-
Original Articles
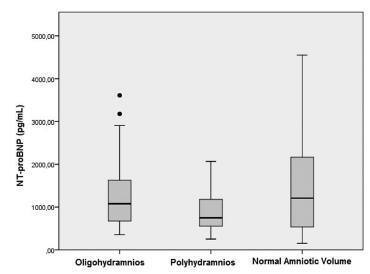
The Association between N-terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels in the Umbilical Vein and Amniotic Fluid Volume Abnormalities
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(4):177-182
04-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticlesThe Association between N-terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels in the Umbilical Vein and Amniotic Fluid Volume Abnormalities
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(4):177-182
04-01-2016Views125See moreAbstract
Purpose
The amniotic fluid volume (AFV) is known as a predictor for the wellness of a fetus. We aimed to investigate whether N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NTproBNP) levels reflect AFV abnormalities in otherwise normal fetuses.
Methods
We recruited 24 women with isolated oligohydramnios, 23 women with isolated polyhydramnios, and 36 women with normal AFV at a tertiary referral center. NT-proBNP levels in umbilical venous samples and the individual characteristics of the three groups were compared. One-way ANOVA and Kruskal-Wallis analysis of variance were used for multi-group comparisons of continuous variables. When a significant difference was detected, the Scheffe test was performed as a post-hoc analysis. Proportions were compared using the Chi-square (2) test.
Results
Maternal age, body mass indices, weight gained in pregnancy and NT-proBNP levels were similar among the three groups. