Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo8
03-18-2025
To describe women's experience of pregnancy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
A qualitative study conducted in a private maternity hospital, from May, 2020 to November, 2021, with women aged ≥ 18 years, gestational age ≥ 36 weeks at birth and ≥ 24 hours post-partum. Data collected through semi-structured interviews, recorded, transcribed, and analyzed adopting Krippendorff's Content Analysis as theoretical-methodological framework.
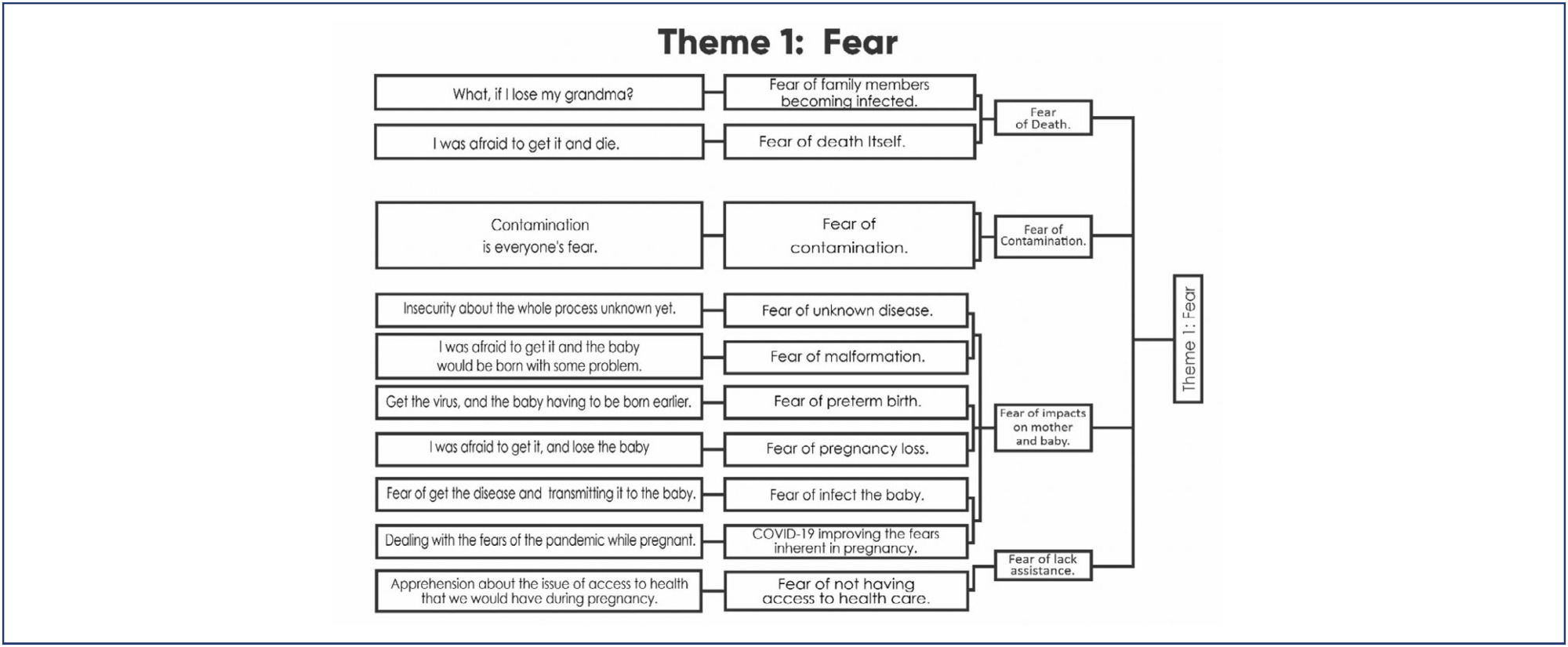
Four main themes emerged: Fear, Taking care and celebrating pregnancy: adjusting to the new reality, Harms of Isolation, and Benefits of Isolation. The fear of contamination and its impact on the health of mother and child resulted in the adoption of severe social isolation, including from those considered sources of support by the expecting mother. Overwhelmed, some of the participants reported loneliness and psychic suffering. The opportunity to focus on the pregnancy, the preparations for the arrival of the child, and the family made isolation a beneficial and positive period for other women.
The experience of pregnancy in the Pandemic was an event outside of the ordinary and common. The expecting mother faced her worst fears on a daily basis and attended prenatal care, in order to ensure her child would be born healthy. The celebration of the baby's life, amid so many deaths, had to be adjusted to the virtual environment. It was a tense, solitary, and ambiguous period, which demanded a lot from the mental health of some participants, but to others, brought advantages that would not have been possible in different times.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo98
01-23-2025
To determine if maternal erythrocytosis is a risk factor for small-for-gestational age at term at 3,400-m altitude in pregnant women without intercurrent disease.
Analytical study of retrospective cohorts at Cusco, a city at 3,400-m altitude. Our participants were 224 and 483 pregnant women with and without exposure to maternal erythrocytosis, respectively. A logistic regression with the goodness of fit to the proposed model was also performed with the Hosmer and Lemeshow test, evaluating the small-for-gestational-age results with or without exposure to hemoglobin >14.5 g/dl.
The incidence of small-for-gestational-age was 6.9% for this entire cohort. The maternal erythrocytosis during gestation without any maternal morbidity at 3,400-m altitude has an ORa=0.691 (p=0.271) for small-for-gestational-age at term. Inadequate prenatal control has an ORa=2.115 (p=0.016) for small-for-gestational-age compared to adequate prenatal control.
Maternal erythrocytosis in pregnant women without any morbidity is not a risk factor for small-for-gestational-age at 3,400 m-altitude.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo97
01-23-2025
Our aims to compare level of serum ischemia modified albümin(IMA) between healthy and preeclamptic pregnancies and to evaluate the relationship of IMA with preeclampsia, preeclampsia severity and perinatal outcomes.
Our study is a prospective case-control study. A total of 134 pregnant women (66 preeclamptic and 68 healthy pregnant) between 18-45 years of age and between 24- 41 gestational weeks participated. Serum IMA levels were measured by the Albumin Cobalt Binding (ACB) test.
The mean IMA values were found to be significantly higher in the preeclampsia group compared to the control group (p<0,001). Patients were divided into 3 groups; severe preeclampsia(n=29), non-severe preeclampsia(n=37) and healthy pregnant(n=68). Statistically significant difference was not found between severe preeclampsia and non-severe preeclampsia (p=0.505). The performance of IMA values in predicting the development of preeclampsia among all participants was evaluated with Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis. According to the ROC analysis, the best cut-off value at which the maximum area under the curve (AUC) was obtained was found when IMA>0.98(AUC: 0.690 95% Confidence Interval (CI): 0.600-0.781 p<0.001). When IMA threshold value of >0.98 was taken to predict preeclampsia; the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated as 65.15%, 64.71%, 64.18%, and 65.67%, respectively.
IMA level may be a useful new marker in recognizing and predicting preeclampsia. However, despite the power of recognizing the disease, serum IMA levels do not give an idea about the severity of the disease. More comprehensive studies are needed in order to use IMA levels in the diagnosis of preeclampsia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo69
09-18-2024
To compare the effectiveness and safety of non-mRNA versus mRNA COVID-19 vaccines on pregnant women and their newborns in a systematic review with meta-analysis.
We searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Central in May 2023.
The search strategy yielded 4451 results, 16 studies were fully reviewed. We selected case-control studies analysing non-mRNA versus mRNA vaccines. Data collection and analysis: we assessed the risk of bias using the Cochrane Risk of Bias in Non-randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool. Standardised mean differences were pooled using random-effect models.
