Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):454-459
09-25-2020
Streptococcus agalactiae is an important pathogen in neonates and pregnant women. Neonatal invasive infections due to S. agalactiae are life-threatening and preventive strategies for this challenge of human have become a concern. The aim of the present study was to determine the prevalence of rectovaginal colonization, related risk factors and antibiotic resistance pattern of S. agalactiae among pregnant women in Iran.
The present study was performed on 240 pregnant women. Vaginal and rectal swabs were obtained from all of the women and then were transferred to the laboratory. The isolation and identification of S. agalactiae was performed by standard microbiological tests and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay. The antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of the isolates were determined by the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion. Polymerase chain reaction was used to detect ermB and mefA genes in erythromycin-nonsusceptible isolates.
Out of 240 pregnant women, 16 cases (6.7%) were colonized by S. agalactiae. There is no significant association between demographic-obstetric factors and maternal S. agalactiae colonization in the pregnant women. Linezolid, vancomycin and ampicillin were the most effective antibiotics against S. agalactiae. The ermB gene was present in 6 (35.29%) S. agalactiae isolates. However, the mefA gene was not detected in any of the isolates.
Given the relatively significant prevalence of S. agalactiae colonization in the pregnant women in the present study and the risk of serious neonatal infections, the screening of pregnant mothers for the bacteria seems necessary. Our findings highlight the importance of appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis during pregnancy for the prevention of early onset S. agalactiae-neonatal infection and comorbidity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):628-632
11-07-2019
Although mature cystic teratoma (MCT) is benign, malignant transformation (MT) occurs in ~ 1% to 2% of all cases, and usually consists of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which accounts for ~ 80% of the cases. Spindle-cell (sarcomatoid) carcinoma (SCSC) is an uncommon type of SCC, comprising up to 3% of all cases. The lack of characteristic symptoms and specific imaging findings may lead to preoperative misdiagnosis. Moreover, the clinicopathologic characteristics, the treatment, the prognostic factors and the mechanism of MT have not yet been well understood due to the rarity of such tumors, especially in women of reproductive age. The authors present a case of a 34- year-old patient with 14 weeks of gestation who was diagnosed with an adnexal mass suggestive of ovarian teratoma. A laparoscopy salpingo-oophorectomy was performed after 6 months of delivery, and the histological exam revealed a sarcomatoid SCC in the MCT.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):43-46
01-01-2018
Gestational syphilis is a prevalent disease in Brazil and other low and medium income countries. Desensitization to penicillin is recommended for pregnant women with syphilis who are allergic to β-lactams. This is a descriptive study utilizing outpatient medical records from 2011 to 2015 from a mother and child hospital that is part of the national healthcare system in the South of Brazil, which performs an average of 3,600 birth assistances per year. All cases of pregnant women with syphilis and presumptive diagnosis of β-lactam allergy during the study period were included. The patients referred for desensitization originated from the hospital prenatal care service, as well as from municipal/state antenatal care services. Oral desensitization was performed in the obstetric emergency room, and adult and pediatric intensive care units were available at all times. Ten patients underwent desensitization during the period of study. Personal history of urticaria was the most common reaction that demanded desensitization. All patients tolerated the procedure well, and showed no adverse reactions.We report a successful program of oral desensitization. None of the patients presented adverse reactions or complications, a fact that corroborates the feasibility and safety of the desensitization protocol. Oral administration of penicillin comes at a low cost, and optimizes the use of time and resources.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):384-396
08-01-2017
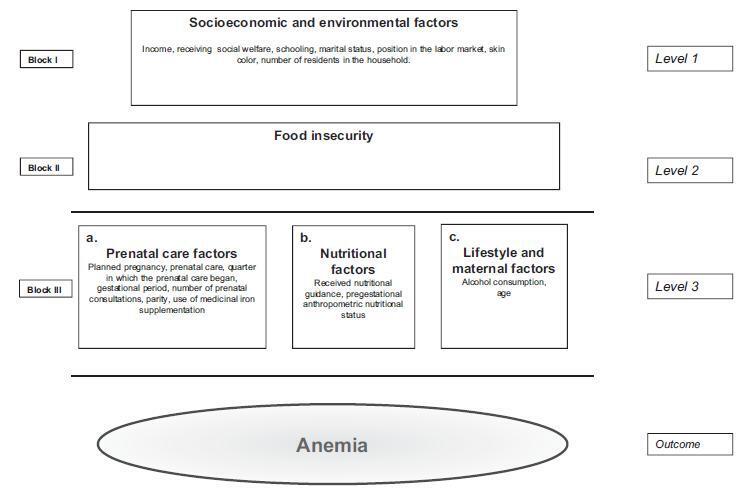
To identify the prevalence of anemia and its relation to food insecurity (FI) and other determinants in pregnant women.
A cross-sectional, cohort-nested study, with the participation of 245 pregnant women who were cared for at Family Health Units in the municipality of Santo Antônio de Jesus, Bahia, Brazil. The participants underwent blood tests for hemoglobin levels, anthropometric examinations, and answered a structured questionnaire. The hemoglobin (Hb) parameter (Hb < 11 g/dL) was used for the classification of the diagnosis of anemia. Food insecurity was evaluated using the North American short-scale food insecurity assessment. Logistic regression was adopted for the statistical analyses, based on a hierarchical conceptual model that enabled the measurement of the decomposition of the total effect of its non-mediated and mediated components using the proposed hierarchical levels.
