Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(1):13-19
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000100002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the impact of dietary counseling on controlling weight gain in pregnant women, who were served in a public health service facility. METHODS: the study was conducted at a known health unit located in the metropolitan region of the city of Porto Alegre, in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Three hundred and fifteen pregnant women between the 10th and 29th week of gestation were randomized to Control and Intervention Groups. The Intervention Group received dietary counseling according to nutritional status, and pregnant women in the Control Group were instructed to follow the routine of the health service facility. Weight and height were measured, and the body mass index (BMI) was calculated. The pre-gestational nutritional status was determined according to the following BMI criteria: low weight (<18.5 kg/m²), eutrophy (18.5 to 24.9 kg/m²), overweight (25.0 to 29.9 kg/m²), and obesity (>30 kg/m²). The nutritional status during pregnancy was determined according to the BMI curve for gestational age adopted by the Health Ministry of Brazil. Data were analyzed by the relative risk and respective 95% confidence interval, and by the Student's t-test and χ2 test. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05. RESULTS: the assessment of nutritional status before pregnancy showed that 28.0% of the women were overweight and 4.1% were underweight. In the first and last interview during pregnancy, the rates of prevalence of excessive weight were 36.2 and 46.0%, respectively. The intervention proved to be effective in reducing the rate of weekly weight gain of pregnant women with excess weight (342.2 versus 420.2; p=0.015) and the prevalence of clinical complications (9.2 versus 24.85; p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: dietary counseling was effective in decreasing the weight gain of pregnant women who were overweight and reducing clinical complications, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, infant low weight, and prematurity in the Intervention Group.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(9):426-432
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000900003
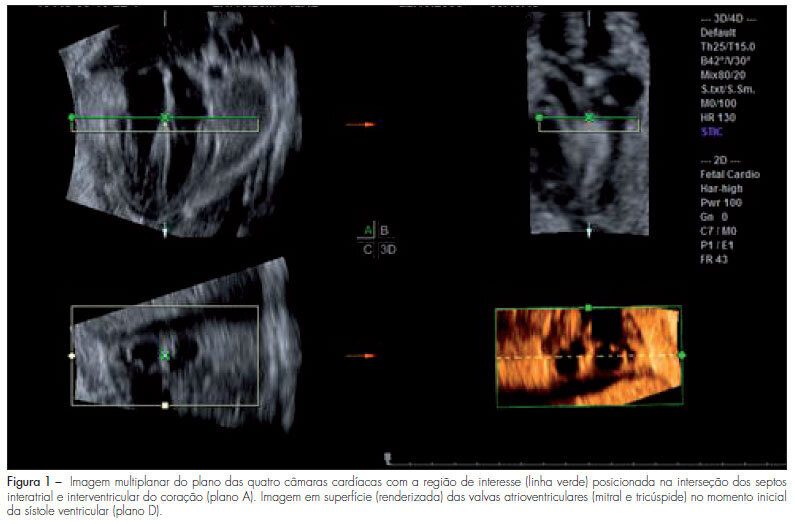
PURPOSE: to evaluate the areas of the atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral) of normal fetuses by the use of three-dimensional ultrasound (3DUS) and the spatiotemporal image correlation (STIC) method. METHODS: a cross-sectional study was conducted on 141 women between the 18th and the 33rd week of pregnancy. Cardiac volumes were measured with a volumetric transabdominal transducer attached to the Voluson 730 Expert equipment. The four chamber plane was used as reference, with the region of interest (ROI) positioned from the ventricles, and the area of the valves was obtained manually. To determine the correlation of the areas with gestational age, scatter plots were constructed and the Pearson correlation coefficient (r) was calculated. Means, medians, standard deviations (SD) and maximum and minimum values were calculated. The simple linear regression model was used to determine reference ranges of valve areas according to the gestational age by the Altman method, with the level of significance set at p<0.05. To calculate the intraobserver reproducibility, we used the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and the Bland-Altman graph. RESULTS: the mitral and tricuspid valve areas were correlated to the gestational age (r=0.80 for the tricuspid and r=0.79 for the mitral valve) and the mean value of the tricuspid and mitral valves increased from 0.22±0.10 cm² and 0.23±0.10 cm² on the 18th week to 0.92±0.29 cm² and 1.08±0.41 cm² on the 33rd of pregnancy, respectively. The intraobserver reproducibility resulted in an ICC=0.993 (95%CI 0.987; 0.996) and the mean difference was 0.01 cm² (SD±0.2 cm² and CI95%±0.4 cm²). CONCLUSION: reference intervals for the areas of the mitral and tricuspid valve between the 18th and the 33rd week of gestation were determined and proved to be highly reproducible.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(9):420-425
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000900002
