Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo82
12-04-2024
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) has been evolving since 1978, with the number of techniques performed increasing over the years. Despite continued advances, some couples continue to have difficulties getting pregnant, and it has recently been considered that the microbiome of the female genital tract (FGT) may influence embryo implantation and the establishment of pregnancy. This review aims to evaluate the role of probiotics on reproductive outcomes in infertile women on ART. A search throughout medical databases was performed, and six articles met the criteria. Five studies showed improvements in pregnancy rates, with only one demonstrating statistical significance. One article showed no improvement but reported a statistically significant reduction in the miscarriage rate in the probiotic group. Further research is needed to evaluate the true potential of probiotics, namely to assess whether they effectively modulate the FGT microbiome and if these changes are maintained over time.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo30
07-26-2024
To evaluate the mode of delivery according to Robson classification (RC) and the perinatal outcomes in fetal growth restriction (FGR) and small for gestational age (SGA) fetuses.
Retrospective cohort study by analyzing medical records of singleton pregnancies from two consecutive years (2018 and 2019). FGR was defined according to Delphi Consensus. The Robson groups were divided into two intervals (1–5.1 and 5.2–10).
Total of 852 cases were included: FGR (n = 85), SGA (n = 20) and control (n=747). FGR showed higher percentages of newborns < 1,500 grams (p<0.001) and higher overall cesarean section (CS) rates (p<0.001). FGR had the highest rates of neonatal resuscitation and neonatal intensive care unit admission (p<0.001). SGA and control presented higher percentage of patients classified in 1 - 5.1 RC groups, while FGR had higher percentage in 5.2 - 10 RC groups (p<0.001). FGR, SGA and control did not differ in the mode of delivery in the 1-5.1 RC groups as all groups showed a higher percentage of vaginal deliveries (p=0.476).
Fetuses with FGR had higher CS rates and worse perinatal outcomes than SGA and control fetuses. Most FGR fetuses were delivered by cesarean section and were allocated in 5.2 to 10 RC groups, while most SGA and control fetuses were allocated in 1 to 5.1 RC groups. Vaginal delivery occurred in nearly 60% of FGR allocated in 1-5.1 RC groups without a significant increase in perinatal morbidity. Therefore, the vaginal route should be considered in FGR fetuses.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(10):568-574
12-11-2023
Pregnancy in women with lupus poses a higher risk of complications compared with the general population. The present study aimed to determine and describe the obstetric and neonatal outcomes of pregnant women with lupus.
We conducted an observational retrospective study of pregnant women with the diagnosis of lupus, who were selected and followed at the Maternal-Fetal Medicine Clinic of our institution between January 2013 and July 2018. We analyzed 59 pregnancies and 52 newborns, and collected data regarding sociodemographic features, the preconception period, pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum and the newborn. A descriptive analysis of the variables was performed.
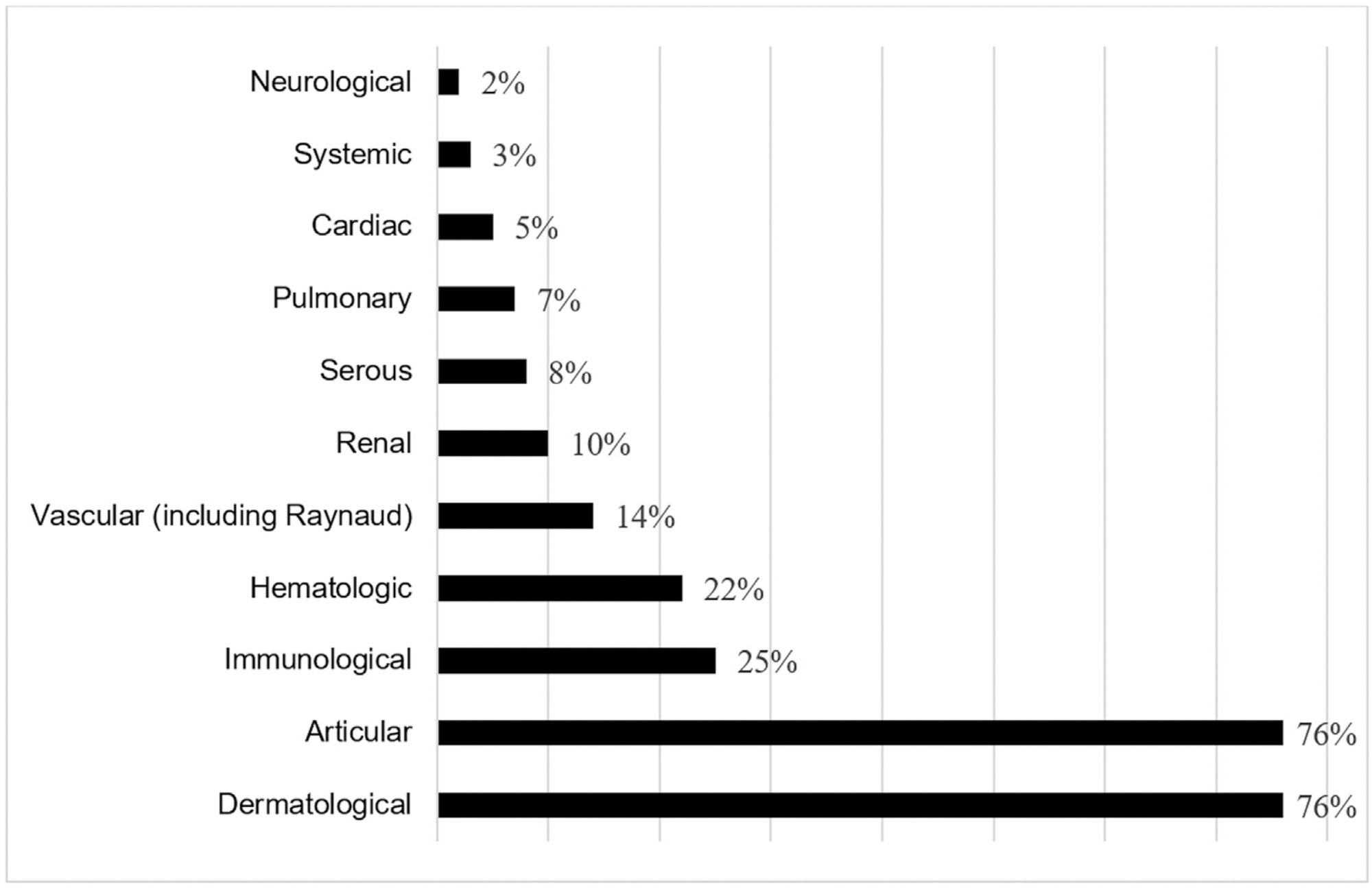
In 58% of the cases, the pregnancy was uneventful. We registered flares in 25% of the cases, preeclampsia in 3%, fetal growth restriction in 12%, gestational loss in 10%, preterm labor in 10%, postpartum complications in 20%, and small for gestational age newborns in 17% of the cases.
