Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(6):281-286
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000600003
PURPOSE: to assess the prevalence and risk factors associated with near miss and other severe maternal morbidity at a reference tertiary maternity. METHODS: this is a cross-sectional study on severe maternal morbidity at the Hospital e Maternidade Celso Pierro, Campinas, São Paulo, between October 2005 and July 2006, identified from infirmary, admission and delivery unit logbooks. Pregnant and post-partum women with severe maternal morbidity were identified according to clinical criteria proposed by Waterstone. Later, cases with more severe morbidity, called extremely severe maternal morbidity, were reclassified using Mantel criteria, based on organic dysfunction and clinical management. RESULTS: there were 114 severe maternal morbidity cases among 2,207 birth deliveries, with a ratio of other severe morbidity and extremely severe morbidity near miss of 44.9 and 6.8 cases/1,000 live births, respectively. Mean gestational age at delivery was 35 weeks, and 87% came from the reference area for the maternity service. Hypertension (severe pre-eclampsia) represented 96% of other severe morbidity, while hemorrhage represented 60% of all extremely severe cases, followed by hypertension. The prevalence of extremely severe morbidity among the severe morbidity cases was not associated with marital status, schooling, maternal age, type of delivery, parity, gestational age at birth and home place. CONCLUSIONS: the other morbidities were 6.6 times more frequent than near miss, and it was not possible to differentiate both groups by epidemiological risk factors.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(2):80-86
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000200006
PURPOSE: to describe the clinical and laboratorial profile of HELLP syndrome patients admitted at an Obstetric Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and included in a randomized clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of dexamethasone in this clinical setting. METHODS: the present study is a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial design to evaluate the efficacy of dexamethasone in patients with HELLP syndrome. This sample of patients was composed of patients in the puerperium, with the diagnosis of HELLP syndrome (diagnosis made before or after delivery) who were not chronic corticosteroid users and not carriers of any chronic disease which could modify HELLP syndrome's laboratorial parameters. Patients who were too critical or whose condition did not allow them to consent to participate were not included. Data were extracted from the records used in the randomized clinical trial. Age, parity, gestational age at admission and delivery, time of diagnosis (before or after delivery), HELLP syndrome classification (partial or complete), arterial blood pressure, and diuresis at admission were considered for analysis. Among laboratorial findings, hemoglobin, platelet count, liver enzymes, LDH, and serum bilirubin were analyzed. Complications presented by the patients were also analyzed as well as need of blood transfusions and duration of hospitalization. Analysis was made by the Epi-Info 3.3.2 program. RESULTS: one hundred and five patients were analyzed. Age varied from 14 to 49 years (means of 26.7). Regarding parity, 56 patients (53.8%) were primiparas. Analyzing the timing of the diagnosis, 47 patients (45.2%) had the diagnosis before delivery. The mean gestational age in these patients was 32.4 weeks. Hemorrhagic manifestations were observed in 36 patients (34.3%), oliguria was present in 49 patients (46.7%) and criteria for acute renal failure were seen in 21 (20%) of the cases. Hemotransfusions were necessary in 35 (33.3%) patients. Seven patients (6.7%) had pulmonary edema and four patients died, corresponding to 3.8% of the cases. The mean time from diagnosis of HELLP syndrome to discharge or death was 10.3 days, varying from 1 to 33 days. CONCLUSIONS: HELLP syndrome is an ominous diagnosis, which implicates in elevated maternal morbimortality. Among complications, oliguria and hemorrhagic manifestations were the most common findings and hemotransfusions were frequently required. Lethality reached 3.8%.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):19-24
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100004
