-
Review Article03-18-2025
Efficacy of vitamin C supplementation during pregnancy in the prevention of preterm birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo1
Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy of vitamin C supplementation during pregnancy in the prevention of preterm birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo1
Views169Abstract
Objective:
Preterm birth is a leading global cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity, with oxidative stress playing a role in its pathogenesis. Vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant, may help reduce this risk. This study assessed the effectiveness of vitamin C supplementation, both alone and with vitamin E, in preventing preterm birth compared to a placebo.
Data source:
Databases were systematically searched in PubMed, Cochrane and Embase in December 2023 and updated in May 2024.
Study Selection:
Included RCTs evaluated vitamin C's effect on preterm birth and related neonatal outcomes.
Data collect:
Statistical analyses used a random-effects model for pooled risk ratios (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed with the I² statistic.
Data synthesis:
Seventeen RCTs (21,567 patients) were analyzed. Vitamin C supplementation showed no significant difference compared to placebo for preterm birth (RR 1.04; 95% CI 0.96, 1.14). No significant differences were observed for neonatal death (RR 0.77; 95% CI 0.55, 1.08), NICU admission (RR 1.03; 95% CI 0.95, 1.13), preterm PROM (RR 1.04; 95% CI 0.63, 1.71), or birth weight (MD 52.41; 95% CI −19.65, 124.47). A slight decrease in gestational age was observed (MD 0.26; 95% CI −0.02, 0.55).
Conclusion:
Vitamin C supplementation alone or in combination with vitamin E does not significantly prevent preterm birth or improve related neonatal outcomes.
Key-words Ascorbic acidFetal membranes, premature ruptureGestational ageIntensive care units, neonatalPregnancyPremature birthVitamin C supplementationVitamin ESee more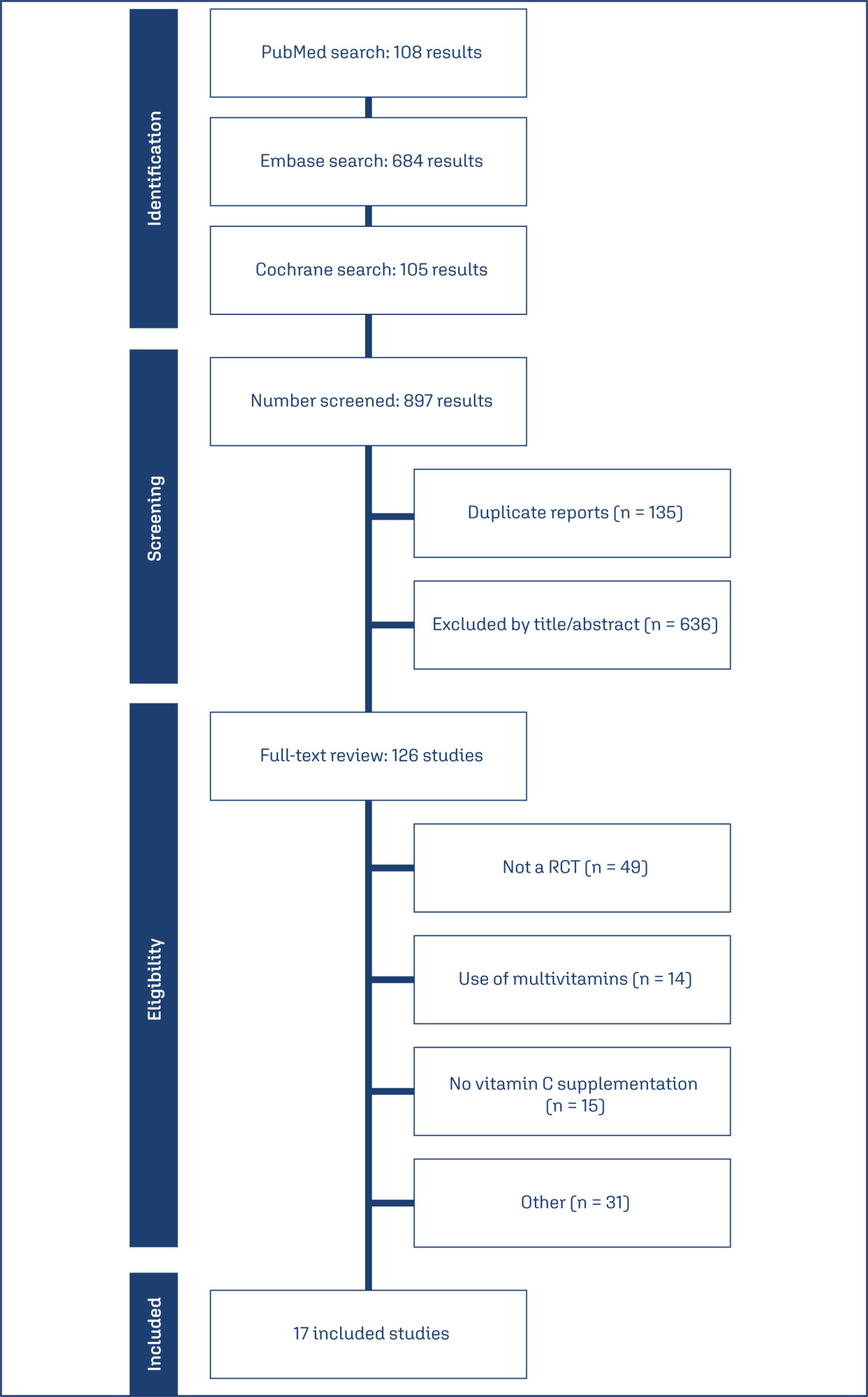
-
Original Article08-15-2019
Pregnancy Among Women with Kidney Transplantation: A 20-Years Single-Center Registry
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(7):419-424
Abstract
Original ArticlePregnancy Among Women with Kidney Transplantation: A 20-Years Single-Center Registry
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(7):419-424
Views140See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess maternal and perinatal outcomes in pregnancies after kidney transplantation in a tertiary center in Brazil.