The prevalence of anemia in the studied population was of 21.8%, and the average hemoglobin was 12.06 g/dL (standard deviation [SD]: 1.27). Food insecurity was identified in 28.16% of the pregnant women. The average maternal age was 25.82 years (SD: 5.94). After ranking, the variables positively associated with anemia remained significant: FI (odds ratio [OR] =3.63; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.77-7.45); not undergoing prenatal care (OR = 5.15;95%CI: 1.43-18.50); multiparity (OR = 2.27;95%CI: 1.02-5.05); and non-supplementation of iron medication (OR = 2.45; 95%CI: 1.04-5.76). The results also indicated that the socioeconomic and environmental factors were largely mediated by food insecurity and factors regarding prenatal care.
In the present study, the chance of occurrence of anemia in pregnant women was significantly higher,mainly among women: in situations of food insecurity, not undergoing prenatal care, not having received iron supplements, and who are multiparous.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):128-141
03-01-2017
To evaluate the effect of supplementation with omega-3 sources on the fatty acid composition of human milk.
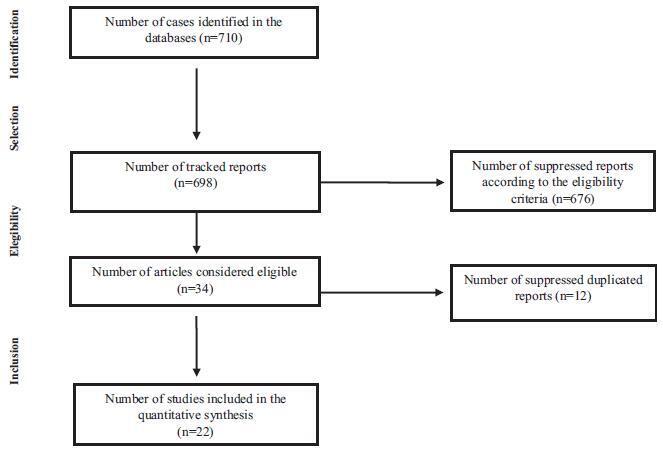
The review consisted of the search for articles published in PubMed, Biblioteca Virtual de Saúde (Virtual Health Library[VHL]) andWeb of Science databases using the following keywords: fatty acids, omega-3, human milk and supplementation; for this purpose, we have used the program of research to integrate the services for the maintenance of autonomy (PRISMA) checklist. The following selection criteria were used: articles in English, Portuguese, Spanish or Italian, published between 2000 and 2015, and about studies performed in humans. We found 710 articles that met the established criteria; however, only 22 of them were selected to be part of this study.
All studies found a positive relationship between the consumption of omega- 3 sources and their concentration in humanmilk. The differences in the findings are due to the distinct methods used, such as the specific time of the omega-3 supplementation, the type of omega-3 source offered, as well as the sample size.
Although the studies were different in several methodological aspects, it was possible to observe the importance of omega-3 supplementation during gestation and/or the puerperium.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):246-252
05-01-2016
to evaluate the quality of life of HIV positive (HIVþ) pregnant women using the HIV/AIDS Target Quality of Life (HAT-QoL) instrument.
cross-sectional study, conducted between May 2014 and November 2015 , with HIVþ pregnant women selected by convenience sampling. Sociodemographic and behavioral data were collected through interviews, and the HAT-QoL questionnaire was applied. Clinical and laboratorial data were collected from medical records.
twenty-seven pregnant women participated in the study. Their mean age was 27 years (standard deviation - SD: 7.3). The majority (59%) had up to 8 years of education, 52% identified themselves as white, 56% were unemployed, and 59% had a household income higher than the minimum wage. The mean infection time by the virus was 68.4 months (5.7 years). The majority (74%) were contaminated with HIV through sexual intercourse, and 67% declared not having a HIVþrelative. Regarding the use of condoms, 41% reported using them sporadically, and the same number did not have proper knowledge about them. Only 23 patients (85%) reported having been prescribed antiretrovirals. Fourteen (64%) had a CD4 count higher than 500 cells/mm3, and 13 pregnant women (59%) had an undetectable viral load. The scores from the quality of life questionnaire dimensions that were more affected are: infection "disclosure concerns" (mean: 39.8; SD: 27.1), followed by "financial concerns" (mean: 49.1; SD: 36), and "HIV acceptance" (mean: 49.1; SD: 35.8). The dimension with the best score was "medication concerns" (mean: 80.8; SD: 26.5).
quality of life has been increasingly used as a clinical outcome evaluation parameter. The results of this study contribute to the establishment of interventions based on the needs of HIVþ pregnant women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(11):498-504
11-01-2015
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005286
To evaluate the risk factors for morbidity and mortality in an obstetric intensive care unit at a university hospital.
Observational cross-sectional study with 492 pregnant/puerperal women. Patients were admitted to the obstetric intensive care unit over a period of one year, being informed about the proposals of the study and a questionnaire was applied. The analysis was performed using Microsoft Excel 2013 and GraphPad Prism 6. To evaluate risk factors, χ2 tests were used.
The main risk factors to near miss were: non-white race (OR=2.5; PR=2.3); marital status (married women) (OR=7.9; PR=7.1), schooling (primary) (OR=3.1; PR=2.8), being from the countryside (OR=4.6; PR=4.0), low income (OR=70; PR=5.5), gestational hypertensive disorders (OR=16.3; PR=13.2), receiving prenatal care (OR=5.0; PR=4.254) and C-section before labor (OR=39.2; PR=31.2).
The prevalence of near miss was associated with socioeconomic/clinical factors and care issues, revealing the importance of interventions to improve these indicators. Additionally, we suggest a better curriculum insertion of this subject in the discipline of the medical course due to the importance of avoiding the near miss using adequate medical education. The importance of correct prenatal care is emphasized in order to identify potential risks, to provide nutritional support to pregnant women, to treat potential diseases and to establish a maternal immunization program, as well as providing better care regarding the clinical features of the patients, in order to reduce obstetrical and neonatal risk.