Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):430-432
Mirror syndrome is an unusual pathological condition in which maternal edema in pregnancy is seen in association with severe fetal and/or placental hydrops. The disease can be life-threatening for both the mother and the fetus. The pathogenesis is poorly understood, and may be confused with preeclampsia, even though distinguishing features can be identified. We report a rare case of mirror syndrome with maternal pulmonary edema associated with fetal hydrops due to Patau syndrome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):322-331
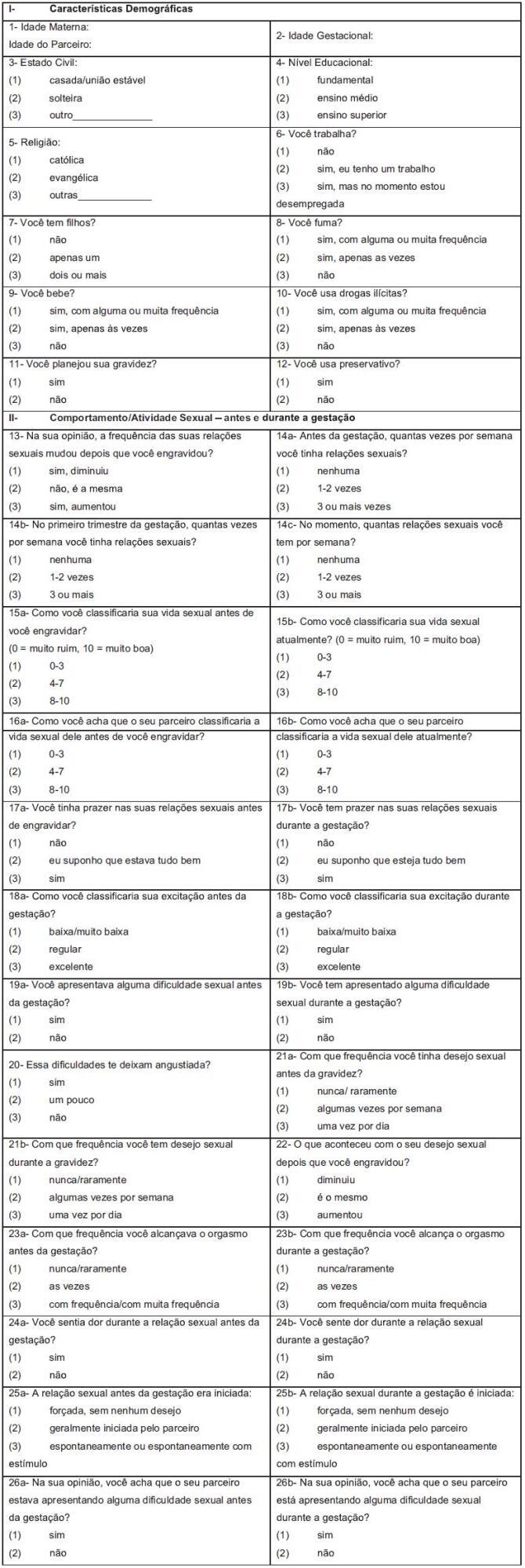
To establish the Pregnancy Sexual Response Inventory (PSRI) scores for each domain before and during pregnancy, and to publish the Brazilian Portuguese version of the PSRI.
Pregnant women were recruited during antenatal care; the PSRI was administered to 244 women prenatally at Faculdade de Medicina de Botucatu, at Universidade do Estado de São Paulo (UNESP, in the Portuguese acronym). The PSRI scores were estimated based on the Kings Health Questionnaire (KHQ) and the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item short form survey (SF-36). The raw scale type was used to standardize the minimal value and amplitude of each domain. For each domain, the score varied from 0 to 100, and the composite score was obtained as the domain average. The composite score before and during pregnancy was determined by the sum of the scores of all specific domains for each divided by the full domain number. The categorization of the scale into quartiles was established when all PSRI-specific and composite scores were combined.
The composite and specific scores for each domain were categorized into quartiles: 0 < 25 as “very bad;” 25 < 50 as “bad;” 50 < 75 as “good” and 75 to 100 as “excellent.” The mean scores were lower during pregnancy than before pregnancy in 8 of the 10 domains. The Brazilian Portuguese PSRI version is presented.
