Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo1
03-18-2025
Preterm birth is a leading global cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity, with oxidative stress playing a role in its pathogenesis. Vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant, may help reduce this risk. This study assessed the effectiveness of vitamin C supplementation, both alone and with vitamin E, in preventing preterm birth compared to a placebo.
Databases were systematically searched in PubMed, Cochrane and Embase in December 2023 and updated in May 2024.
Included RCTs evaluated vitamin C's effect on preterm birth and related neonatal outcomes.
Statistical analyses used a random-effects model for pooled risk ratios (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed with the I² statistic.
Seventeen RCTs (21,567 patients) were analyzed. Vitamin C supplementation showed no significant difference compared to placebo for preterm birth (RR 1.04; 95% CI 0.96, 1.14). No significant differences were observed for neonatal death (RR 0.77; 95% CI 0.55, 1.08), NICU admission (RR 1.03; 95% CI 0.95, 1.13), preterm PROM (RR 1.04; 95% CI 0.63, 1.71), or birth weight (MD 52.41; 95% CI −19.65, 124.47). A slight decrease in gestational age was observed (MD 0.26; 95% CI −0.02, 0.55).
Vitamin C supplementation alone or in combination with vitamin E does not significantly prevent preterm birth or improve related neonatal outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo2
03-18-2025
Statins are the most widely used pharmacological class for treating hyperlipidemia, although they are contraindicated during pregnancy. This study aims to demonstrate the clinical effects of statins in pregnant women through an interactive review. Fifteen original articles were selected, in English or Portuguese, within of five years. Statins have not been associated with the development of fetal malformations and their use may be useful in preventing unfavorable cardiovascular outcomes, with the