Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):690-696
To evaluate the prevalence of hypertensive disorders, perinatal outcomes (preterm infants, low birthweight infants and Apgar score < 7 at the 5th minute and fetal deaths) and the cesarean rates in pregnant women hospitalized for delivery at the Maternidade Hilda Brandão da Santa Casa de Belo Horizonte, Belo Horizonte, state of Minas Gerais, Brazil, from March 1, 2008 to February 28, 2018.
A case-control study was performed, and the groups selected for comparison were those of pregnant women with and without hypertensive disorders. Out of the 36,724 women, 4,464 were diagnosed with hypertensive disorders and 32,260 did not present hypertensive disorders
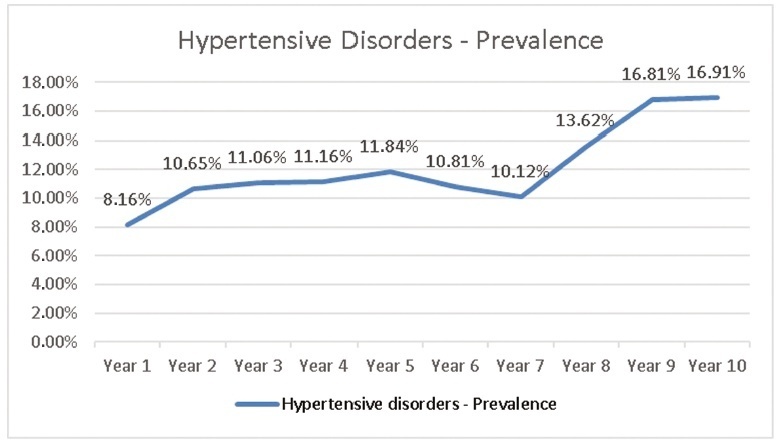
The prevalence of hypertensive disorders was 12.16%; the perinatal outcomes and cesarean rates between the 2 groups with and without hypertensive disorders were: preterm infants (21.70% versus 9.66%, odds ratio [OR] 2.59, 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.40-2.80, p < 0.001); low birthweight infants (24.48% versus 10.56%; OR 2.75; 95% CI, 2.55-2.96; p < 0.001); Apgar score < 7 at the 5th minute (1.40% versus 1.10%; OR 1.27; 95% CI, 0.97-1.67; p = 0.84); dead fetuses diagnosed prior to delivery (1.90% versus 0.91%; OR 2.12; 95% CI, 1.67-2.70; p < 0.001); cesarean rates (60.22% versus 31.21%; OR 3.34; 95% CI, 3.14-3.55; p < 0.001).
Hypertensive disorders are associated with higher rates of cesarean deliveries and higher risk of preterm infants, low birthweight infants and a higher risk of fetal deaths.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(8):505-510
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000800002
Purpose: to evaluate if multiple courses of antenatal corticosteroids are more effective than single ones to reduce morbidity and mortality of preterm infants. Methods: retrospective study of 184 newborns with gestational age less than 34 weeks from a tertiary-level hospital in São Paulo from January 1988 to December 1998. The patients were divided into two groups: single course (n=135) - newborns whose mothers were exposed to a complete single course (2 doses of betamethasone or 4 doses of dexamethasone between 24 h and 7 days prior to delivery); multiple courses (n=49) - newborns whose mothers were exposed to two or more complete courses. The primary clinical outcomes for the two groups were: frequency of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), intra-hospital mortality and combined neonatal morbidity (including the presence of the following: RDS, peri-intraventricular hemorrhage, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, necrotizing enterocolitis, sepsis or intra-hospital death). Numerical data were compared by Student's t test or Mann-Whitney test and categorical data by chi² or Fisher exact test, with the odds ratio and its confidence interval. Results: there were no differences between the groups that received single or multiple courses of antenatal corticosteroids in regard to the occurrence of RDS (single course: 22% and multiple course: 18%), intra-hospital mortality (single course 18% and multiple 12%) and combined neonatal morbidity (single course 62% and multiple 63%). Conclusions: multiple courses of antenatal corticosteroids did not reduce the morbidity and mortality of preterm infants. This study emphasizes the present guidelines that recommend the use of one single course of corticosteroid for fetal maturation in pregnant women at risk for preterm delivery.