Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(12):536-543
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001200002
PURPOSES: To identify and to analyze maternal mortality causes, according to hospital complexity levels. METHODS: A descriptive-quantitative cross-sectional study of maternal deaths that occurred in hospitals in Paraná, Brazil, during the periods from 2005 to 2007 and from 2008 to 2010. Data from case studies of maternal mortality, obtained by the State Committee for Maternal Mortality Prevention, were utilized. The study focused on variables such as site and causes of death, hospital transfer, and avoidability. Maternal mortality rate, proportions, and hospital lethality ratio were calculated according to subgroups of low and high-risk pregnancy reference hospitals. RESULTS: Maternal mortality rate, including late maternal deaths, was 65.9 per 100.000 live-borns (from 2008 to 2010). Almost 90% of all maternal deaths occurred in the hospital environment, in both periods. The hospital lethality ratio at the high-risk pregnancy reference hospital was 158.4 deaths per 100,000 deliveries during the first period and 132.5/100,000 during the second, and the main causes were pre-eclampsia/eclampsia, puerperal infection, urinary tract infection, and indirect causes. At the low-risk pregnancy reference hospitals, the hospital lethality ratios were 76.2/100,000 and 80.0/100,000, and the main causes of death were hemorrhage, embolism, and anesthesia complications. In 64 (2005 - 2007) and in 71% (2008 - 2010) of the cases, the patients died in the same hospital of admission. During the second period, 90% of the casualties were avoidable. CONCLUSIONS: Hospitals of both levels of complexity are having difficulties in treating obstetric complications. Professional training for obstetric emergency assistance and the monitoring of protocols at all hospital levels should be considered by the managers as a priority strategy to reduce avoidable maternal deaths.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(10):459-465
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001000005
PURPOSES: To assess whether an enoxaparin-based intervention using a score system was effective in improving perinatal outcome in women with thrombophilia. METHODS: Study Design: Prospective, not randomized, uncontrolled, performed at a Clinic of High-Risk Pregnancy from November 2009 to November 2011. We included women with a diagnosis and therapeutic intervention for thrombophilia acquired and/or inherited in the current pregnancy. The obstetric and perinatal outcomes of pregnant women before the intervention were compared with outcomes after the intervention, and statistically analyzed using the χ2 test with Yates correction, considered significant when p<0.05. The initial dose of low-molecular-weight Heparin (LMWH) was guided by a scoring system based on the clinical and gestational history of the patients and screening tests for acquired and/or inherited thrombophilia. RESULTS: We included 84 pregnant women with 175 pregnancies before diagnosis, 20.0% of which resulted in fetal ou perinatal death, 40.0% resulted in abortion, 17.7% developed preeclampsia/eclampsia, 10.3% resulted in full-term births, and 29.7% in premature births. In the 84 pregnancies after intervention, 6.0% resulted in fetal ou perinatal death, 1.2% in abortion, 4.8% developed preeclampsia/eclampsia, 22.6% resulted in premature birth, and 70.2% in full-term birth. A significant reduction in the rate of stillbirths/perinatal death (p<0.05) and abortion (p<0.0001) and a significant increase (p<0.05) in the number of live births were observed after intervention. CONCLUSION: Enoxaparin-based intervention using a score system in pregnant women with thrombophilia is effective in improving perinatal outcome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(10):473-477
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001000007
PURPOSES: To evaluate the hemodynamic patterns of the ophthalmic artery by Doppler analysis in women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), comparing them to normal pregnant women. METHODS: A prospective case-control study that analyzed the ophthalmic artery Doppler indices in two groups: one consisting of 40 women diagnosed with GDM and the other of 40 normal pregnant women. Included were pregnant women with GDM criteria of the American Diabetes Association - 2012, with 27 weeks of pregnancy to term, and excluded were women with hypertension, use of vasoactive drugs on or previous diagnosis of diabetes. Doppler analysis was performed in one eye with a 10 MHz linear transducer and the Sonoace 8000 Live Medison® equipment . The following variables were analyzed: pulsatility index (PI), resistance index (RI), peak velocity ratio (PVR), peak systolic velocity (PSV) and end diastolic velocity (EDV). To analyze the normality of the samples we used the Lillefors test, and to compare means and medians we used the Student's t-test and Mann-Whitney test according to data normality, with the level of significance set at 95%. RESULTS: The median and mean values with standard deviation of the variables of the ophthalmic artery Dopplervelocimetry group GDM and normal pregnant women were: IP=1.7±0.6 and 1.6±0.4 (p=0.7); IR=0.7 and 0.7 (p=0.9); RPV=0.5±0.1 and 0.5±0.1 (p=0.1), PSV=33.6 and 31.9 cm/sec (p=0.7); VDF=6.3 and 7.9 cm/sec (p=0.4). There was no significant difference in the means and medians of these variables between the two groups of pregnant women. CONCLUSIONS: The ophthalmic artery hemodynamic patterns, analyzed by means of a Doppler technique remained unchanged in the group of pregnant women with GDM compared to the group of normal pregnant women, suggesting that the time of exposure to the disease during pregnancy was too short to cause significant vascular disorders in the central territory.