PURPOSE: to compare the patterns of fetal heart rate (FHR) in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. METHODS: a prospective and comparative study performed between January 2008 and July 2009. The inclusion criteria were: singleton pregnancy, live fetus, pregnant women without clinical or obstetrical complications, no fetal malformation, gestational age between 24 and 27 weeks (2nd trimester - 2T) or between 36 and 40 weeks (3rd trimester - 3T). Computerized cardiotocography (System 8002 - Sonicaid) was performed for 30 minutes and the fetal biophysical profile was obtained. System 8002 analyzes the FHR tracings for periods of 3.75 seconds (1/16 minutes). During each period, the mean duration of the time intervals between successive fetal heart beats is determined in milliseconds (ms); the mean FHR and also the differences between adjacent periods are calculated for each period. The parameters included: basal FHR, FHR accelerations, duration of high variation episodes, duration of low variation episodes and short-term variation. The dataset was analyzed by the Student t test, chi-square test and Fisher's exact test. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05. RESULTS: eighteen pregnancies on the second trimester were compared to 25 pregnancies on the third trimester. There was a significant difference in the FHR parameters evaluated by computerized cardiotocography between the 2T and 3T groups, regarding the following results: mean basal FHR (mean, 143.8 bpm versus 134.0 bpm, p=0.009), mean number of transitory FHR accelerations > 10 bpm (3.7 bpm versus 8.4 bpm, p <0.001) and >15 bpm (mean, 0.9 bpm versus 5.4 bpm, p <0.001), mean duration of high variation episodes (8.4 min versus 15.4 min, p=0.008) and mean short - term variation (8.0 ms versus 10.9 ms, p=0.01). The fetal biophysical profile showed normal results in all pregnancies. CONCLUSION: the present study shows significant differences in the FHR characteristics when the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy are compared and confirms the influence of autonomic nervous system maturation on FHR regulation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(11):549-555
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001100006
PURPOSE: the purpose of this research was to evaluate the morphological aspects and vasculature of the corpus luteum (CL) based on ultrasound parameters during early pregnancy and to assess their relationship with early pregnancy loss. METHODS: this was a prospective cohort study of 90 pregnant patients between 6 and 8 weeks plus 6 days weeks of gestation. We included women at low risk, without acute or chronic systemic disease and with spontaneous conception. Exclusion criteria: use of drugs or smoking, drugs inducing ovulation, history of more than one abortion, no heartbeat visible in the embryo and impossibility of visualization of the corpus luteum. The size, volume, morphological aspects, resistive index, and peak systolic velocity of the corpus luteum were measured by transvaginal sonography. RESULTS: ninety patients were included in the study. Maternal age ranged from 15 to 41 years (mean 28.6±5.8 years). The corpus luteum could be visualized in 87 patients (96.7%), 79 patients had normal pregnancies (90.1%), whereas spontaneous losses occurred in 8 cases (9.9%). In a comparison of the survivors and losses, there was no difference in mean CL diameter (21.8 versus 20.0 mm; p=0.108, Mann-Whitney test), mean CL volume (4.2 versus 3.0 cm³; p=0.076, Mann-Whitney test), mean resistive index (0.55 versus 0,58; p=0.220, Mann-Whitney test), peak systolic velocity (15 versus 15 cm/s; p=0.757, Mann-Whitney test). There was a positive relation between maternal age and resistive index. CONCLUSIONS: no apparent correlation was found between the morphological and vascular aspects of the corpus luteum in early normal pregnancies and first-trimester pregnancy losses.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(8):405-411
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000800008
PURPOSE: the aim of this study was to describe perinatal and maternal outcomes of pregnancies complicated by sickle cell disease (SCD), comparing to pregnancies of women with sickle cell trait (SCT). METHODS: this was a retrospective cohort study, covering the period from March 2001 to April 2008, which included all pregnant women with SCD (n=42) followed up at a university hospital in the Southeast region of Brazil. The maternal and perinatal outcomes were compared to those of pregnant women with SCT (n=56) who were followed up at the same service. RESULTS:SCD-SS was diagnosed in 42 (82.4%) pregnant women and SC in 9 (17.6%). Mean (±SD) maternal age was significantly lower in the SCD group (26.0 years) compared to SCT women (28.7±7.1 years; p=0.018). The following maternal complications were more common among women with SCD in comparison to SCT: urinary tract infection (25.5 versus 8.9%; p=0.04), pneumonia (23.5 versus 1.8%; p=0.002), pulmonary hypertension (15.7 versus 0%; p=0.002), and blood transfusion during delivery or postpartum (33.3 versus 5.4%; p=0.001). Adverse perinatal outcome was more frequent in the SCD group compared to the SCT group: prematurity (49 versus 25%, p=0.01); mean gestational age at delivery (35.2 versus 37.9 weeks, p<0.001); fetal distress (56.9 versus 28.6%, p=0.006); birth weight <2,500 g (62.7 versus 17.9%, p<0.001); mean birth weight (2,183 versus 2,923 g, p<0.001), and small for gestational age infants (29.4 versus 10.7%, p=0.029). Two maternal deaths (3.9%) occurred in the group with SCD. CONCLUSION: Pregnant women with SCD are at greater risk for maternal morbidity and for adverse perinatal outcomes than women with SCT.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(7):352-358
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000700008
PURPOSE: to evaluate the antenatal and postnatal risk factors of neonatal death in pregnancies with absent (DZ) or reverse (DR) end-diastolic flow in the umbilical artery. METHODS: a cross-sectional retrospective study based on data from 48 medical records of singleton pregnancies with DZ or DR, and gestational age of 24 to 34 weeks, at a maternity in the Brazilian Northeast. Mean age was 27.3 (SD: 7.9) years. Twenty (41.7%) patients were primiparas. Hypertensive disorders were found in 44 (91.7%) cases. Thirty-five women (72.9%) had DZ and 13 (27.1%) had DR. Univariate analysis was firstly done (Student's t-test and Fisher's exact test) correlating the parameters with the assessed outcome (neonatal death). Variables that showed significant association were included in the logistic regression model (Wald statistics). The level of significance was set at 5%. RESULTS: The perinatal mortality rate was 64.6% (31/48). There were five stillbirths and 26 neonatal deaths. The mean gestational age at diagnosis was 27.9 (SD: 2.8) weeks. Deliveries before 24 hours after diagnosis occurred in 52.1% of the cases. Cesarean section was performed in 85.4% of the sample. The newborns weighed 975.9 g on average (SD: 457.5). Twenty-four (57.1%) presented Apgar scores below 7 in the first minute and 21.4% in the fifth minute. Gestational age at diagnosis, birth weight and Apgar of the first minute proved to be variables significantly related to neonatal death (p values were: 0.008, 0.004, and 0.020, respectively). The Odds Ratio was 6.6, 25.3 and 13.8 for neonatal death, when the diagnosis was established at the 28th week, weight was <1000 g and first minute Apgar score was <7, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: gestational age at diagnosis, birth weight and Apgar score at the first minute were factors that could predict neonatal death in pregnancies with DV or DR determined by umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(5):229-233
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000500005
PURPOSE: to assess a possible association between polymorphism of the progesterone receptor gene (PROGINS) and recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA). METHODS: in this case-control study, 85 women with at least three previous spontaneous abortions without an identifiable cause (RSA Group) and 157 women with at least two previous term pregnancies without pathologies and no previous miscarriage (Control Group) were selected. An amount of 10 mL of peripheral blood was collected by venipuncture and genomic DNA was extracted by the DTAB/CTAB method, followed by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) under specific conditions for this polymorphism and by amplification by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The bands were visualized with an ultraviolet light transilluminator and the gels were photographed. Differences in the PROGINS genotype and allele frequencies between groups were analyzed by the χ2 test, with the level of significance set at p<0.05. The Odds Ratio (OR) was also used, with 95% confidence intervals 95%CI. RESULTS: PROGINS genotypic frequencies were 72.3% T1T1 and 27.7% T1T2 for the RSA group and 764% T1T1, 22.3% T1T2 and 1.3% T2T2 for the control group. There were no differecnes between groups when the genotype and allele frequencies were analyzed: respectively p=0.48 (OR: 0.8) and p=0.65 (OR: 0.9). CONCLUSIONS: our results suggest that PROGINS polymorphism is not associated with RSA.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(4):198-201
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000400008
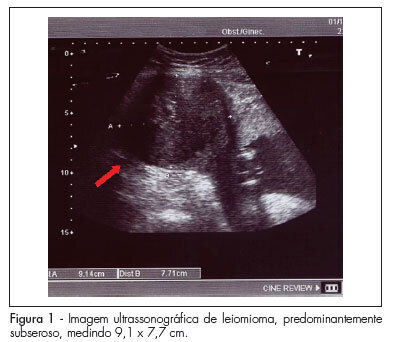
Uterine leiomyomas are characterized as a benign disease and are observed in 2 to 3% of all normal pregnancies. Out of these, about 10% may present complications during pregnancy. We present a case of a pregnant patient sought emergency obstetric care at the 17th week, complaining of severe pain, presenting with painful abdominal palpation and sudden positive decompression. Ultrasonography revealed a myoma nodule measuring 9.1 x 7.7 cm; the patient was hospitalized and medicated, being also submitted to laparotomy and myomectomy due to worsening of her condition. Prenatal care revealed no further abnormalities, with resolution of gestation at 39 weeks. The newborn weighed 3,315 g, with Apgar scores of 9 and 10. In such cases, clinical treatment should always be attempted and surgery should be considered only in selected cases, mainly in the impossibility of conservative treatment or when the patient's clinical features require immediate intervention. In this case, myomectomy was effective against maternal-fetal obstetric complications.