Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):32-42
Pregnancy is needed for the perpetuation of the human species, and it leads to physiological adaptations of the various maternal organs and systems. The eye, although a closed space, also undergoes some modifications, most of which are relatively innocuous, but they may occasionally become pathological. For women, pregnancy is a susceptibility period; however, for many obstetricians, their knowledge of the ocular changes that occur during pregnancy tends to be limited. For this reason, this is a important area of study as is necessary the development of guidelines to approach those changes. Of equal importance are the knowledge of the possible therapies for ophthalmological problems in this period and the evaluation of themode of delivery in particular conditions. For this article, an extensive review of the literature was performed, and a summary of the findings is presented.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):11-19
To evaluate the relation between changes the body mass index (BMI) percentile, reflected in the Atalah curve, and perinatal outcomes.
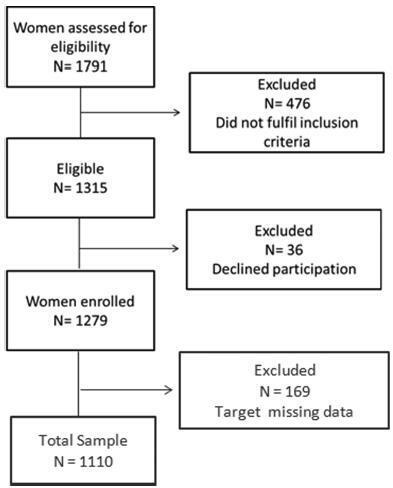
A cross-sectional study with 1,279 women was performed. Data regarding gestational weight, sociodemographic characteristics and perinatal outcomes were collected through medical charts, prenatal card and interviews in the postpartum period. Women could be classified according to the Atalah curve in the following categories: low weight, adequateweight, overweight, and obese. The BMIwas calculated at the first and at the last prenatal care visits, and these values were compared.
An increase in the BMI category according to the Atalah classification occurred in 19.9% of pregnant women, and an increase of 3.4, 5.8 and 6.4 points of BMI were found for women respectively classified in the adequate weight, overweight and obese categories at the first prenatal visit. Women with high school education presented a lower chance of increasing their BMI (odds ratio [OR] 0:47 [0.24- 0.95]). Women who evolved with an increase in the the Atalah classification were associated with cesarean section (OR 1.97-2.28), fetalmacrosomia (OR 4.13-12.54) and large for gestational age newborn (OR 2.88-9.83).
Pregnant women who gained enough weight to move up in their BMI classification according to the Atalah curve had a higher chance of cesarean section and macrosomia. Women classified as obese, according to the Atalah curve, at the first prenatal visit had a high chance of cesarean section and delivering a large for gestational age newborn.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):653-658
To identify the prevalence of pyelonephritis during pregnancy and to analyze the clinical and laboratorial aspects, perinatal results and complications.
A transversal study of 203 pregnant women who had pyelonephritis during pregnancy and whose labor took place between 2010 and 2016 at a hospital in the state of Santa Catarina, Brazil. The analysis was based on medical records as well as on the hospital’s database. Clinical and laboratory conditions, antibiotics, bacterial resistance, perinatal outcomes and complications were all taken into account. The data was compared using the Mann-Whitney test and the Chi-square test.
A prevalence of 1.97% with pyelonephritis was evidenced, with most patients having it during the second trimester of gestation. The bacteriamost commonly found in the urine cultures was Escherichia coli, in 76.6% of cases, followed by Klebsiella pneumoniae (8.7%). Ceftriaxone had the lowest bacterial resistance (only 3.5% of the cases). On the other hand, ampicillin and cephalothin presented higher bacterial resistance, 52% and 36.2%, respectively. The risk of very premature delivery was more than 50% higher in patients with pyelonephritis.
Ampicillin and first-generation cephalosporins are associated with a higher bacterial resistance while ceftriaxone proved to have a high efficacy for the treatment of pyelonephritis due to low bacterial resistance. Patients with pyelonephritis showed a higher risk for very premature delivery (< 32 weeks). In this casuistry, there were no others significant differences in the overall perinatal outcomes when compared with the routine service series.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):670-675
To describe the experience of a distance education course on sexual issues during pregnancy and after birth for residents.