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(9):409-413
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000900004
PURPOSE: To evaluate, in healthy women in the second trimester of pregnancy, a possible association between sexual function and quality of life, and between sexual function and sexual satisfaction. METHODS: This cross-sectional study involved 51 pregnant women managed at a low-risk antenatal care clinic. Sexual function was evaluated through the Sexual Quotient - Female Version (QS-F) questionnaire. Quality of life and sexual satisfaction were evaluated though the brief version of the World Health Organization Quality of Life questionnaire (WHOQOL-bref). Inclusion criteria were pregnancy between 15-26 weeks, maternal age 20 or more years, at least five years of scholling, in a relationship with a single partner for the last 6 months, having sexual intercourse with vaginal penetration in the last 15 days. We excluded women with a history of sexual violence, previous or current depression, habitual abortion or obstetric complications in the index pregnancy (premature rupture of membranes, preterm labor or hemorrhage). The χ² and Fisher exact tests were used for statistical analyses and p<0.05 was considered significant. RESULTS: Most of the participants (64.8%) obtained "regular to excellent" grades on the QS-F and 58.8% classified their quality of life as "good". As to sexual satisfaction, 35.3 and 15.7% declared that they were "satisfied" and "very satisfied" with their sexual life, respectively. The study detected significant associations between "bad to poor" QS-F grades with a "poor" quality of life (p=0.002), and with "regular to good" and "good to excellent" QS-F grades with "satisfaction" or "high" sexual satisfaction" (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: Sexual function is associated with quality of life and with sexual satisfaction in healthy women in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(8):381-385
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000800007
PURPOSE: To assess perinatal factors associated with term newborns with pH<7.1 in the umbilical artery and 5th min Apgar score<7,0. METHODS: Retrospective case-control study carried out after reviewing the medical records of all births from September/1998 to March/2008, that occurred at the General Hospital of Caxias do Sul. The inclusion criterion was term newborns who presented a 5th min Apgar score <7.0 and umbilical artery pH<7.10. In the univariate analysis, we used the Student's t-test and the Mann-Whitney test for continuous variables, the c² test for dichotomous variables and risk estimation by the odds ratio (OR). The level of significance was set at p<0.05. RESULTS: Of a total of 15,495 consecutive births, 25 term neonates (0.16%) had pH<7.1 in the umbilical artery and a 5th min Apgar score <7.0. Breech presentation (OR=12.9, p<0.005), cesarean section (OR=3.5, p<0.01) and modified intrapartum cardiotocography (OR=7.8, p<0.02) presented a significant association with the acidosis event. Among the fetal characteristics, need for hospitalization in the neonatal intensive care unit (OR=79.7, p <0.0001), need for resuscitation (OR=12.2, p <0.0001) and base deficit were associated with the event (15.0 versus -4.5, p<0.0001). CONCLUSION: Low Apgar score at the 5th min of life associated with pH<7.1 in the umbilical artery can predict adverse neonatal outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(7):296-303
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000700002
PURPOSE: To determine the pattern of alcohol use before and during pregnancy and associated risk factors in puerperal women hospitalized in a public university hospital in Southeastern Brazil. METHODS: Between June and September 2009, 493 puerperae were consecutively evaluated. Those with cognitive impairment were excluded from the study. The AUDIT and CAGE questionnaires were used to diagnose alcohol use/abuse before pregnancy, in addition to the T-ACE during pregnancy. Another questionnaire was applied to collect sociodemographic data, such as age, educational level, marital status, and household income. The χ² test was used in the statistical analysis and the Odds Ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (95%CI) were calculated. A p-value <0.05 was considered to be