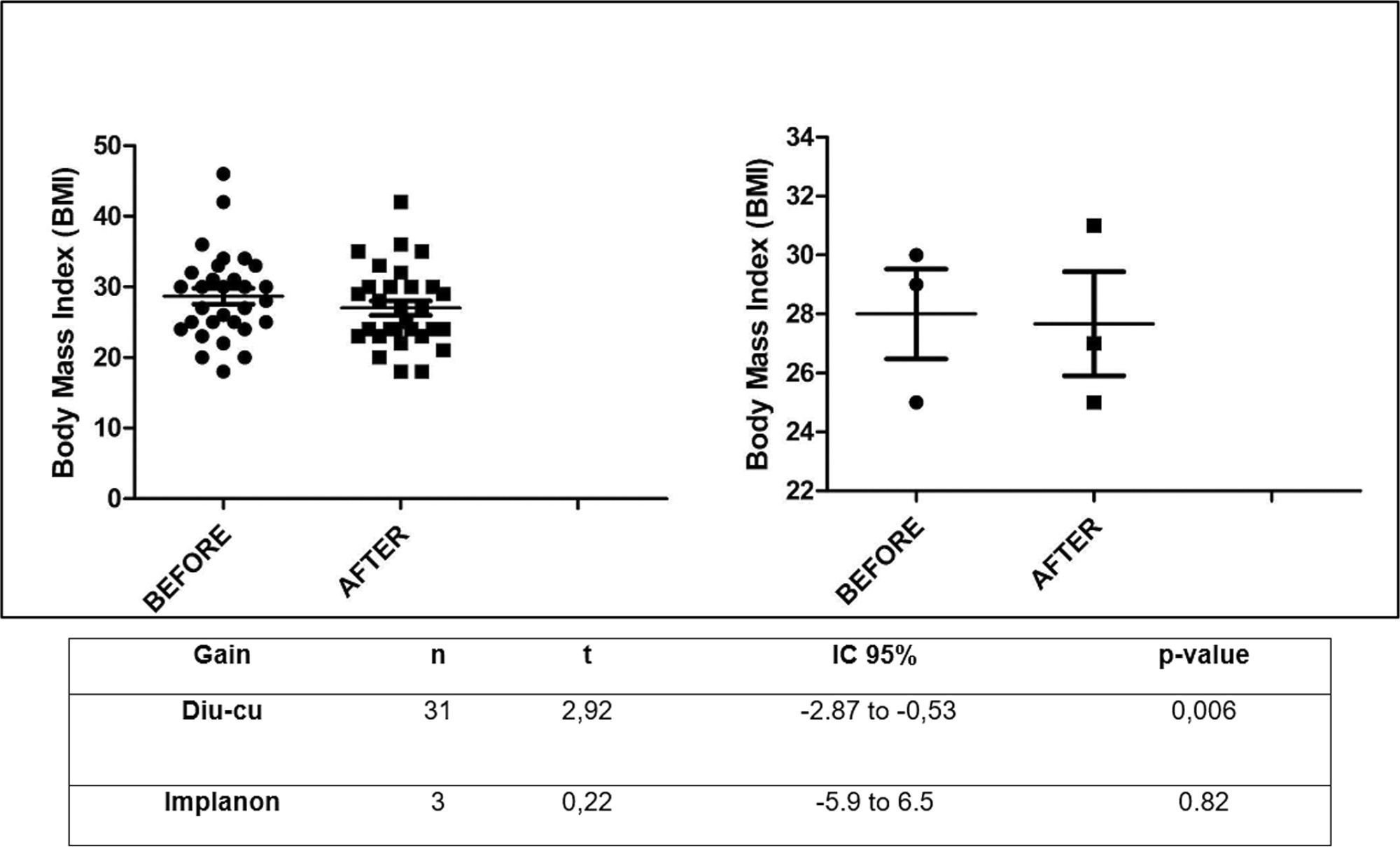
-
Trabalhos Originais
Prevalence and correlates of hiv infection and syphilis in prostitutes attending a STD/AIDS reference center
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):151-154
04-10-1998
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisPrevalence and correlates of hiv infection and syphilis in prostitutes attending a STD/AIDS reference center
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):151-154
04-10-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300005
Views77See moreA retrospective study examining medical records of female prostitutes attending the STD/AIDS Reference Center in Vitória, Brazil from January/93 to December/96 was conducted. During this period, 180 women received medical and psychological care in this clinic. Mean age was 25.9 year (SD=6.8). Out of 180, 140 agreed to be tested for HIV, of whom 12 (8.6%) had a positive result. Among 157 women who agreed to be tested for syphilis, 144 (91.7%) had a negative result, while 13 (8.3%) had a positive one. According to the educational degree, 6 (3.3%) women were illiterate, 114 (63.3%) attended elementary school, 37 (20.6%) attended secondary school, 7 (3.9%) went to college and 16 gave no information. One hundred and forty-one patients (78.3%) were single, 17 (9.4%) married, 10 (5,5%) divorced and 4 (2.2%) widows. The frequency of condom use was: always, 56 (31.3%), sometimes, 93 (52.0%), and 30 (16.8%) never used condoms. Other STDs were reported by 89 (49.4%) women and 9 (5.0%) reported intravenous (IV) drug use. There was a significant difference between the HIV positive and the negative group only regarding IV drug abuse (p=0.031) and syphilis infection (p=0.014). The present study showed prevalence rates of HIV infection among prostitutes in Vitória much higher than those found in the general population. There is a pressing need to improve medical assistance and educational campaigns especially designed to reach this population of women, and focusing the importance of regular condom use and the risks associated with IV drug abuse.
-
Artigos Originais
Evaluation of body mass index of women from an outpatient gynecological general clinic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(2):69-74
07-06-2005
Summary
Artigos OriginaisEvaluation of body mass index of women from an outpatient gynecological general clinic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(2):69-74
07-06-2005DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000200005
Views78See morePURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of overweight, obesity, and associated factors among women who visited a general gynecologic clinic in a secondary hospital of reference. METHODS: the following variables were studied: age, race, educational level, family income, job (paid work done by the women), type of the women's job, current partner, menstrual cycle characteristics at the time of interview, and body mass index (BMI). The patients were divided into three groups, according to their BMI values: <25 kg/m² (normal), between 25-29 kg/m² (overweight) and >30 kg/m² (obesity). The odds ratio (OR) and respective 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were calculated in the overweight and obese groups. Subsequently, the OR was calculated and adjusted for other variables. RESULTS: among the 676 studied women, 89.8% had received up to 8 years of formal education, 83.0% had a partner, 77.6% were Caucasian, 61.4% earned less than 5 minimum wages, and 36.0% of these women were menopausal. The prevalence of overweight was 35.6% and of obesity 24.6%. Overweight was related to age ranging from 50 to 59 years (OR: 3.22; 95% CI: 1.67-6.20) and menopause (OR: 1.52; 95% CI: 1.03-2.26), and obesity was related to menopause (OR: 2.57; 95% CI: 1.66-4.00) and to age range above 40 years (OR: 2.95; 95% CI: 1.37-6.37). According to the multiple regression analysis, only obesity was associated with age range above 40 years (OR: 2,51; 95% CI: 1.05-6.00). CONCLUSION: the prevalence rates of overweight and obesity were high in our sample of low-income women and those with less education. Obesity was associated with women aged over 40. Attempts should be made to reduce the prevalence of overweight and obesity in women.