Most pregnancies in women with lupus have favorable obstetric and neonatal outcomes. Prenatal counseling, adequate multidisciplinary surveillance, and optimized treatment of the disease are fundamental pillars for these good results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):596-601
11-01-2017
To investigate the clinical and sonographic parameters associated with adverse fetal outcomes in patients with congenital parvovirus B19 infection managed by intrauterine transfusion.
This was a single-center retrospective study conducted from January 2005 to December 2016 that assessed patients with singleton pregnancies with fetal parvovirus infection confirmed by a polymerase chain reaction of the amniotic fluid or fetal blood samples who underwent at least one intrauterine transfusion. The maternal characteristics, sonographic findings and parameters related to intrauterine transfusion were compared between the two groups (recovery/non-recovery), who were categorized based on fetal response after in-utero transfusions. Progression to fetal death or delivery without fetal recovery after the transfusions was considered nonrecovery and categorized as an adverse outcome.
The final analysis included ten singleton pregnancies: seven of which were categorized into the recovery group and three of which into the non-recovery group. The baseline characteristics were similar between the groups. All fetuses were hydropic at the time of diagnosis. No significant differences related to sonographic or intrauterine transfusion parameters were identified between the groups; however, the nonrecovery group tended to have an increased number of sonographic markers and lower fetal hemoglobin and platelet levels before the transfusion.
We were unable to firmly establish the clinical or sonographic parameters associated with adverse fetal outcomes in patients with parvovirus infection managed with intrauterine transfusions; however, edema, placental thickening and oligohydramnios may indicate greater fetal compromise and, subsequently, adverse outcomes. However, further studies are necessary, mainly due to the small number of cases analyzed in the present study.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):308-313
06-01-2016
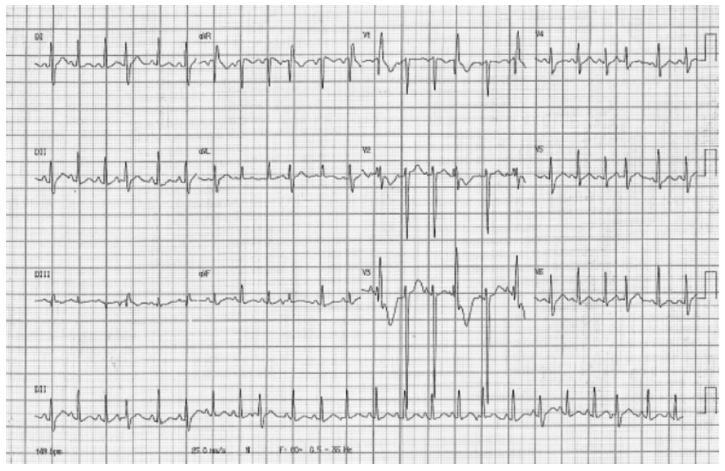
Pathophysiological mechanisms of peripartum cardiomyopathy are not yet completely defined, although there is a strong association with various factors that are already known, including pre-eclampsia. Peripartum cardiomyopathy treatment follows the same recommendations as heart failure with systolic dysfunction. Clinical and experimental studies suggest that products of prolactin degradation can induce this cardiomyopathy. The pharmacological suppression of prolactin production by D2 dopamine receptor agonists bromocriptine and cabergoline has demonstrated satisfactory results in the therapeutic response to the treatment. Here we present a case of an adolescent patient in her first gestation with peripartum cardiomyopathy that evolved to the normalized left ventricular function after cabergoline administration, which was used as an adjuvant in cardiac dysfunction treatment. Subsequently, despite a short interval between pregnancies, the patient exhibited satisfactory progress throughout the entire gestation or puerperium in a new pregnancy without any cardiac alterations. Dopamine agonists that are orally used and are affordable in most tertiary centers, particularly in developing countries, should be considered when treating peripartum cardiomyopathy cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):578-584
11-03-2015
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005445
To estimate the future pregnancy success rate in women with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss.