significant. RESULTS: Before pregnancy, the CAGE was positive in 50/405 (12.3%) women and the AUDIT identified alcohol use in 331 (67.1%), which was of low risk in 233 (47.3%), risky in 73 (14.8%), and harmful or indicating possible alcohol dependence in 25 (5%). During pregnancy, the CAGE was positive in 53/405 (13.1%) women and the T-ACE in 84 (17%); the AUDIT identified alcohol use in 114 women, which was of low risk in 73 (14.8%), risky in 27 (5.5%), and harmful or indicating possible alcohol dependence in 14 (2.8%). During pregnancy, alcohol use was more frequent (OR=2.8; 95%CI 1.2 - 6.2) among women with a lower educational level (8.8 versus 3.3%) and more frequent (OR=3.8; 95%CI 1.3 - 11.1) among those who did not cohabit with a partner (6 versus 1.7%). Among pregnant women who drank alcohol, 49/114 (43%) were advised to stop drinking. CONCLUSIONS: Alarming alcohol use was observed during pregnancy, especially among pregnant women with a lower educational level and those who did not cohabit with a partner. There was a low frequency of counseling aimed at abstinence and the AUDIT was the instrument that most frequently diagnosed alcohol consumption.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(6):268-273
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000600005
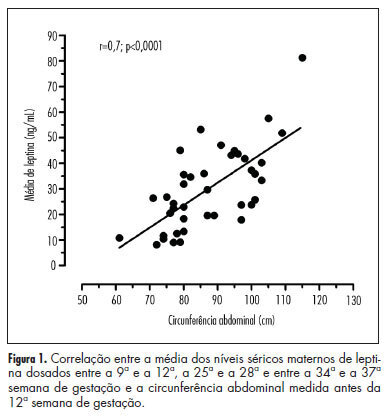
PURPOSE: To evaluate the correlation between maternal waist circumference measured before the 12th week of gestation and serum leptin levels during pregnancy, as well as to compare the leptin levels of women with and without abdominal obesity diagnosed in early pregnancy. METHODS: Prospective study including 40 pregnant women receiving low-risk prenatal care, older than 20 years, nonsmokers, with singleton pregnancies and without chronic disease. Waist circumference was measured before the 12th week and serum leptin levels were measured between the 9th and 12th, 25th and 28th and 34th and 37th weeks of gestation. According to waist circumference measurement, the cohort was divided into two groups: with and without abdominal obesity. The Mann-Whitney and χ² tests were used to assess the differences between groups. The Pearson correlation coeffient was used to assess the association between waist circumference and serum leptin levels during pregnancy. The level of significance was set at p<0.05. RESULTS: The mean weight and body mass index of patients with abdominal obesity (74.4±11.0 kg/28.9±4.1) was higher than that of patients without abdominal obesity (55.6±5.9 kg/21.1±2.4) (p=0.001). The mean leptin levels in pregnant patients with abdominal obesity (41.9±3.5 ng/mL) was higher than in patients without abdominal obesity (23.6±2.7 ng/mL) (p<0.0002). A positive correlation was obtained between the waist circumference measured during the same period and the mean serum leptin levels (r=0.7; p<0.0001). CONCLUSIONS: Waist circumference measured before the 12th week of pregnancy is a valid and simple method to predict the serum leptin levels throughout pregnancy. Pregnant women with abdominal obesity diagnosed before 12th week have higher mean serum leptin levels during pregnancy than those without abdominal obesity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(4):147-152
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000400002
PURPOSE: To assess medication adherence therapeutic during pregnancy in a sample of Brazilian women during the post-partum period. METHODS: We conducted a cross-sectional study in the obstetric unit of a university hospital, Brazil, between August and November 2010. We recruited patients aged 18 years or more, with a gestational age of more than 22 weeks whose newborns weighed more than 500 g. Patients were excluded if they used sedatives or other mind-altering drugs. Data were collected after labor using a structured questionnaire containing questions about sociodemographic characteristics, medication use, number of previous pregnancies, contraceptive methods, prenatal care, and medication adherence. Medication adherence was assessed using the four-item Morisky medication adherence scale - MMAS-4, groups were compared by the Fisher exact Test and Kruskal-Wallis Test and Χ2 de Pearson Test. RESULTS: Mean age was 22.5 years (SD=6.5), and 53.8% of the pregnant women had initiated prenatal care during the first trimester of pregnancy. Of the 130 patients interviewed, 96.9% had used at least one prescribed drug during pregnancy, with an average of 2.8 drugs per patient. The major classes prescribed were antianemics (55.1%), analgesics, anti-inflammatories, and antipyretics (19.0%) and anti-infectives (7.2%). 71.6% took two to four drugs. Only 19.2% of patients were considered adherent. The variables that showed a negative influence on adherence were: higher level of education, having one's own income, earlier prenatal care and previous abortion. CONCLUSION: Our findings indicate that, although most of the patients used prescribed drugs during pregnancy, the rate of medication adherence was low, which indicates the need for further investigation about the impact of non-adherence during pregnancy and its causes.