Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(2):84-90
To analyze and compare the frequency of cesarean sections and vaginal deliveries through the Robson Classification in pregnant women attended at a tertiary hospital in two different periods.
Cross-sectional, retrospective study of birth records, comprising 4,010 women, conducted from January 2014 to December 2015 in the only public regional referral hospital for the care of high- risk pregnancies, located in Southern Brazil.
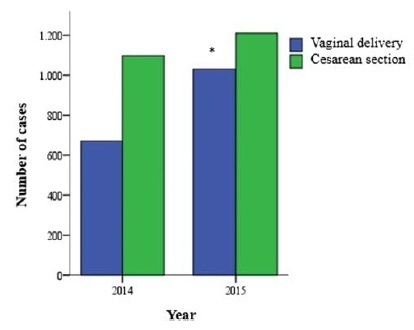
The overall cesarean section rate reached 57.5% and the main indication was the existence of a previous uterine cesarean scar. Based on the Robson Classification, groups 5 (26.3%) and 10 (17.4%) were the most frequent ones. In 2015, there was a significant increase in the frequency of groups 1 and 3 (p < 0.001), when compared with the previous year, resulting in an increase in the number of vaginal deliveries (p < 0.0001) and a reduction in cesarean section rates.
The Robson Classification proved to be a useful tool to identify the profile of parturients and the groups with the highest risk of cesarean sections in different periods in the same service. Thus, it allowsmonitoring in a dynamic way the indications and delivery routes and developing actions to reduce cesarean rates according to the characteristics of the pregnant women attended.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(2):145-147
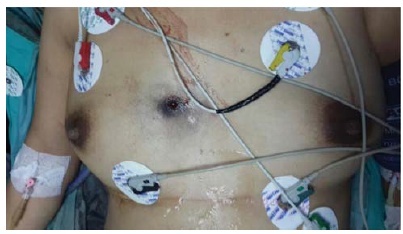
Transmediastinal gunshot wounds (TGWs) may lead to life-threatening injuries of vital organs such as large vessels, the esophagus, and lungs. Although they are not commonly encountered in pregnant women, additional caution should be given to these patients. Physical examination for the diagnosis and the choice of treatment modality contain controversial points in hemodynamically stable patients, and resuscitation has excessive importance due to physiological changes in pregnancy. We present a hemodynamically stable 26-week pregnant woman brought to the emergency department for TGW. She had a 1-cm diameter of bullet entrance hole on the right anterior 4th intercostal space, 2 cm lateral to the sternum, and a 3-cm diameter exit hole on the right posterior 12th intercostal space on the midscapular line.With our conservative approach, she had an uncomplicated pregnancy period, and gave birth to a healthy baby at term.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):845-848
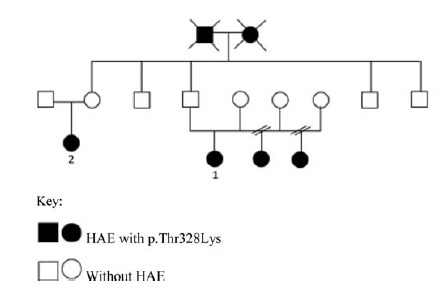
To verify the efficacy of short-term prophylaxis for vaginal or cesarean section childbirth with plasma-derived C1-inhibitor concentrate in pregnant women. They should have hereditary angioedema (HAE) and normal plasma C1-inhibitor.
Case report of pregnant women diagnosed with HAE with normal C1- inhibitor who had been treated with intravenous C1-inhibitor concentrate for prophylaxis of angioedema attacks when hospitalized for delivery. The exon 9 of the Factor 12 (F12) genotyping gene was performed by automatic sequencing in all patients.
Three cases of pregnant women with HAE with normal serum level of C1- inhibitor are reported. The genetic test detected the presence of a pathogenic mutation in the F12 gene. Deliveries occurred uneventfully and patients had no HAE symptoms in the following 72 hours.