PURPOSE: The aim of this article is to evaluate the use of nevirapine HIV-infected pregnant women in our service. METHODS: a retrospective study was performed between January 2003 and December 2006 analysing all women prescribed nevirapine in pregnancy. Exclusion criteria included: (1) women who started nevirapine before pregnancy, (2) patients with abnormal baseline liver enzymes, and (3) women with incomplete liver biochemistry data. Evaluated parameters included age, weeks of exposure to nevirapine, gestational age in the begginning of medication, weeks of follow-up, viral load, CD4 cells count and serum aminotransferase levels. The incidence of adverse hepatic and/or cutaneous effects was determined and correlated to the CD4 cells count. Statistical analysis were performed using Fisher’s exact test and t-Student test when appropriate, with a statistical significance level of p<0,05. RESULTS: one hundred fifty-seven women met the inclusion criteria. Thirty-one (19.7%) presented cutaneous and/or hepatic toxicity. Skin rash accounted for 77.4% of toxicities and liver function abnormalities were noted in 22.6% of women exhibiting toxicities. Grade 1, 2 and 3 hepatotoxicities were observed in 0.6, 2.5 and 1.3%, respectively. Baseline CD4 counts, viral loads and transaminases were similar in pregnant women with nevirapine adverse effects and those without reaction. Median absolute CD4 cell counts were 465.4 and 416.6 cells/µL in women with and without side effects, respectively (p=0.3). All patients who experienced hepatotoxicity had pretreatment CD4 counts superior to 250 cells/µL. CONCLUSIONS: The incidence of adverse events with nevirapine in our study was high, but most of them were cutaneous. There was no correlation between high CD4 counts and adverse events when analysing both cutaneous and hepatic reactions; nevertheless, hepatotoxicity occurred only in pregnant women with CD4 counts >250 cells/µL.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(9):484-489
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000900008
In Brazil, where 90% of the childbirths occur in hospitals, 67.1% of the cases of maternal death are due to direct obstetric causes, mainly hypertensive disorders, but a quarter of the deaths are due to indirect obstetric causes. As maternal death is a rare event, estimated in 76/100,000, the study of severe maternal morbidity, following international literature, can contribute to qualify obstetrical care. Maternal morbidity is a continuum that ends with death, but there is a separate group, with extreme severity, known as near miss. From the literature review, there are the difficulties to obtain an operational definition of the cases of extremely severe morbidity or near miss. The prevalence ranged from 0.80-8.23%, according to the defining criteria and health care provided at the region. The characterization of severe maternal morbidity and near miss allows for monitoring the process of obstetrical care and could help to qualify treatment of maternal urgencies and emergencies, interrupting the process that can lead to death.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(8):387-395
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000800002
PURPOSE: to identify the main maternal risk factors involved in early-onset neonatal sepsis, evaluating the risk associations between bacterial vaginosis and isolated microorganisms found in the maternal urine culture and in the newborn blood culture in the delivery room. METHODS: randomized longitudinal cohort study involving 302 mothers and their newborns. All neonates were followed up for seven days in order to diagnose sepsis. RESULTS: the outcomes were the following: 16 (5.3%) early-onset neonatal sepsis cases (incidence of 53 cases per 1,000 live births). The average number of prenatal appointments with a doctor was 5.2 (SD=1.8). The number of women with prenatal follow-up was 269 (89.1%), but only 117 (43.4%) of them went to six or more medical appointments, 90 (29.8%) had premature rupture of membranes before delivery, but only 22 (7.3%) had it for more than 18 hours. A total of 123 women (40.7%) complained of vaginal discharge, but only 47 (15.6%) of them had bacterial vaginosis, 92 (30.4%) complained of urinary infection, but only 23 (7.6%) of them had bacteriuria, two (0.7%) had fever at home, 122 (40.4%) received intra-partum antibiotic prophylaxis, 40 (13.2%) had premature delivery and 37 (12.3%) had low-birth-weight babies. Gestational age was a significant risk factor (RR=92.9; IC95%:12.6-684.7), as well as the number of prenatal appointments (RR=10,8; IC95%:1,4-80,8), fever (RR=10,0; IC95%:2,3-43,5), low-birth-weight (RR=21,5; IC95%:7,3-63,2) and early neonatal death (RR=89,4; IC95%:11,16-720,6). A significant difference of 5% was found in the comparison of the averages of lower number of prenatal appointments, prematurity and lower birth weight. CONCLUSIONS: the major microorganism isolated in the newborns’ blood culture was the Streptococcus agalactiae. Prematurity, lack of prenatal follow up and low birth weight were the risk factors more associated with early neonatal sepsis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(7):370-375