This prospective educational intervention study was conducted by investigators from the Universidade Federal de São Paulo, Brazil, between April and September 2014. The participants were 219 physicians (residents from the 1st to the 6th years). The duration of the course was of 24 hours (10 video lectures and online chats). At baseline, the participants answered questions about their training, attitude and experience regarding sexual issues during pregnancy and after birth; before and after the course, they answered questions to assess their knowledge about the topic; at the end of the course, they answered questions on the quality of the course. The Student t-test was used to compare the before and after scores of the knowledge tests; values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
A total of 143 residents concluded the course; most were in their 1st (27.2%) or 3rd (29.4%) years of residency. There was a significant increase in themean scores of the questionnaires that assessed the knowledge of the topic: 4.4 (1.6) versus 6.0 (1.3; maximum score: 10), before and after the course respectively (p < 0.0001). Most of the participants (74.1%) declared that the quality of the course as a whole reached their expectations, and 81.1% would recommend the course to a friend.
The online Sexology course for Obstetrics and Gynecology residents increased their knowledge about the sexual issues during pregnancy and after birth, and fulfilled the participants’ expectations. The experience described heremay serve as a model for other sexuality courses targeting similar audiences.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):640-644
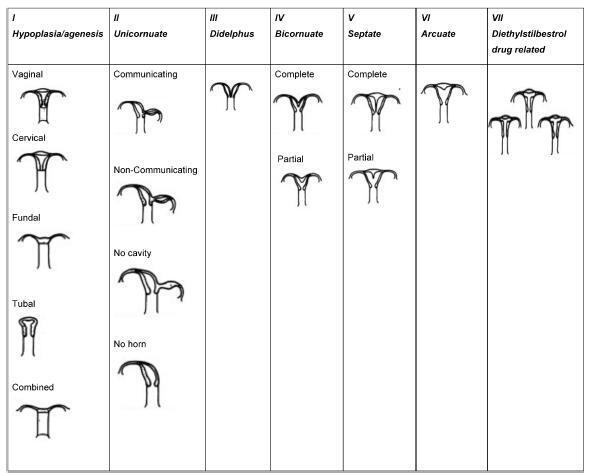
Approximately 1 in every 76,000 pregnancies develops within a unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn.Müllerian uterus anomalies are often asymptomatic, thus, the diagnosis is a challenge, and it is usually made during the gestation or due to its complications, such as uterine rupture, pregnancy-induced hypertension, antepartum, postpartum bleeding and intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). In order to avoid unnecessary cesarean sections and the risks they involve, the physicians should consider the several approaches and for how long it is feasible to perform labor induction in suspected cases of pregnancy in a unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn, despite the rarity of the anomaly. This report describes a case of a unicornuate uterus in which a pregnancy developed in the non-communicating rudimentary horn and the consequences of the delayed diagnosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):576-582
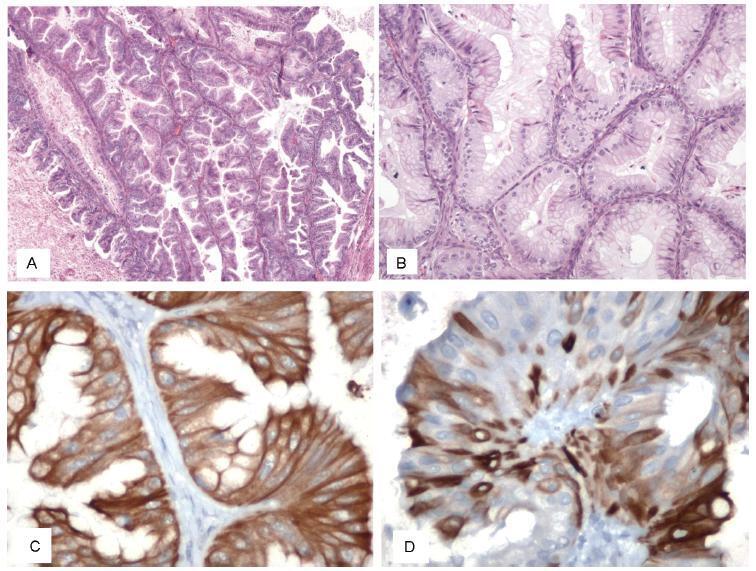
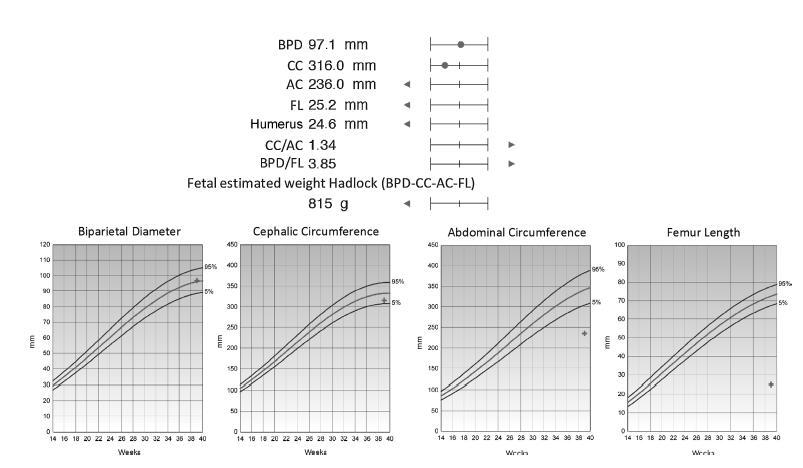
