Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(9):470-479
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000900008
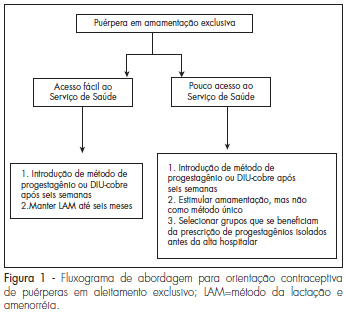
Adequate postpartum contraception is recommended in order to prevent mother and infant morbidity. The mother-infant benefits of lactation are well recognized, and exclusive, regular and frequent breastfeeding is an effective contraceptive method for amenorrheic patients. However, the resumption of fertility varies among women and access to health services is not guaranteed in many regions of the world. We searched the articles in Medline (PubMed) related to the subject published between 1971 to April 2008 and selected the most relevant articles in the literature about postpartum contraception. Short interpregnancy intervals increase maternal and fetal complications and therefore effective postpartum contraception is imperative. The ideal method prescribed should be effective and safe, id est, should not interfere with lactation or alter the hemostatic system. During the postpartum period, ideally non-hormonal methods should be used because they do not alter lactation or hemostasis. However, in populations with difficult access to health or with an early start of calorie supplementation to the newborn, the option should be for progestogens-only contraceptives, ideally initiated after six weeks or earlier in special situations.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(9):470-477
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000900006
PURPOSE: to assess the prevalence of the risk of post-partum depression in women in the post-natal ward of a hospital in São Paulo city, in the southeastern region of Brazil, and analyze the associated factors, including domestic violence (DV). METHODS: this was a descriptive, cross-sectional study. The participants were 133 women with at least 20 weeks of gestation age, who delivered their babies from August to September 2005 in a tertiary maternity in the city of São Paulo (Brazil). They were interviewed using the Portuguese version of the Abuse Assessment Screen for the diagnosis of violence and filled out a self-evaluation questionnaire for post-partum depression (Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale). Variables were presented as absolute and relative frequencies. The chi2 or Fisher exact tests were used to analyze possible associations between the variables of interest and post-partum depression. The value of 5% was considered significant. RESULTS: risk for post-partum depression was detected in 24 women (18%). A total of 38.3% of the participants interviewed had a history of abuse. There was an association between DV after they were 15 years old and risk of depression (p=0.036). The prevalence of abuse in the group of women at risk for post-partum depression was 58.3% and this was significantly higher than the 33.9% observed in the control group. CONCLUSIONS: the probability of presenting depression was high among the post-partum women attended at a tertiary maternity in the southeast of Brazil. The DV after they were 15 years old was significantly associated with risk of post-partum depression.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(5):260-266
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000500007
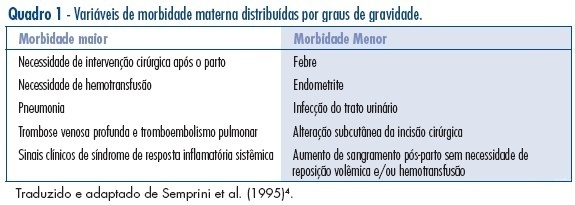
PURPOSE: to evaluate puerperal morbidity in HIV-infected and HIV non-infected puerperal women. METHODS: longitudinal and controlled study performed from July 2001 to September 2003, in 205 pregnant women admitted for birth delivery at Odete Valadares Maternity, divided in two groups: HIV-infected women (82) and HIV non-infected women (123). Postpartum morbidity evaluation was performed from birth delivery up to 15 days postpartum. Morbidity was categorized as minor (postpartum hemorrhage, fever and endometritis) or major (blood transfusion, deep alterations of the surgical wound and indication for surgical intervention), and was evaluated both according to the presence or absence of HIV infection and the mode of delivery. Continuous variables were analyzed by the Student’s t-test, and categorical variables were analyzed by chi2 and Fisher’s exact test using Epi-Info 2000 (CDC, Atlanta). RESULTS: puerperal morbidity was observed in 18 patients from the HIV group (22%) and in 17 patients from the control group (14%) with predominance of minor morbidity, without statistical significance, except for an increased risk of endometritis in the HIV group (RR=1.05; CI 95%:1.01-1.10). No significant difference was observed concerning the mode of delivery between the two groups. There were only two major morbidities: blood transfusion and necrotizing fasciitis. CONCLUSIONS: HIV-infected and non-infected puerperal women have a similar morbidity, despite the lower morbidity in the HIV non-infected group and the increased risk of endometritis in the HIV group. Clinical puerperium follow-up is a strategic control tool for an early identification of maternal morbidity.