potential to reduce oxidative stress and angiogenic dysfunction. However, the use of statins to prevent pre-eclampsia in humans has not been properly clarified and further studies are needed. Pravastatin is considered safer than statins for use during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo5
03-18-2025
To determine the validity of the angle of progression (AoP) in predicting delivery mode among women in the second stage of labor.
This prospective cohort study was conducted at the Obstetrics and Gynecology unit (OBGYN) of two hospitals in Vietnam. Transperineal ultrasound was performed for each woman to measure the progression angle in the second phase of labor.
A total of 725 women with singleton pregnancies with cephalic presentation at term
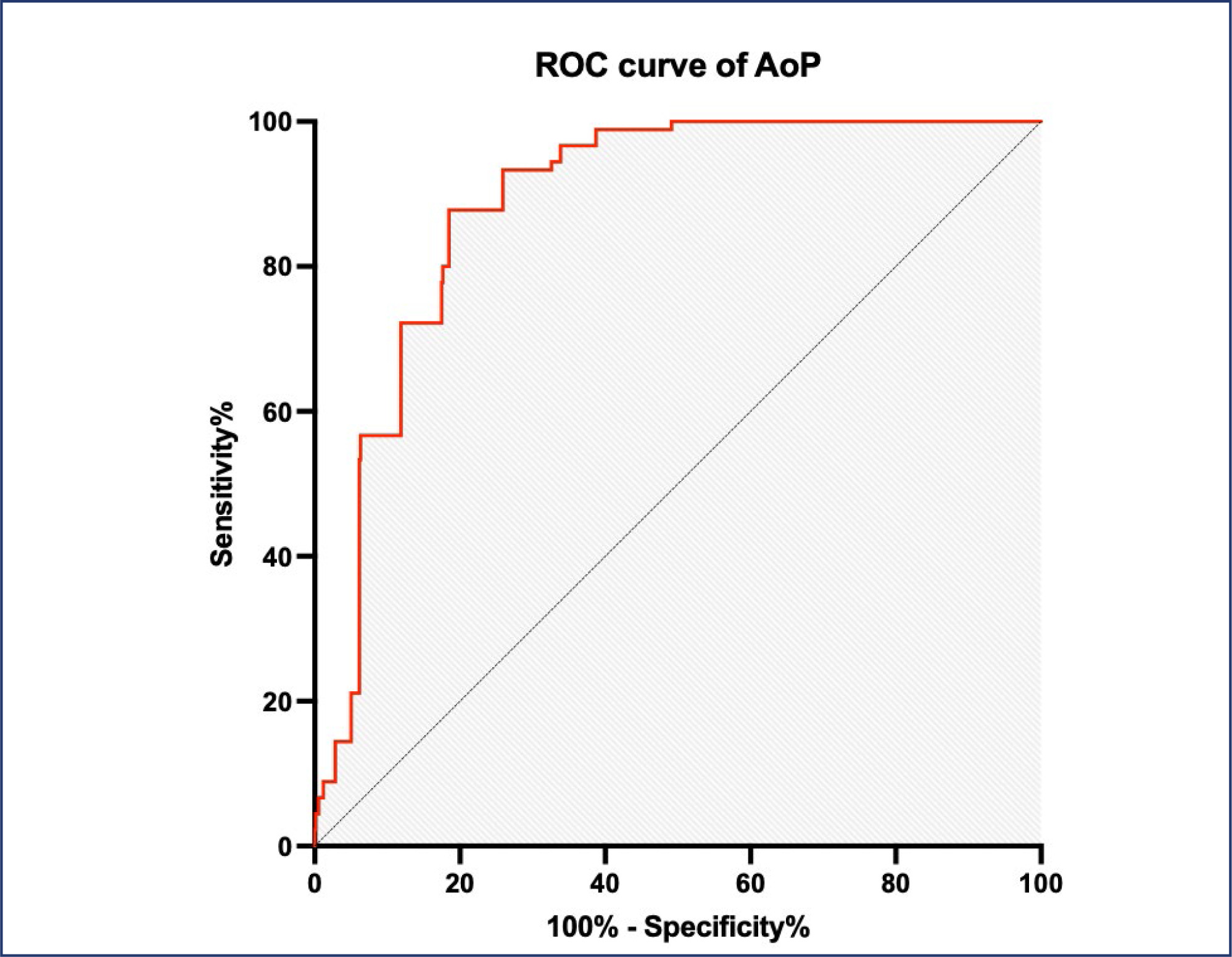
Transperineal ultrasound was used to measure the angle of progression in the second labor phase and to identify the delivery method.
The rate of vaginal birth in women with an AoP ≥ 120° on transperineal ultrasound was 70.2%. The optimal cutoff point of AOP ≥122° with sensitivity and specificity for vaginal birth were 87.8% and 80.7%, respectively the area under the ROC curve of 0.887 (p<0.0001). The study's sample size was restricted owing to deficiencies in resources and time.
The likelihood of achieving spontaneous vaginal delivery can be predicted by the angle of progression measured with transperineal intrapartum ultrasonography during the second stage of labor in women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo8
03-18-2025
To describe women's experience of pregnancy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
A qualitative study conducted in a private maternity hospital, from May, 2020 to November, 2021, with women aged ≥ 18 years, gestational age ≥ 36 weeks at birth and ≥ 24 hours post-partum. Data collected through semi-structured interviews, recorded, transcribed, and analyzed adopting Krippendorff's Content Analysis as theoretical-methodological framework.