This study allowed the establishment of the PSRI composite and specific scores for each domain, and the categorization of scores into quartiles: very bad, bad, good and excellent. In addition, the Brazilian Portuguese version of the PSRI is presented in full for application in the Brazilian population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):313-321
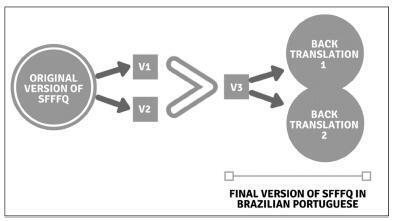
To translate and culturally adapt the short-formFood Frequency Questionnaire (SFFFQ) for pregnant women, which contains 24 questions, into Brazilian Portuguese.
Description of the process of translation and cultural adaptation of the SFFFQ into Brazilian Portuguese. The present study followed the recommendation of the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research for translation and cultural adaptation with the following steps: 1) preparation; 2) first translation; 3) reconciliation; 4) back translation; 5) revision of back translation; 6) harmonization; 7) cognitive debriefing; 8) revision of debriefing results; 9) syntax and orthographic revision; and 10) final report. Five obstetricians, five dietitians and five pregnant women were interviewed to contribute with the language content of the SFFFQ.
Few changes were made to the SFFFQ compared with the original version. These changes were discussed with the research team, and differences in language were adapted to suit all regions of Brazil.
The SFFFQ translated to Brazilian Portuguese can now be validated for use in the Brazilian population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):309-312
To study the structure ofmaternalmortality caused by abortion in the Tula region.
The medical records of deceased pregnant women, childbirth, and postpartum from January 01, 2001, to December 31, 2015, were analyzed.
Overall, 204,095 abortion cases were recorded in the Tula region for over 15 years. The frequency of abortion was reduced 4-fold, with 18,200 in 2001 to 4,538 in 2015. The rate of abortions per 1,000 women (age 15-44 years) for 15 years decreased by 40.5%, that is, from 46.53 (2001) to 18.84 (2015), and that of abortions per 100 live births and stillbirths was 29.5%, that is, from 161.7 (2001) to 41.5 (2015). Five women died from abortion complications that began outside of the hospital, which accounted for 0.01% of the total number. In the structure of causes of maternal mortality for 15 years, abortion represented 14.3% of the cases. Lethality mainly occurred in the period from 2001 to 2005 (4 cases). Among thematernal deaths, many women died in rural areas after pregnancy termination at 18 to 20 weeks of gestation (n = 4). In addition, three women died from sepsis and two from bleeding.
The introduction of modern, effective technologies of family planning has reduced maternal mortality due to abortion.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):242-250
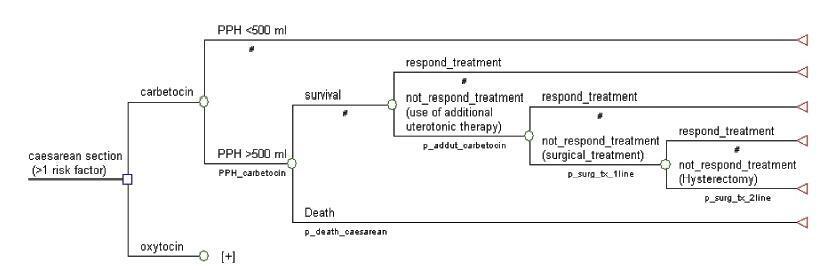
To assess the cost-effectiveness of carbetocin versus oxytocin for prevention of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) due to uterine atony after vaginal delivery/ cesarean section in women with risk factors for bleeding.
A decision treewas developed for vaginal delivery andanother one for cesarean, in which a sequential analysis of the results was obtained with the use of carbetocin and oxytocin for prevention of PPH and related consequences. A third-party payer perspective was used; only directmedical costs were considered. Incremental costs and effectiveness in terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) were evaluated for a one-year timehorizon. The costs were expressed in 2016 Colombian pesos (1 USD = 3,051 Col$).
In the vaginal delivery model, the average cost of care for a patient receiving prophylaxis with uterotonic agents was Col$ 347,750 with carbetocin and Col$ 262,491 with oxytocin,while theQALYs were 0.9980 and 0.9979, respectively. The incremental costeffectiveness ratio is above the cost-effectiveness threshold adopted by Colombia. In the model developed for cesarean section, the average cost of a patient receiving prophylaxis with uterotonics was Col$ 461,750 with carbetocin, and Col$ 481,866 with oxytocin, and the QALYs were 0.9959 and 0.9926, respectively. Carbetocin has lower cost and is more effective, with a saving of Col$ 94,887 per avoided hemorrhagic event.
In case of elective cesarean delivery, carbetocin is a dominant alternative in the prevention of PPH compared with oxytocin; however, it presents higher costs than oxytocin, with similar effectiveness, in cases of vaginal delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):209-224
To review the existing recommendations on the prenatal care of women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), based on currently available scientific evidence.
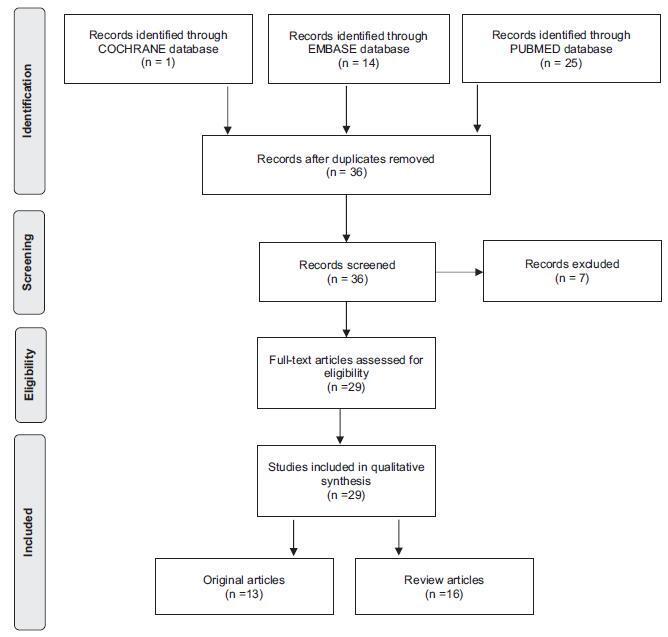
An integrative review was performed by two independent researchers, based on the literature available in the MEDLINE (via PubMed), EMBASE and The Cochrane Library databases, using the medical subject headings (MeSH) terms “systemic lupus erythematosus” AND “high-risk pregnancy” OR “prenatal care.” Studies published in English between 2007 and 2017 were included; experimental studies and case reports were excluded. In cases of disagreement regarding the inclusion of studies, a third senior researcher was consulted. Forty titles were initially identified; four duplicates were excluded. After reading the abstracts, 7 were further excluded and 29 were selected for a full-text evaluation.
Systemic lupus erythematosus flares, preeclampsia, gestation loss, preterm birth, fetal growth restriction and neonatal lupus syndromes (mainly congenital heartblock) were the major complications described. The multidisciplinary team should adopt a specific monitoring, with particular therapeutic protocols. There are safe and effective drug options that should be prescribed for a good control of SLE activity.
Pregnant women with SLE present an increased risk for maternal complications, pregnancy loss and other adverse outcomes. The disease activity may worsen and, thereby, increase the risk of other maternal-fetal complications. Thus, maintaining an adequate control of disease activity and treating flares quickly should be a central goal during prenatal care.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(3):163-167
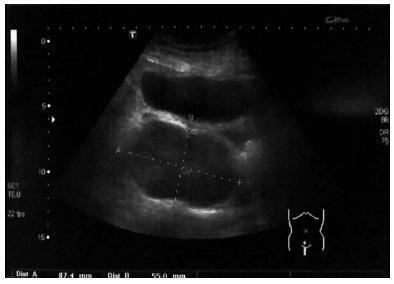
Melanomas of the female genital tract may occur in the vulva, the vagina, the ovary or the cervix.Pregnancy has been considered an aggravating factor in the evolution and prognosis of melanoma. A 35-year-old female presented with vaginal bleeding 2 months after a term cesarean delivery. An endovaginal ultrasound revealed a lesion in the uterine cervix. The pathological report revealed a small round-cell neoplasm, and the immunohistochemistry confirmed the diagnosis of malignant melanoma. A positron emission tomography revealed an expansive hypermetabolic lesion centered on the cervix, and hypermetabolic lesions in the liver and right kidney. Non-surgical treatment was provided, with biochemotherapy followed by ipilimumab and nivolumab. The patient died one year later. Postpartum vaginal bleeding, even if late-onset, should be investigated, as it may be a pregnancy-associated malignant melanoma, which has a poor prognosis.