We identified 8 prospective and retrospective studies with a total of 32,153 patients. Non-mRNA vaccines were associated with a higher incidence of fever (OR 2.67; 95% CI 2.08-3.43; p<0.001), and a lower incidence of fetal or neonatal death (OR 0.16; 95% CI 0.08-0.33; p<0.001). In subgroup analyses, the Jansen vaccine (Ad26.COV2.S) was found to have a higher rate of premature labor/delivery (OR 4.48; 95% CI 1.45-13.83; p=0.009) and missed/spontaneous abortion (OR 1.90; 95% CI 1.09-3.30; p=0.02), as compared with the Pfizer (BNT162b2) vaccine.
non-mRNA vaccines are associated with a lower incidence of fetal or neonatal death among pregnant women who receive a Covid19 vaccine, although at an increased rate of pyrexia compared with mRNA vaccines. Other studies are required for better assessment.
CRD42023421814
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo68
09-06-2024
To evaluate the association between the dietary patterns (DPs) of pregnant women with GDM (gestational diabetes mellitus) and the birth weight (BW) of the infants.
Cross-sectional study with 187 adult pregnant women with GDM attended at a maternity in Rio de Janeiro from 2011 to 2014. Dietary intake was assessed in the third trimester using a semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire (FFQ). The outcomes were BW and weight adequacy for gestational age (GA). Reduced Rank Regression (RRR) was used to explain the following response variables: density of carbohydrates, fibres, and saturated fatty acids. Statistical analyzes included multinomial logistic regression models.
The mean BW was 3261.9 (± 424.5) g. Three DPs were identified, with DP 3 (high consumption of refined carbohydrates, fast foods/snacks, whole milk, sugars/sweets, and soft drinks and low consumption of beans, vegetables, and low-fat milk and derivatives) being the main pattern, explaining 48.37% of the response variables. In the multinomial logistic regression analysis no statistically significant association was found between the tertiles of DPs and BW or the adequacy of weight for GA, even after adjustments of confounding covariates.
No significant associations were found between maternal DPs in the third trimester of pregnancy and infant BW or adequacy of weight for GA.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo28
06-03-2024
This systematic review accompanied by a meta-analysis aimed to estimate the prevalence of syphilis in pregnant women in Brazil and describe its associated factors.
Following the establishment the search strategies and the registration of the review protocol in PROSPERO, we conducted a search for relevant articles in the Pubmed, LILACS, Science Direct, SciELO and Web of Science databases. Our inclusion criteria were cross-sectional studies published between 2005 and 2023, with no language restrictions. The combined prevalence of syphilis infection was estimated using the random effects model in the R Software with a 95% confidence interval (95% CI) and p < 0.01 as statistically significant.
A total of 24 articles were recruited, which together investigated 221,884 women. The combined prevalence of syphilis in pregnant women in Brazil was 1.79% (95% CI: 1.24-2.57%), and the main factors associated with its occurrence were black and brown skin color, low education and factors related to the partner.
There was a high prevalence of syphilis in pregnancy in Brazil, mainly associated with socioeconomic factors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo27
04-09-2024
To evaluate whether the continuous support provided by doulas influences the endogenous release of serotonin in parturients.
This pilot study included 24 primigravidae at term. Of these, 12 women received continuous doula support (Experimental Group), whereas the other 12 received the usual assistance without doula support (Control Group). Blood samples were collected from all the women at the active and expulsion stages of labor and at the fourth period of labor (Greenberg period) for evaluation of their serotonin levels using high-performance liquid chromatography.
The average serotonin concentrations in the control and experimental groups were respectively 159.33 and 150.02 ng/mL at the active stage, 179.13 and 162.65 ng/mL at the expulsion stage, and 198.94 and 221.21 ng/mL at the Greenberg period. There were no statistically significant differences in serotonin concentrations between the two groups at the active and expulsion stages of labor. By contrast, within the experimental group, a significant increase in serotonin concentration was observed in the Greenberg period compared with the levels in the active and expulsion stages (p < 0.05).
The novelty of this study relies on the ability to correlate the influence of the continuous support offered by doulas with the release of serotonin in parturients, with the results suggesting that the assistance received during labor can modulate the levels of hormone release in the Greenberg period.
RBR-4zjjm4h