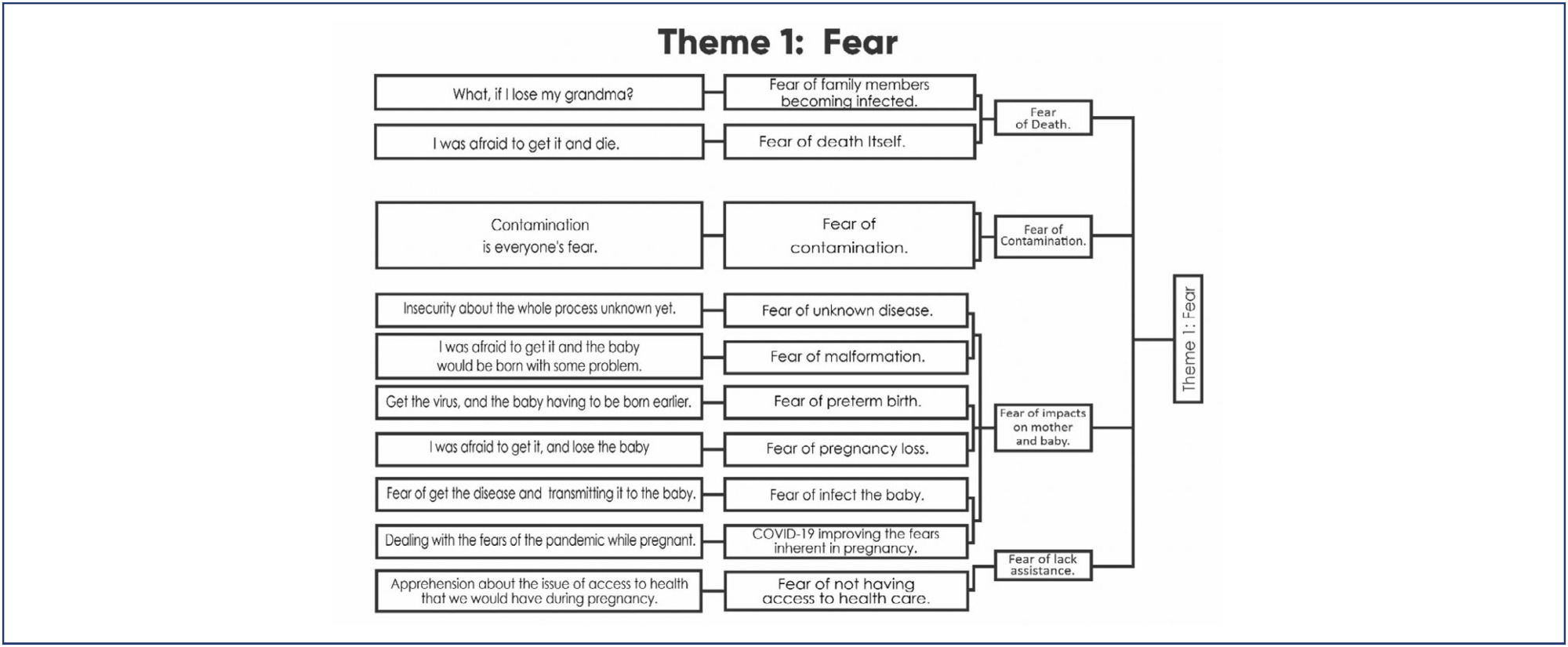
Four main themes emerged: Fear, Taking care and celebrating pregnancy: adjusting to the new reality, Harms of Isolation, and Benefits of Isolation. The fear of contamination and its impact on the health of mother and child resulted in the adoption of severe social isolation, including from those considered sources of support by the expecting mother. Overwhelmed, some of the participants reported loneliness and psychic suffering. The opportunity to focus on the pregnancy, the preparations for the arrival of the child, and the family made isolation a beneficial and positive period for other women.