The clinical management and decision-making in pregnancies in which there is suspicion of lethal fetal malformations during the prenatal period, such as lethal skeletal dysplasia (SD), demand a multidisciplinary approach coordinated by an experienced physician. Based on the presentation of a case of osteogenesis imperfecta type IIA, we offer and discuss recommendations with the intention of organizing clinical and laboratory investigations aiming toward the clinical management, prognosis, and etiological diagnosis of these malformations, as well as genetic counselling to patients who wish to become pregnant.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):560-568
To characterize the most common peripheral and central neurological disorders during pregnancy.
Original research and review of the literature on neurological complications during pregnancy. We searched for keywords related to the topic on different databases.
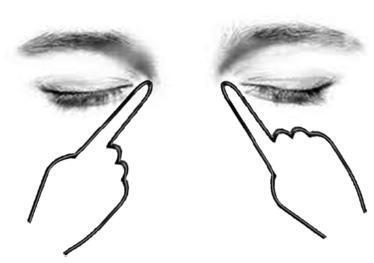
Pregnancy involves physiological changes that can trigger peripheral neurological and/or central nervous system pathologies, which can sometimes be associated with hypertensive disorders. A definitive diagnosis of neurological disorders can be made according to the trimester of pregnancy and the clinical findings. Carpal tunnel syndrome and peripheral facial palsy are common peripheral neurological disorders, more frequent in the second half of pregnancy. Central nervous disorders are more complex and a precise diagnosis must be made in order to improve perinatal outcomes, provide correct management and treatment and to prevent acute and long-term complications.
It is possible to achieve a precise diagnosis,management and treatment of neurological disorders during pregnancy, but these require a multidisciplinary approach, crucial to improve perinatal outcomes.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):513-515
Acute abdomen secondary to epithelial ovarian cancer rupture during pregnancy is a rare event. Our aim is to present how the work of a coordinated multidisciplinary team in a case of ruptured epithelial ovarian cancer during pregnancy is feasible to obtain the best results possible. A 34-year-old woman during the 37th week of her first gestation presented with an acute abdomen. During laparotomy, a ruptured 16.5-cm left ovarian tumor was detected; the tumor was extirpated and sent to pathologic evaluation. In the meantime, a Kerr cesarean section was performed, and a healthy female neonate was born. The tumor was diagnosed as a cystadenocarcinoma; therefore, the family and the combined surgical team (obstetricians and a surgical oncologist) decided to complete a definitive radical ovarian cancer surgery: hysterectomy, right salpingooophorectomy, lymphadenectomy, omentectomy and appendectomy. The patient’s postoperative evolution was uneventful, and she was sent to adjuvant chemotherapy.