-
Review Article02-28-2022
Perinatal Outcomes after Fetal Endoscopic Tracheal Occlusion for Isolated Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia: Rapid Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):74-82
Abstract
Review ArticlePerinatal Outcomes after Fetal Endoscopic Tracheal Occlusion for Isolated Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia: Rapid Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):74-82
Views179Abstract
Objective
To compare the perinatal outcomes of fetuses with isolated congenital diaphragmatic hernia after fetal endoscopic tracheal occlusion (FETO) and antenatal expectant management.
Data sources
In this rapid review, searches were conducted in the MEDLINE, PMC, EMBASE and CENTRAL databases between August 10th and September 4th, 2020. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs), quasi-RCTs or cluster-RCTs published in English in the past ten years were included.
Study selection
We retrieved 203 publications; 180 studies were screened by abstract. Full-text selection was performed for eight studies, and 1 single center RCTmet the inclusion criteria (41 randomized women; 20 in the FETO group, and 21 in the control group).
Data collection
Data collection was performed independently, by both authors, in two steps (title and abstract and full-text reading).
Data synthesis
There were no cases of maternal mortality. The mean gestational age at delivery was of 35.6±2.4 weeks in the intervention group, and of 37.4±1.9 weeks among the controls (p<0.01). Survival until 6 months of age was reported in 50% of the intervention group, and in 5.8% of the controls (p<0.01; relative risk: 10.5; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.5-74.7). Severe postnatal pulmonary hypertension was found in 50% of the infants in the intervention group, and in 85.7% of controls (p=0.02; relative risk: 0.6; 95%CI: 0.4-0.9). An analysis of the study indicated some concerns of risk of bias. The quality of evidence was considered moderate to low.
Conclusion
Current evidence is limited but suggests that FETO may be an effective intervention to improve perinatal outcomes.
Key-words congenital diaphragmatic herniasPrenatal ultrasonographyPrognosissystematic reviewultrasound diagnosisSee more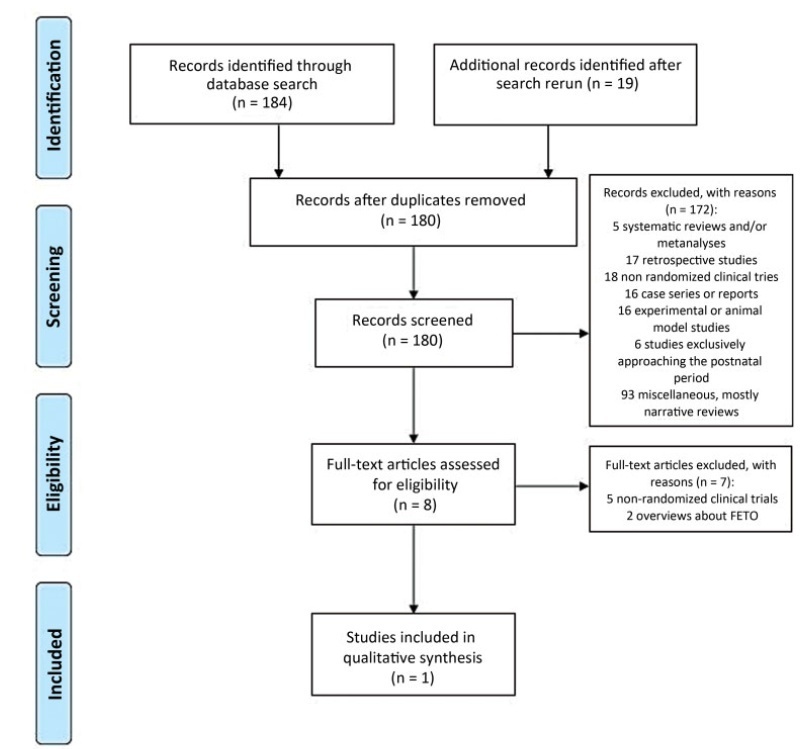
-
Original Article05-18-2020
Local References for Ultrasound-Estimated Fetal Weight Based on 2,211 Singleton Pregnancies in the City of Curitiba, South of Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(4):174-180
Abstract
Original ArticleLocal References for Ultrasound-Estimated Fetal Weight Based on 2,211 Singleton Pregnancies in the City of Curitiba, South of Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(4):174-180
Views183See moreAbstract
Objective
To develop reference curves of estimated fetal weight for a local population in Curitiba, South of Brazil, and compare them with the curves established for other populations.
Methods
An observational, cross-sectional, retrospective study was conducted. A reference model for estimated fetal weight was developed using a local sample of 2,211 singleton pregnancies with low risk of growth disorders and well-defined gestational age. This model was compared graphically with the Hadlock and Intergrowth 21st curves.
Results
Reference curves for estimated fetal weight were developed for a local population. The coefficient of determination was R2 = 99.11%, indicating that 99.11% of the fetal weight variations were explained by the model. Compared with Hadlock curves, the 50th, 90th, and 97th percentiles in this model were lower, whereas the 10th percentile nearly overlapped, and the 3rd percentile was slightly higher in the proposed model. The percentiles were higher in the proposed model compared with the Intergrowth 21st curves, particularly for the 3rd, 10th, and 50th percentiles.
Conclusion
We provide a local reference curve for estimated fetal weight. The proposed model was different from other models, and these differences might be due to the use of different populations for model construction.
-
Original Article10-10-2013
Maternal and perinatal outcomes in women with decreased amniotic fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(8):342-348
Abstract
Original ArticleMaternal and perinatal outcomes in women with decreased amniotic fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(8):342-348
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000800002
Views133PURPOSE: To determine maternal and perinatal outcomes in pregnant women with low amniotic fluid, according to the amniotic fluid index (AFI). METHODS: A cohort study conducted on 176 patients admitted to the high risk ward of Instituto de Medicina Integral Prof. Fernando Figueira (IMIP), in Recife, Pernambuco, Brazil. Amniotic fluid was measured by the amniotic fluid index, and classified as low when between 5.1 and 7.9 cm, moderate oligohydramnios between 3.1 and 5.0 cm, and severe oligohydramnios when less than or equal to 3.0 cm. To determine the difference between the three groups of categorical variables studied the chi-square and Fisher exact tests were used, when applicable, and for the numerical variables the Mann-Whitney test was applied, with the level of significance set at 5%. RESULTS: Fetal malformation more frequently occurred when oligohydramnios was severe. Hypertensive disorders, however, were associated with moderate oligohydramnios. There was similarity between the three groups in relation to premature rupture of membranes and other causes. Low amniotic fluid was more frequently diagnosed when tested at the gestational age of 32 weeks or earlier. Regarding the perinatal outcomes, the incidence of Apgar score <7 in the 1st and 5th minutes, perinatal death, neonatal jaundice and pulmonary hypoplasia was higher when oligohydramnios was moderate to severe. CONCLUSIONS: Maternal and perinatal causes and outcomes in pregnant women with low amniotic fluid vary with respect to their AFI, severe oligohydramnios being associated with fetal malformation and other adverse perinatal outcomes.
Key-words Amniotic fluidFetal membranes, premature ruptureHypertensionOligohydramniosPrenatal ultrasonographySee more