The experience of pregnancy in the Pandemic was an event outside of the ordinary and common. The expecting mother faced her worst fears on a daily basis and attended prenatal care, in order to ensure her child would be born healthy. The celebration of the baby's life, amid so many deaths, had to be adjusted to the virtual environment. It was a tense, solitary, and ambiguous period, which demanded a lot from the mental health of some participants, but to others, brought advantages that would not have been possible in different times.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo9
03-18-2025
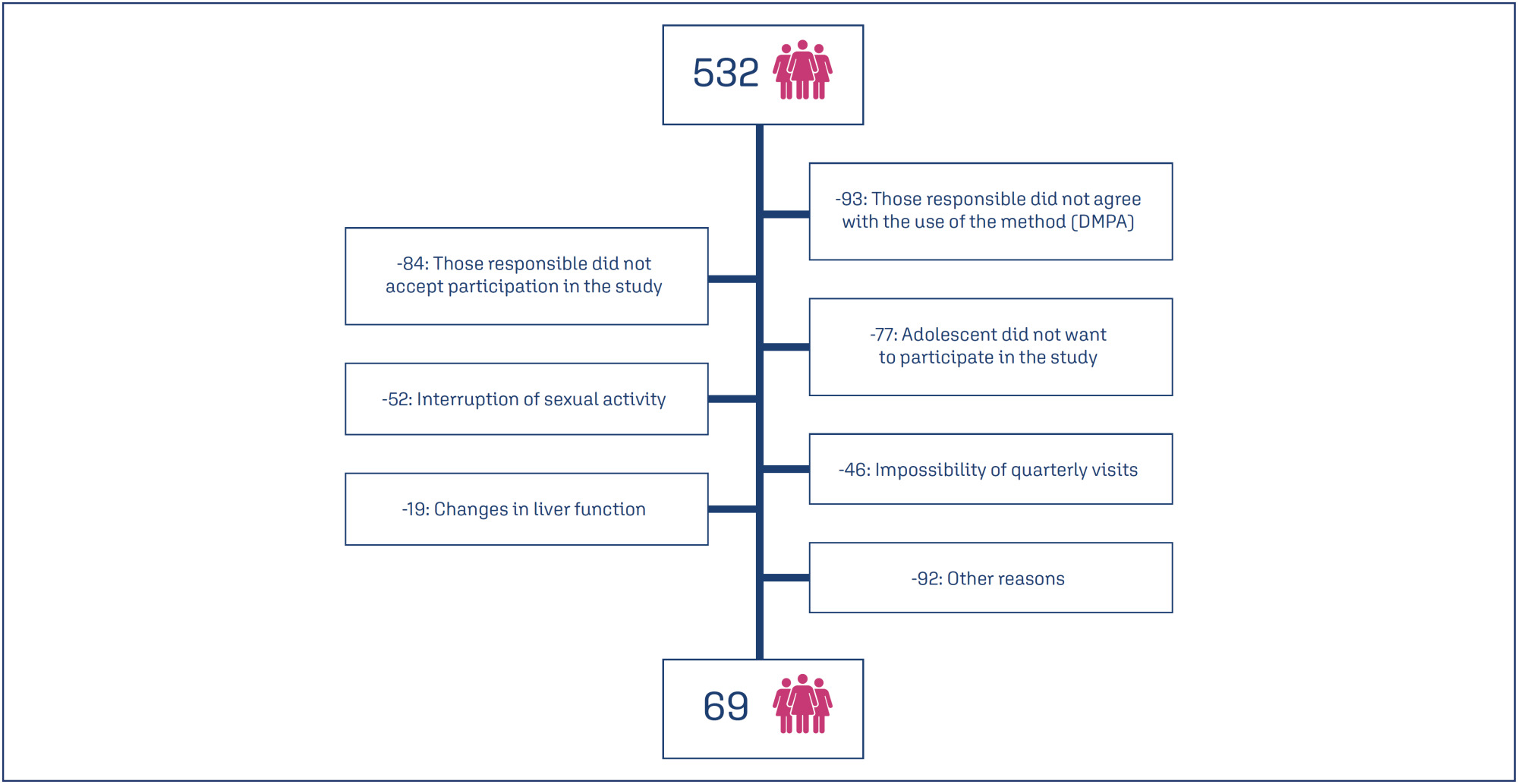
To evaluate the continuation rate, satisfaction, and reasons for discontinuation of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) in adolescents treated in a mental health service.
Prospective cohort study conducted in a reference unit for the care of adolescents with mental disorders (MDs) and intellectual disabilities (IDs). All patients received a gynecological consultation and an educational group on contraceptive methods. Sociodemographic data on age, education and gynecological data (menarche, coitarche, regularity of menstrual cycles and presence of symptoms) were collected. Follow-up was quarterly for 12 months, during which symptoms, desire to continue, and satisfaction with the use of the quarterly injectable were assessed.