A retrospective cohort study including 103 women seen at a clinic for recurrent pregnancy loss (loss group) between January 2006 and December 2010 and a control group including 204 pregnant women seen at a low-risk prenatal care unit between May 2007 and April 2008. Both groups were seen in the university teaching hospital the Maternidade Climério de Oliveira, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. Reproductive success rate was defined as an alive-birth, independent of gestational age at birth and survival after the neonatal period. Continuous variables Means and standard deviations (SD) were compared using Student's t-test and nominal variables proportions by Pearson χ2test.
Out of 90 who conceived, 83 (91.2%) had reproductive success rate. There were more full-term pregnancies in the control than in the loss group (174/187; 92.1 versus 51/90; 56.7%; p<0.01). The prenatal visits number was satisfactory for 76 (85.4%) women in the loss group and 125 (61.3%) in the control (p<0.01). In this, the beginning of prenatal care was earlier (13.3; 4.2 versus 19.6; 6.9 weeks). During pregnancy, the loss group women increased the weight more than those in the control group (58.1 versus 46.6%; p=0.04). Although cervix cerclage was performed in 32/90 women in the loss group, the pregnancy duration mean was smaller (34.8 weeks; SD=5.6 versus 39.3 weeks; SD=1.6; p<0.01) than in the control group. Due to gestational complications, cesarean delivery predominated in the loss group (55/83; 64.7 versus 73/183; 39.5%; p<0.01).
A very good reproductive success rate can be attributed to greater availability of healthcare services to receive pregnant women, through prenatal visits (scheduled or not), cervical cerclage performed on time, and available hospital care for the mother and newborn.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):446-454
10-01-2015
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005264
To reduce the percentage of cesareans among pregnant women at UNIMED Jaboticabal by redesigning the care delivery model.
Descriptive study conducted at an institution in São Paulo State starting in 2012 to propose the redesign of the care mode based on Continued Improvement Science adapted to the health area. To measure the results of changes we selected nine indicators and their targets.
The percentage of natural births reached the target of 40% after seven months of implementation of the interventions. The percentage of natural births reached 66% among pregnant women in SUS. The perinatal mortality rate decreased by 25% from 2012 to 2014, and the prematurity rate was 3 per 100 live births in 2014. The percentage of pregnant women from UNIMED with six or more prenatal consultations reached 95%. The hospital costs for childbirth care decreased by 27% compared to 2012 and 2013. This reduction was not sustainable and the per capita cost returned to the same level in 2014. The remuneration of all obstetricians increased by 72% from 2012 to 2014.Unimed's costs attributed to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) decreased by 61% from 2012 to 2013. The cost was the same for 2013 as it was for 2014 while the admission rate among newborns at UNIMED decreased by 55%. The percentage of pregnant women participating in courses to prepare for birth did not reach the goal set at 80%. The percentage of pregnant women satisfied and very satisfied with care delivery reached 86%.
This project achieved its objectives by reducing the percentage of C-sections among pregnant women of UNIMED Jaboticabal representing a concrete example of achieving the Triple Aim in health: to improve the experience of care and the health outcomes of populations and individuals and to perform these two tasks at a lower cost.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):216-221
05-01-2015
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005272
To compare obstetric outcomes of induced preterm twin births (under 32 weeks gestation) with those spontaneously conceived.
Prospective study of twin pregnancies (25 induced and 157 spontaneously conceived) developed over a period of 16 years in a tertiary obstetric center. Demographic factors, obstetric complications, gestational age at delivery, mode of delivery, birth weight and immediate newborn outcome were compared.
The analysis of obstetrical complications concerning urinary or other infections, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, fetal malformations, intrauterine fetal death, intrauterine growth restriction and intrauterine discordant growth reveal no significant statistical differences between the two groups. First trimester bleeding was higher in the induced group (24 versus 8.3%, p=0.029). The cesarean delivery rate was 52.2% in spontaneous gestations and 64% in induced gestations. Gestational age at delivery, birth weight, Apgar scores at first and fifth minutes, admissions to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and puerperal complications show no statistically significant differences between the two groups. These results were independent of chorionicity and induction method.
The mode of conception did not influence obstetric and neonatal outcomes. Although induced pregnancies have higher risk of first trimester bleeding, significant differences were not observed regarding other obstetric and puerperal complications and neonatal results.