C1-inhibitor concentrate could be useful to prevent angioedema attacks during and after delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):834-840
Thrombocytopenia, defined as platelet count < 150,000mm3, is frequently diagnosed by obstetricians since this parameter is included in routine surveillance during pregnancy, with an incidence of between 7 and 12%. Therefore, decisions regarding subsequent examination and management are primordial. While most of the cases are due to physiological changes, as gestational thrombocytopenia, other causes can be related to severe conditions that can lead to fetal or maternal death. Differentiating these conditions might be challenging: they can be pregnancy-specific (pre-eclampsia/ HELLP syndrome [hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets]), or not (immune thrombocytopenia purpura, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura or hemolytic uremic syndrome). Understanding the mechanisms and recognition of symptoms and signs is essential to decide an adequate line of investigation. The severity of thrombocytopenia, its etiology and gestational age dictates different treatment regimens.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):787-792
Urinay incontinence (UI) is amajor public health problemthat can harm women in any period of life, including during the gestational period. Urinary incontinence during pregnancy has been studied because this condition can reduce the quality of life and interfere in several aspects of the maternal-fetal binomial. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of UI in nullipara pregnant women and to identify risk factors associated with UI in this population.
This is a case-control study in which we invited nullipara women between 12 and 20 weeks of pregnancy to participate in the research. They were asked to answer a specific questionnaire, write a 3-day bladder diary, and undergo a urogynecological evaluation including pelvic organ prolapse quantification (POP-Q), empty stress supine test (ESST), and pelvic floor muscle assessment.
A total of 70 out of 73 patients accepted to participate in the study, and the prevalence of UI in this population was 18.3%. Tobacco use was identified as an independent risk factor for UI in pregnant women (odds ratio 8.0). All other factors analyzed were not significantly associated to UI in pregnancy.
Urinary incontinence can be a major problem in pregnancy.We identified the use of tobacco as a risk factor for developing UI in pregnancy, which provides an extra reason to encourage patients to quit smoking.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):705-711
To determine pregnancy outcomes in women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who were treated with hydroxychloroquine in a tertiary center.
A retrospective study involving pregnant women with SLE who had antenatal follow-up and delivery in between 1 January 2007 and 1 January 2017. All participants were retrospectively enrolled and categorized into two groups based on hydroxychloroquine treatment during pregnancy.