Eight hundred and sixty-two sexually active adolescents were supported, 532 adolescents chose to use the quarterly injectable, and 69 of these agreed to participate in the study. The mean age of users was 15.5 years (SD=0.91). After 12 months of follow-up, 34 (49.3%) of the 69 adolescents continued to use the method and 36 (52.3%) were satisfied. Among the 33 (47.8%) who discontinued use, the most common reasons were irregular bleeding and weight gain.
Adolescents with intellectual disabilities and/or other mental disorders showed a significant rate of continuation and satisfaction with the use of the depot medroxyprogesterone acetate at 12 months, and the most common reasons for discontinuation were irregular uterine bleeding and weight gain.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo98
01-23-2025
To determine if maternal erythrocytosis is a risk factor for small-for-gestational age at term at 3,400-m altitude in pregnant women without intercurrent disease.
Analytical study of retrospective cohorts at Cusco, a city at 3,400-m altitude. Our participants were 224 and 483 pregnant women with and without exposure to maternal erythrocytosis, respectively. A logistic regression with the goodness of fit to the proposed model was also performed with the Hosmer and Lemeshow test, evaluating the small-for-gestational-age results with or without exposure to hemoglobin >14.5 g/dl.
The incidence of small-for-gestational-age was 6.9% for this entire cohort. The maternal erythrocytosis during gestation without any maternal morbidity at 3,400-m altitude has an ORa=0.691 (p=0.271) for small-for-gestational-age at term. Inadequate prenatal control has an ORa=2.115 (p=0.016) for small-for-gestational-age compared to adequate prenatal control.
Maternal erythrocytosis in pregnant women without any morbidity is not a risk factor for small-for-gestational-age at 3,400 m-altitude.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo99
01-23-2025
The aim of the study was to identify non-pharmacological therapeutic resources used by physiotherapists for pain relief during labor and childbirth.
This is a cross-sectional study conducted from January to March 2021, followed the STROBE guidelines. It included Brazilian physiotherapists with a minimum of two years in obstetric care experience. Data were collected using a 33-item online questionnaire, which covered sociodemographic details and the utilization of non-pharmacological resources. Descriptive analysis was used to determine participant characteristics. Associations between sociodemographic variables, specialist titles, participation in scientific events, and methods for pain relief methods during childbirth were assessed using chi-square or Fisher’s exact tests. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 23.0, with a significance level set at 5% (p < 0.05).
A total of 114 Brazilian physiotherapists participated in this study. Participants chose to utilize non-pharmacological therapies and resources that are within the scope of physiotherapists’ practice for labor pain. Kinesiotherapy with the use of devices was the most employed technique for pain relief during the birthing process.
The study highlights the prevalent use of non-pharmacological therapeutic resources, particularly kinesiotherapy with devices, among Brazilian physiotherapists for labor pain relief.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo87
10-23-2024
To compare access and suitability of antenatal care between years 2020 and 2022 among postpartum individuals at a Hospital in Florianopolis, and evaluate factors associated with antenatal suitability.
Observational, cross-sectional, and quantitative study carried out in 2022. Collected data were compared with the database of a previous similar study carried out in the same setting in 2020. Data were extracted from medical records and prenatal booklets, in addition to a face-to-face questionnaire. Adequacy was measured using the Carvalho and Novaes index and health access was qualitatively evaluated. Socio-demographic and antenatal variables were analyzed. A statistical significance level of 0.05 was considered. Open-ended questions were categorized for analysis.
395 postpartum individuals were included. Antenatal care was adequate for 48.6% in 2020 and 69.1% in 2022. Among the barriers to access, 56% reported difficulty in scheduling appointments and/or exams and 23% complained of reduced healthcare staff due to strikes, COVID-19, among others. Adequate antenatal care was associated with being pregnant in 2022, being referred to high-risk units (PNAR), and not reporting difficulties in access. Also, it was associated with twice the chance of investigation for gestational diabetes (GDM) and syphilis.
The 2022 post-vaccination period showed higher antenatal adequacy. The main difficulty for postpartum individuals was scheduling appointments and/or exams. Having antenatal care in 2022, no reports of difficulty in access, and follow-up at a high-risk unit were associated with antenatal adequacy.