Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(4):171-176
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000400003
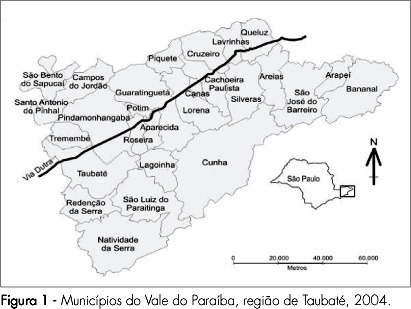
PURPOSE: to apply geoprocessing techniques for the spatial birth profile analysis of each municipality. METHODS: ecological and exploratory study, using data from the Health Information System about born alive babies in 2004, and using geoprocessing techniques. The spatial autocorrelations of the variables: cesarean section, mother's schooling, low birth weight, Apgar score at five minutes, prematurity, number of medical appointments and adolescent mothers, besides the map with the index of human development were estimated. For the detection of spatial events aggregates, Moran's I M statistics, through the program Terra View 3.13 (developed by INPE and available to the public) was used. Spatial maps with those variables were built, and Pearson's correlation coefficients, estimated. RESULTS: results have shown that the rate of born alive babies, from mothers with school level over primary school and from cesarean sections, presented a spatial pattern visually identifiable and significant spatial self-correlation. Low birth weight, prematurity, Apgar score, number of pre-natal appointments and adolescent mothers have presented a random spatial pattern, showing that, in this analysis scale, those markers have not discriminated the risk groups, despite their unquestionable predictive value for children's morbidity-mortality at individual level. There has been a positive correlation between cesarean section and schooling, and between cesarean section and human development index; and a negative correlation between adolescent mothers and human development index, with statistical significance (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: this methodology has allowed us to identify spatial clusters for the variables cesarean section and mother's schooling, besides deepening our knowledge on birth profile in the municipalities, presenting good potential on how to direct actions for specific areas.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(3):148-155
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000300008
Good prenatal care is essential to guarantee maternal and perinatal health. Nowadays, with the constant progress on the diagnostic methods and changes in diseases panorama, like increased frequency of diabetes and sexually transmitted diseases, several diagnostic procedures have been studied. These challenges difficult the selection of prenatal exams by the clinicians, in order to improve maternal and perinatal outcome. This review aimed to evaluate the main prenatal routine exams, according to the best current scientific evidences.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(1):10-16
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000100003
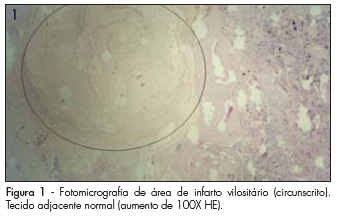
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of histopathological changes, in human placentas, related to hypertensive syndromes. METHODS: a transversal study that compares histopathological changes identified in 43 placentae from hypertensive pregnant women (HypPr), with the ones from 33 placentae from normotensive pregnant women (NorPr). The weight, volume and macroscopic and microscopic occurrence of infarctions, clots, hematomas, atherosis (partial obliteration, thickness of layers and presence of blood vessels hyalinization) and Tenney-Parker changes (absent, discreet and prominent), as well as the locating of infarctions and clots (central, peripheral or the association of both) have been analyzed. The χ2 and t Student tests have been used for the statistical analysis, as well as medians, standard deviations and ratios. It has been considered as significant, p<0.05. RESULTS: the macroscopic study of HypPr placentae have presented lower weight (461.1 versus 572.1 g) and volume (437.4 versus 542.0 cm³), higher infarction (51.2 versus 45.5%; p<0.05: OR=1.15) and clots (51.2 versus 15.1%; p<0.05; OR=5.4) ratios, as compared to the NorPr's. In the HypPr and NorPr, microscopic clots have occurred in 83.7 versus 45.5% (p<0.05; OR=4.3), respectively. Atherosis and Tenney-Parker changes have been statistically associated to the hypertensive syndromes (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the obtained data allow us to associate lower placentary weight and volume, higher ratio of macro and microscopic infarction, clots, atherosis and Tenney-Parker changes to placentae of gestations occurring with hypertensive syndromes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):620-625
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001200006
PURPOSE: to compare delivery and pregnancy follow-up among adolescent and non-adolescent pregnant women whose delivery occurred in a tertiary hospital from Região de Lisboa (Portugal). METHODS: retrospective study with 10,656 deliveries. Pregnancy follow-up, delivery type, need of episiotomy and severe lacerations, Apgar index at the fifth minute and the delivery weight have been evaluated. The pregnant women were divided into two groups, over and under 20 years old. The group with women under 20 was further subdivided in pregnant women under or over 16. The χ2 test has been used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: adolescents presented worse follow-up: first appointment after 12 weeks (46.4 versus 26.3%) and less than four appointments (8.1 versus 3.1%), less dystocia (21.5 versus 35.1%), less caesarian sections (10.6 versus 20.7%), and lower need for inducing labor (16.5 versus 26.5%). There was no significant difference concerning gestational age at delivery and ratio of low weight newborns. Among adolescents, the ones under 16 had more low weight newborns (12 versus 7.4%) and more deliveries between 34 and 37 weeks (10.8 versus 4.2%). CONCLUSIONS: in a hospital attending adolescents with social and psychological support, the fact of them having had a worse follow-up in the pre-natal phase, their performance has not been worse. Nevertheless, special attention might be given to pregnant women under 16.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):614-619
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001200005
PURPOSE: This paper has aimed at estimating the prevalence of infections by Chlamydia trachomatis and by Neisseria gonorrhoeae in pregnant women from six Brazilian cities, identifying its association with socio-economical and demographic variables. METHODS: This study has been part of a multicentric nationwide transversal research, with samples of pregnant women attended from 2004 to 2005 in basic attention pre-natal services from six Brazilian cities (Manaus, Fortaleza, Goiânia, Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo and Porto Alegre). Cervico-vaginal samples have been collected from all the pregnant women, and have afterwards been submitted to the hybrid capture technique in order to identify chlamydia and gonococcus. Socio-demographic, medical, sexual and obstetric information have been collected through specific questionnaires. The Odds Ratio (OR) has been used to evaluate risk factors associated to infection by gonorrhea and chlamydia. Statistical analysis has been done with the t-Student, χ2 and Fisher's exact tests. RESULTS: Three thousand and three pregnant women with an average age of 23.8 years old (±6.9) took part in the study. Infection prevalence by chlamydia and gonococcus were 9.4 and 1.5, respectively. Ten per cent of the pregnant women with chlamydia have presented gonococcus simultaneously. The risk of presenting one of those infections was two times higher for the women under 20. The infection main predictors have been: age under 20, race/black, single/separated and report of over one partner in the previous year. CONCLUSIONS: This study has observed high prevalence of infection by Chlamydia trachomatis and by Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Brazilian pregnant women. The main risk factor for the infection has been to be under 20 years old.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):494-498
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001000003
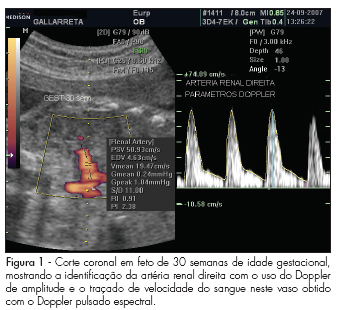
PURPOSE: to describe values found for the resistance index (RI), pulsatility index (PI) and the systole/diastole (S/D) ratio of fetal renal arteries in non-complicated gestations between the 22nd and the 38th week, and to evaluate whether those values vary along that period. METHODS: observational study, where 45 fetuses from non-complicated gestations have been evaluated in the 22nd, 26th, 30th and 38th weeks of gestational age. Doppler ultrasonography has been performed by the same observer, using a device with 4 to 7 MHz transducer. For the acquisition of the renal arteries velocity record, a 1 mm to 2 mm probe has been placed in the mean third of the renal artery for the evaluation through pulsed Doppler ultrasonography. The measurement of RI, PI and S/D ratio from three consecutive waves was performed with the automatic mode. To detect significant