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000700008
Studies have shown possible risk relations among oral illnesses, mainly periodontal disease and adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as prematurity, low birth weight and preeclampsia. The explanation for this hypothesis is based on the fact that periodontal disease is an infectious state, which may increase maternal serum cytokines through the release of such agents directly from the periodontal pocket or by through the dissemination of pathogenic bacteria, inducing systemic production. This assumption is based on the knowledge that the physiopathology of the pregnancy complications cited above is associated with the presence of some cytokines in the maternal serum. The present study work has the objective to review literature in search of evidence to these alleged associations. Although a number of clinical studies have been found in this review, we noticed a lack of methodological standards, what limits the conclusions about this topic. On the other side, the fact that periodontal disease is not yet a confirmed risk factor for adverse pregnancy outcomes does not reduce the importance of oral health maintenance during pregnancy, since it is important to allow adequate feeding without pain and bleeding in order to maintain an adequate nutritional supply.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):19-24
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000100004
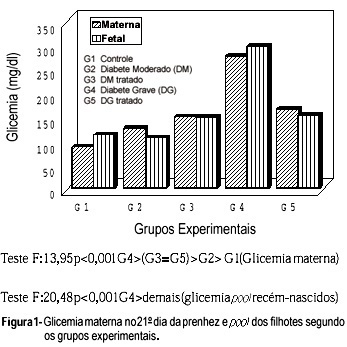
Fetal and placental effects of insulin therapy on pregnancy of diabetic rats were studied. Alloxan was administered intravenously at the dose of 42 mg/kg of body weight. Five experimental groups were formed: control (G1, n=12), non-treated rats with moderate diabetes (G2, n=10), insulin-treated rats with moderate diabetes (G3, n=11),non-treated rats with severe diabetes (G4, n=12) and insulin-treated rats with severe diabetes (G5, n=10). Six hundred and thirty-four newborn rats and placentas wereprocured. The perinatal result of insulin therapy was directly related to the quality of glycemia control. Thus, inadequate control of moderate diabetes produced levels of moderate hyperglycemia, did not interfere with the newborn rats' body weight and decreased the proportion of LGA newborn rats. Adequate control of severe diabetes brought the newborn rat glycemia to normal levels, increased the newborn rats' body weight and decreased the proportion of SGA newborn rats. Adequate insulin therapy for severe diabetes diminished the weight of the placentas, but did not change the placental index.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):237-243
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000500002
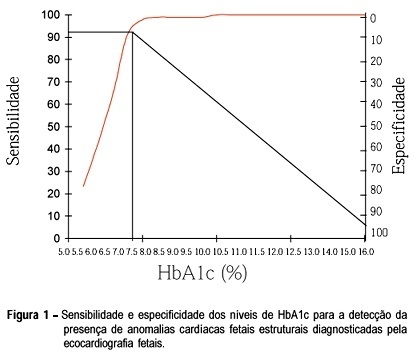
We analyze prospectively the existence of a relationship between the mother's glycemic control, in the first half of pregnancy, and the occurrence of abnormal fetal cardiac abnormalities, in pregnant women with diabetes mellitus. In 127 pregnant women, the level of glycosylated hemoglobin was determined on the first visit during prenatal care. Nine patients had type I diabetes, 77 type II and 41 gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). All mothers were submitted to detailed fetal echocardiography, during the 28th ± 4.127 week of gestation. In 31 (24.4%) of the 127 fetuses cardiac anomalies were detected. In 10 (7.87%) an isolated cardiac anomaly was identified. Mean HbA1c in the group of pregnant women without cardiac anomalies (5.64%) was statistically different from the group with anomalies (10.14%) (p<0.0001). The receiver-operator characteristic, representing the balance between sensitivity (92.83%) and specificity (98.92%) in the diagnosis of structural cardiac abnormalities, showed a cut-off point at the 7.5% HbA1c level. In nine of ten fetuses with structural cardiac anomalies, the maternal level of HbA1c was higher than 7.5%. The difference between means of the groups with and without myocardial hypertrophy diagnosed as isolated anomaly (MCHP) was not statistically significant, when considering both type II diabetes and GDM subgroups. In conclusion, levels of HbA1c higher than 7.5% were associated with most cases of echocardiographycally diagnosed structural cardiac anomalies. On the other hand, this test was not useful to discriminate conceptus with MCHP.