Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):749-756
To describe caffeine consumption during pregnancy and its association with low birth weight (LBW) and preterm birth in the birth cohort of Ribeirão Preto, state of São Paulo, Brazil, in 2010.
Cohort study, with descriptive and analytical approach. Data included 7,607 women and their newborns in Ribeirão Preto, state of São Paulo, Brazil. The women answered standardized questionnaires about reproductive health, prenatal care, life habits, sociodemographic conditions, and information about coffee intake. The independent variable was high caffeine consumption (≥300 mg/day) from coffee during pregnancy, and the dependent variables were LBW (birth weight < 2,500 g) and preterm birth (< 37 weeks of gestational age). Four adjusted polytomous logistic regression models, relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were fitted: biological and sociodemographic conditions; obstetric history; current gestational conditions; and all variables included in the previous models.
A total of 4,908 (64.5%) mothers consumed caffeine, 143 (2.9%) of whom reported high consumption. High caffeine intake was significantly associated with reduced education and with the occupation of the head of the family, nonwhite skin color, not having a partner, higher parity, previous abortion and preterm birth, urinary tract infection, threatened abortion, alcohol consumption and smoking. No association was found between high caffeine consumption and LBW or preterm birth in both
In this cohort, high caffeine intake was lower than in other studies and no association with LBW or preterm birth was found.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):171-179
To evaluate the use of tocolysis in cases of preterm birth due to spontaneous preterm labor in a Brazilian sample.
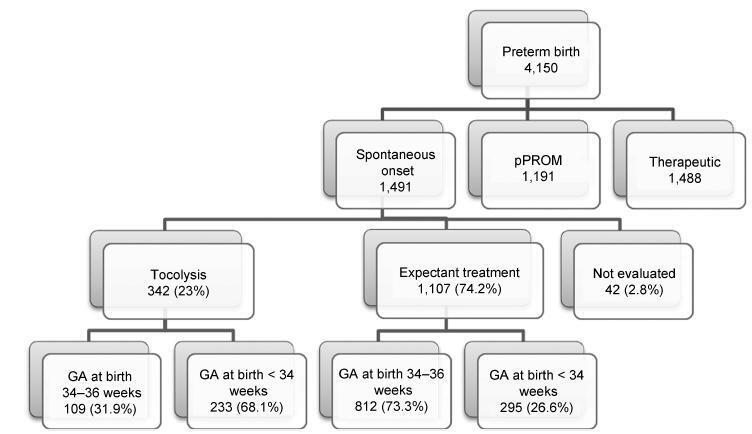
A sample of 1,491 women with preterm birth due to spontaneous preterm labor were assessed, considering treatment with tocolysis or expectant management, according to gestational age at birth (< 34 weeks and 34 to 36 þ 6 weeks) and drugs prescribed. The study took place in 20 Brazilian hospitals from April 2011 to July 2012. Bivariate analyses were conducted to evaluate associations with sociodemographic and obstetric characteristics and odds ratios with their respective 95% confidence intervals were estimated for maternal and neonatal outcomes.
A total of 1,491 cases of preterm birth were considered. Tocolysis was performed in 342 cases (23%), 233 of which (68.1%) were delivered before 34 weeks. Within the expectant management group, 73% was late preterm and with more advanced labor at the time of admission. The most used drugs were calcium channel blockers (62.3%), followed by betamimetics (33%). Among the subjects in the tocolysis group, there were more neonatal and maternal complications (majority non-severe) and an occurrence of corticosteroid use that was 29 higher than in the expectant management group.
Tocolysis is favored in cases of earlier labor and also among thosewith less than 34 weeks of gestation, using preferably calcium channel blockers, with success in achieving increased corticosteroid use. Tocolysis, in general, was related to higher maternal and neonatal complication rates, which may be due to the baseline difference between cases at admission. However, these results should raise awareness to tocolysis use.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):350-356
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600008
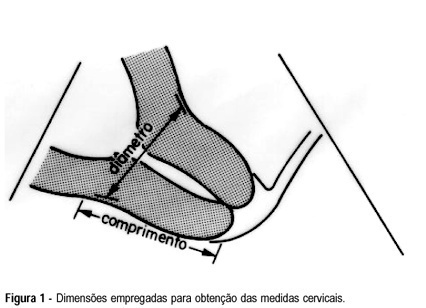
Objective: to evaluate the uterine cervix by digital and transvaginal ultrasound examinations in pregnant women at high risk of having premature delivery. Methods: during the period between February 1995 and September 1997, 38 pregnant women at high risk of having premature delivery between the 20th and 36th week of gestation were examined. These patients were submitted weekly to both digital and transvaginal ultrasound examinations. The digital examination evaluated the uterine cervix using two parameters: length and dilation. The transvaginal ultrasound studied the length and the anteroposterior diameter of the uterine cervix. The behavior of these cervical measurements was analyzed throughout the pregnancies. The two methods were compared regarding cervical evaluation and accuracy of premature birth diagnosis. Results: the rate of premature deliveries was 18.4% (7/38). Digital examination resulted in cervical evaluations with variation coefficients of 30.3% for length and 193% for dilation. Transvaginal ultrasound resulted in cervical evaluations with variation coefficients of 14.7% and 26.5% for the anteroposterior diameter and length, respectively. The cervical length measures obtained on ultrasound were always greater than those obtained on digital examination. Through analysis with the hypothesis test, an indirect relationship was observed between the cervical length and the gestational period for digital examination and ultrasound study (p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively), and a direct relationship between the cervical dilation and the gestational age observed on the digital examination (p<0.01). Conclusions: among the parameters studied by means of the digital and transvaginal ultrasound examinations, the ultrasound cervical length presented the best accuracy in the diagnosis of premature birth, proving to be more reliable for the evaluation of cervical alterations in pregnant women at high risk of premature delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(8):655--6662
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000800010
OBJECTIVE: to characterize the features of pregnant women who had elective preterm delivery, and correlate clinical and obstetrical diagnosis with neonatal results. METHOD: A total of 100 pregnant women admitted in the Obstetric Clinic ward and their respective newborns has been evaluated. The inclusion criteria were: single pregnancy, confirmed gestational age by an early scan, absence of labor symptoms and the presence of a maternal or fetal condition leading to preterm delivery indication. The direct causes of elective preterm delivery were classified in groups, to relate them to the neonatal results, taking into account the gestational age. To assess the neonatal results, the following criteria were analyzed: acidosis; 1st and 5st minute Apgar score lower than 7; intracranial hemorrhage; neonatal death; sepsis and respiratory distress syndrome. Statistical analysis used to correlate the causes of delivery and the gestational age to the neonatal results was done by log-linear models. RESULTS: One patient was excluded from the study due to fetal malformation. The most common direct causes of delivery were prenatal fetal distress (49.5%), hypertensive syndromes (21.2%), intra uterine growth restriction (13.1%) and others (16.2%). Among the main neonatal complications there were asphyxia (33.3%), acidosis (30.4%), respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) (26.3%), sepsis (22.2%), intracranial hemorrhage (21.2%) and neonatal death (13.1%). The cause of delivery was associated with acidosis and RDS by log-linear models and the gestational age was associated with RDS, 1st minute Apgar <7, sepsis, intracranial hemorrhage and neonatal death. CONCLUSIONS: the cause of delivery influences the neonatal results. Nevertheless, the most severe complications are directly dependent on the gestational age of delivery. Therefore, the prenatal diagnosis should be rigorously evaluated by the obstetrician, so that the decision to interrupt the pregnancy could be taken at the suitable moment, thus avoiding neonatal complications.