differences in the indexes' values along gestation, we have compared values obtained at the different gestational ages, through repeated measures ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post-hoc test. RESULTS: There were no significant differences between the right and left renal arteries, when the RI, IP and S/D ratio were compared. Nevertheless, a change in the values of these parameters has been observed between the 22nd week (RI=0.9 ± 0.02; PI=2.4 ± 0.02; S/D ratio=11.6 ± 2.2; mean ± standard deviation of the combined mean values of the right and left renal artery) and the 38th week (RI=0.8 ± 0.03; PI=2.1 ± 0.2; S/D ratio=8.7 ± 2.3) of gestation. CONCLUSIONS: the parameters evaluated (RI, PI and S/D ratio) have presented decreasing values between the 22nd and 38th, with no difference between the fetus's right and left sides.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):486-493
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001000002
PURPOSE: to investigate factors accountable for macrosomia incidence in a study with mothers and progeny attended at a Basic Unity of Health in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. METHODS: a prospective study, with 195 pairs of mothers and progeny, in which the dependent variable was macrosomia (weight at delivery >4,000 g - independent of the gestational age or of other demographic variables), and socioeconomic, previous pregnancies/gestation course, biochemical, behavioral and anthropometric, the independent variables. Statistical analysis has been done by multiple logistic regression. Relative risk (RR) values have been estimated, based on the simple form: RR=OR/ (1 - I0) + (I0 versus OR), in which I0 is the macrosomia incidence in non-exposed people. RESULTS: Macrosomia incidence was 6.7%, the highest value being found in the progeny of women >30 years old (12.8%), white (10.4%), with two or more children (16.7%), with male newborns (9.6%), with height >1,6 m (12.5%), with overweight or obesity as a nutritional pre-gestational state (13.6%), and with excessive gestational gain of weight (12.7%). The final model has shown that having two or more children (RR=3.7; CI95%=1.1-9.9), and having a male newborn (RR=7.5; CI95%=1.0-37.6) were the variables linked to the macrosomia occurrence. CONCLUSIONS: macrosomia incidence was higher than the one observed in Brazil as a whole, but inferior to the one reported in studies from developed countries. Having two or more children and a newborn male were the factors accountable for the occurrence of macrosomia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(6):274-280
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000600002
PURPOSE: to assess the prevalence of group B streptococcus colonization (GBS) in pregnant women in prodrome or in labor. METHODS: vaginal and rectal cultures were collected from 201 pregnant women, in the admission sector of a public maternity center in the northeast region of Brazil (São Luís, Maranhão). The samples obtained were inoculated in a Todd-Hewith's selective culture medium and after that they were sub-cultivated in blood-agar plates. The CAMP (Christie, Atkins, Munch-Petersen) test was used to identify GBS, which was then serologically confirmed by the BioMérieux Api 20 Strep kit microtest. GBS positive samples were submitted to an antibiotic sensitivity test. Sociodemographic variables, gynecological-obstetrical antecedents, and perinatal outcomes were studied. The Epi-Info 3.3.2 programs from World Health Organization and Statistical Package for Social Sciences 14.0 version were used for the statistical analysis. The prevalence ratio was used as risk measure, considering p<0.05 as significance level, and accepting 80% power. RESULTS: the prevalence of SGB colonization in the mothers was 20.4%. There was no association between the sociodemographic variables or gynecological-obstetrical antecedents and a larger presence of SGB colonization. There were two cases of infectious outbreak among neonatal babies from colonized mothers, but hemocultures resulted negative. High resistance rates were found for the following antibiotics: clindamycin, 25.4%; erythromycin, 23.4% and ceftriaxone, 12.7%. CONCLUSIONS: the prevalence of SGB colonization was high among the mothers, similar to what had been described in other studies. The elevated rates of antimicrobial resistance, especially to ceftriaxone indicate the need for further studies to determine the serology of this agent and of orientation protocols for rational use of antimicrobials.