There were 82 pregnancies included with 47 (57.3%) in the hydroxychloroquine group and 35 (42.7%) in the non-hydroxychloroquine group. Amongst hydroxychloroquine users, there were significantly more pregnancies with musculoskeletal involvement (p = 0.03), heavier mean neonatal birthweight (p = 0.02), and prolonged duration of pregnancy (p = 0.001). In non-hydroxychloroquine patients, there were significantly more recurrent miscarriages (p = 0.003), incidence of hypertension (p = 0.01) and gestational diabetes mellitus (p = 0.01) and concurrent medical illness (p = 0.005). Hydroxychloroquine use during pregnancy was protective against hypertension (p = 0.001), and the gestational age at delivery had significant effect on the neonatal birthweight (p = 0.001). However, duration of the disease had a significant negative effect on the neonatal birthweight (p = 0.016).
Hydroxychloroquine enhanced better neonatal outcomes and reduced adverse pregnancy outcomes and antenatal complications such as hypertension and diabetes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):672-675
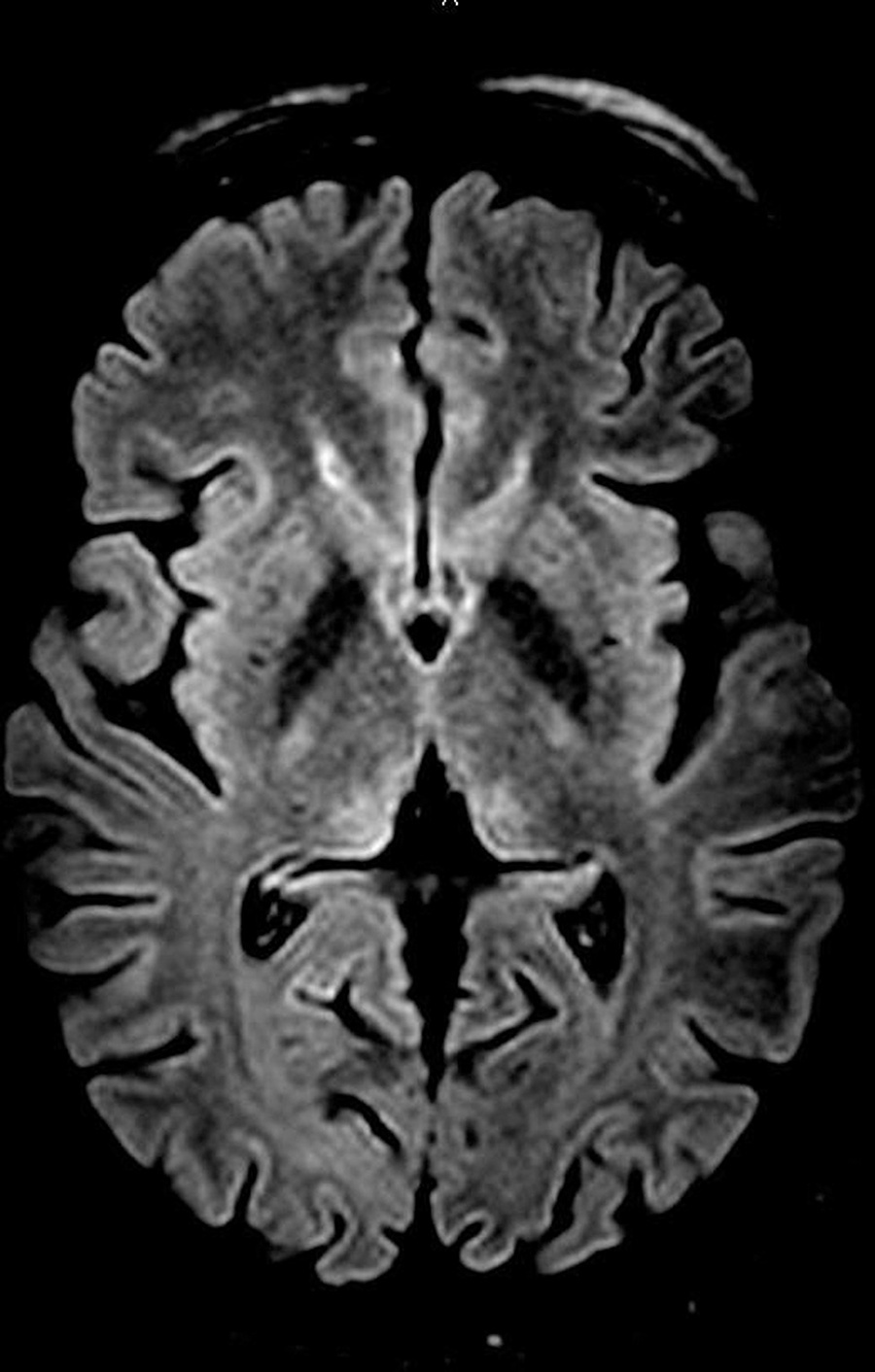
Wernicke encephalopathy (WE) is an acute neurological disorder resulting from vitamin B1 deficiency, which is common in chronic alcoholism. We report a rare case of WE due to hyperemesis gravidarum in a 25-year-old pregnant patient at 13 weeks and 5 days of gestation. Initially, the disease manifested as weakness, mental confusion, anterograde amnesia, and visual and auditory hallucinations. The diagnosis was established after the detection of suggestive findings of WE in the thalamus by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and a rapid improvement in the patient's clinical status subsequent to treatment with thiamine. Hyperemesis is a rare cause of WE, which makes the reported case important in the literature and reinforces the need for attention in clinical practice to rare but important complications of this common condition (hyperemesis gravidarum).
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):562-568
The present comprehensive review aims to show the full extent of what is known to date and provide a more thorough view on the effects of SARS-CoV2 in pregnancy.
Between March 29 and May, 2020, the words COVID-19, SARS-CoV2, COVID- 19 and pregnancy, SARS-CoV2 and pregnancy, and SARS and pregnancy were searched in the PubMed and Google Scholar databases; the guidelines from well-known societies and institutions (Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists [RCOG], American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists [ACOG], International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology [ISUOG], Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics [FIGO]) were also included.
The COVID-19 outbreak resulted in a pandemic with > 3.3 million cases and 230 thousand deaths until May 2nd. It is caused by the SARS-CoV2 virus and may lead to severe pulmonary infection and multi-organ failure. Past experiences show that unique characteristics in pregnancy make pregnant women more susceptible to complications from viral infections. Yet, this has not been reported with this new virus. There are risk factors that seem to increase morbidity in pregnancy, such as obesity (body mass index [BMI] > 35), asthma and cardiovascular disease. Current reports describe an increased rate of pretermbirth and C-section. Vertical transmission