Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):126-133
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000300003
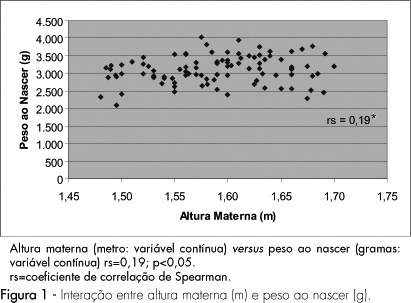
PURPOSE: to evaluate the impact of the nutritional status of pregnant adolescents on the birth weight. METHODS: a cohort study including 97 adolescents and their respective newborns, evaluated from May to June, 2004. Pregnant women from 10 to 19 years old in labor were included in the study, and those with multiple pregnancies, complications, less than 37 weeks gestation, and incomplete data records were excluded. Maternal nutritional status evaluation included height, body mass index (BMI) before pregnancy, gestational weight gain (GWG) and caloric-proteic intake, obtained by habitual food intake recordatory by the end of the third gestational trimester. The association between maternal variables (height, pre-gestational BMI, GWG and intake) and the newborn weight was analyzed by Spearman's correlation test. Statistical significance was assumed when p<0.05. RESULTS: the mean age was 17.8±1.12 years old. Most adolescents (66%) started pregnancy with adequate weight, 29% had low weight and 5% overweight. Most adolescents showed inadequate GWG, caloric and proteic intake. Low birth weight was recorded in 7% of the newborns and insufficient weight was recorded in 37% of them. Maternal height and GWG showed positive and significant BW relation. Pre-gestational BMI and protein intake showed statistically significant inverse correlation with birth weight. No correlation between caloric intake and BW was demonstrated. CONCLUSION: maternal height and GWG influence the newborn nutritional status.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(9):530-535
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000900005
PURPOSE: to compare the incidence of preterm deliveries, and of low birth weight newborns, among primiparous adolescents, from two age groups. METHODS: this is a comparative, cross-sectional clinical study composed of 522 primiparous adolescents whose deliveries occurred at the gestational age of 25 to 42 weeks. The adolescents were divided into 2 groups according to their age; Gprec: from 10 to 15 complete years old (n=104); Gtard: from 16 to 19 complete years old (n=418). The research data were obtained by an individualized, confidential and ethical interview, soon after delivery; and by a written questionnaire with questions about the gestational age in complete weeks, and about the newborns birth weight. The gestational age was calculated at the delivery day, according to the date of the last trustworthy menstrual period, being also confirmed by the earliest pregnancy scanning or by Capurro's index, when there were any doubts about the previously described parameters. All newborns with gestational age under 37 weeks at birth were considered preterm babies. The newborn weight was taken by neonatologists immediately after delivery; all newborns with less than 2,500g were considered to be low weight babies. Thus, we compared prematurity rate and low birth weight among newborns from primiparous puerperal adolescents. The chi² test was used for the statistic analysis and the partition chi² test for the found differences. As the significancy level was 0.05 (alpha =5%), lower levels than that were considered significant. RESULTS: the prematurity rate was not significantly different between the two groups (5.8 and 2.6%). The incidence of low birth weight in Gprec (13.5%) was significantly higher than in Gtard (3.1%). CONCLUSIONS: the group with primiparous adolescents under 15 years old showed a significantly higher risk of low birth weight newborns. However, a statistically significant incidence of prematurity between the groups studied was not verified.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):446-452
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800002
PURPOSE: to describe the obstetric outcomes in pregnant adolescents at a tertiary hospital and to compare the maternal and labor outcomes between precocious and late adolescents. METHODS: in a transversal analytical study, 2058 cases were evaluated, considering 322 (15.65%) from the precocious group and 1736 (84.35%) from the late group that delivered at the "Maternidade Escola Assis Chateaubriand/UFC" from January 1, 2000 to December 31, 2000. The clinical complications in the prenatal period, kind of delivery, indications for cesarean section, birth gestational age at birth, birth weight, comparison of birth weight and gestational age, Apgar score at the first and fifth minute, presence of malformations, and neonatal death were analyzed. The exact Fisher and the chi2 tests were used to compare both groups. The prevalence ratio was calculated. RESULTS: from of total of deliveries, 25.95% belonged to adolescents. The average age was 17.19 years. Prenatal visits were made by 88% of the patients, but 60% had an insufficient number of visits. The most frequent clinical situations were preeclampsia (14.72%), anemia (12.97%) and urinary tract infections (6.37%), with no statistical difference between the groups. Thirty-one and three percent of the births were by cesarean section, preeclampsia being the main indication in the two age groups (25 and 23%, respectively). The frequency of an Apgar score less than 7 at the first minute was 19,9% in the precocious adolescent group and 14,2% in the late adolescent group (x²=6,96, p=0.008). There was no statistical difference regarding prematurity rate (20.2 vs 16.1%), low-birth weight infants (12.4 vs 10.4%), low Apgar score at the fifth minute (5.3 vs 3.3%), congenital malformations (3.1 vs 2.7%), and neonatal death (5.3 vs 3.3%). CONCLUSIONS: the precocious and late pregnant adolescents presented similar pregnancy evolution and obstetric outcomes, except for the differences of the first minute Apgar scores.