Methods
Retrospective cohort of pregnancies in women with kidney transplantation at the Universidade Estadual de Campinas, from January 1995 until December 2017. Medical charts were reviewed, andmaternal and perinatal outcomes were described as means and frequencies. Renal function and blood pressure were evaluated during pregnancy and postpartum.
Results
A total of 22 women had at least 1 pregnancy during the considered timeinterval, and 3 of them had > 1 pregnancy, totalizing 25 pregnancies. The mean age at transplantation was of 24.6 ± 4.2 years old, and the mean time interval until pregnancy was of 67.8 ± 46.3months. Themost frequent complication during pregnancywas hypertension, which affected 11 (64.7%)women. The gestational age at delivery was 34.7 ± 4weeks, and 47% of these pregnancies were preterm (< 37 weeks). A total of 88.2% of the women delivered by cesarean section. Renal function, measured by serum creatinine, remained stable during pregnancy, and the systolic blood pressure increased significantly, while the diastolic blood pressure did not differ during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Pregnancy after kidney transplantation is a rare event. Pre-eclampsia and prematurity were frequent complications, and cesarean section rates were very high. A specialized antenatal and postpartum care with a multiprofessional approach and continuous monitoring of graft function are essential for the early diagnosis of complications and improved outcomes.
-
Original Article10-01-2018
Analysis of the Performance of 11 Formulae for Fetal Weight Estimation in Preterm Fetuses with Abnormal Doppler Velocimetry – A Retrospective Multicenter Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):580-586
Abstract
Original ArticleAnalysis of the Performance of 11 Formulae for Fetal Weight Estimation in Preterm Fetuses with Abnormal Doppler Velocimetry – A Retrospective Multicenter Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):580-586
Views184Abstract
Objective
To assess 11 formulae commonly used to estimate fetal weight in a population of premature fetuses who had abnormal Doppler velocimetry due to early-onset placental insufficiency. The performance of each formula was evaluated in subgroups of fetuses with expected growth and intrauterine growth restriction.
Methods
Data were collected fromfetuses andmothers who delivered at three Brazilian hospitals between November 2002 and December 2013.We used the following formulae: Campbell; Hadlock I, II, III, IV and V; Shepard; Warsof; Weiner I and II; and Woo III.
Results
We analyzed 194 fetuses. Of these, 116 (59.8%) were considered appropriate for gestational age (AGA), and 103 (53.1%) were male. The amniotic fluid volume was reduced in 87 (44.8%) fetuses, and the umbilical artery Doppler revealed absence or inversion of diastolic flow in 122 (62.9%) cases, and the analysis of the ductus venosus revealed abnormal flow in 60 (34.8%) fetuses. The Hadlock formulae using three or four fetal biometric parameters had low absolute percentage error in the estimated fetal weight among preterm fetuses with abnormal Doppler studies who were born within 5 days of the ultrasound evaluation. The results were not influenced by the clinical and ultrasound parameters often found in early-onset placental insufficiency.
Conclusion
In this study, the formulae with the best performance for fetal weight estimation in the analyzed population were Hadlock I and IV, which use four and three fetal biometric parameters respectively to estimate the weight of preterm fetuses with abnormal Doppler studies.
Key-words Birth weightDoppler ultrasoundFetal growth retardationFetal weightPlacental insufficiencyPremature birthprenatal ultrasoundultrasoundSee more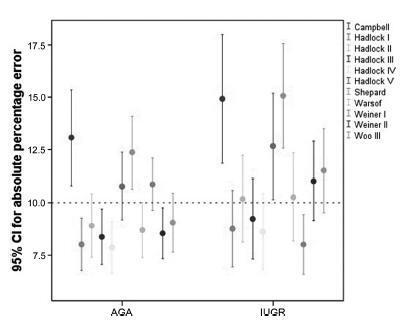
-
Original Article04-01-2017
High Blood Pressure during Pregnancy is not a Protective Factor for Preterm Infants with Very Low Birth Weight. A Case-Control Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):155-161
Abstract
Original ArticleHigh Blood Pressure during Pregnancy is not a Protective Factor for Preterm Infants with Very Low Birth Weight. A Case-Control Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):155-161
Views200See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate whether the presence of maternal blood pressure reduces the risks of morbidity, perinatal mortality and morbidity at 24 months of age in very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs) compared with a control group.
Methods
A retrospective, observational, case-control study. Total 49 VLBWIs were allocated to the study group, called the maternal arterial hypertension group (AHG), and matched with 44 in the control group (CG). The infants were assessed during hospitalization and at 12 and 24 months corrected age at a specialized clinic. For the assessment of growth, the World Health Organization (WHO) Anthro software (Geneva, 2006) was used, and for the psychomotor assessment, the Denver II test was used.
Results
In relation to the antenatal variables, the infants of the AHG had more centralized circulation assessed by Doppler, received more corticosteroids and magnesium sulfate, and were born by cesarean section more frequently. In terms of the postnatal and in-hospital outcomes, the AHG had a higher gestational age at birth (30.7 versus 29.6 weeks) and a lower frequency of 5-minute Apgar scores of less than 7 (26.5% versus 52.3%). The CG had a higher rate of pulmonary dysplasia (30.2% versus 8.3%). There were no differences in terms of hospital mortality, complications, somatic growth and functional problems at 24 months of corrected age.
Conclusion
The presence of maternal hypertension, especially preeclampsia, was not a protective factor against morbidity, mortality and evolution in VLBWIs aged up to 24 months. Therefore, the clinical practice should be focused on prolonging the pregnancy for as long as possible in these conditions as well.
-
Original Article01-01-2014
Perinatal variables and association with very low birthweight newborns in a Brazilian public university hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(1):10-16
Abstract
Original ArticlePerinatal variables and association with very low birthweight newborns in a Brazilian public university hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(1):10-16
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000100004
Views144PURPOSE:
To investigate the association of perinatal variables with the birth of very low birth weight (VLBW) preterm newborns.
METHODS:
It was a retrospective study of the medical records of infants born after spontaneous preterm labor with admission to a neonatal intensive care unit. Preterm infants were divided into two groups: very low birth weight (VLBW) group (weight <1,500 g) and low birth weight (LBW) group (weight ≥1,500 g and <2,500 g). Prenatal variables such as maternal complications during pregnancy and childbirth/postpartum, and fetal/neonatal complications were investigated. Statistical analysis was performed using the Fisher exact test or χ2 test, with calculation of relative risk (RR), and the Student t test for comparison of group means, with the level of significance set at p≤0.05.
RESULTS:
Hemorrhagic comorbidities (p=0.006; RR=1.2) and hypertension (p=0.04; RR=1.5), surgical delivery (p=0.001; RR=0.5), gestational age <33 weeks (p< 0.001; RR=16.7) and Apgar score at 1st and 5th minute (p=0.006; RR=1.6; p=0.01; RR=1.9) were associated with the occurrence of VLBW. Infants with VLBW had a significant association with the occurrence of metabolic comorbidities (p=0.01; RR=1.8), neurological (p=0.01; RR=1.7) and infectious diseases (p=0.001; RR=1.9), hospitalization >4 weeks (p=0.02; RR=1.8) and early neonatal death (p=0.0001; RR=2.9).
CONCLUSIONS:
Factors such as hypertension and bleeding comorbidities during delivery and management of gestational age of less than 33 weeks were associated with the birth of VLBW newborns. This group of infants also showed higher RR for the occurrence of early neonatal death.
Key-words Hospitals, universityInfant, low birth weightInfant, very low birth weightPremature birthPreterm laborSee more -
Original Article11-06-2013
Preterm birth prediction: sequential evaluation of the cervix and the test for phosphorylated protein-1 linked to insulin-like growth factor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(9):394-400
Abstract
Original ArticlePreterm birth prediction: sequential evaluation of the cervix and the test for phosphorylated protein-1 linked to insulin-like growth factor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(9):394-400
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000900003
Views64PURPOSE: To investigate the usefulness of the measurement of cervical length and of the test for phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (phIGFBP-1) performed sequentially in the prediction of preterm birth and the correlation between tests. METHODS: We analyzed data from 101 asymptomatic pregnant women with a history of premature delivery. The ultrasound measurement of cervical length and phIGFBP-1 test were performed in parallel every three weeks, between 24 and 34 week. The best cutoff value for each cervical evaluation was established by the ROC curve, and the two tests were compared using nonparametric tests. We determined the sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of each test and of the association of the exams for the occurrence of delivery before the 37th weeks. RESULTS: There were 25 preterm births (24.8%). The cervix length showed the highest sensitivity and was able to predict preterm birth in all evaluations, with similar accuracy at different gestational ages. The test for phIGFBP-1 was not helpful at 24 weeks, but was able to predict prematurity when performed at 27, 30 and 33 weeks. The combination of tests increased the sensitivity (81.8%) and negative predictive value (93.7%) when compared to the separate use of each test. The mean cervical length was lower in women with a positive test. CONCLUSIONS: Both cervical length and the test for phIGFBP-1 were able to predict premature delivery, and sequential combination of both tests showed a high sensitivity and high negative predictive value.
Key-words Biological markersCervical length measurementCervixInsulin-like growth factor binding protein-1Premature birthRisk assessmentSee more


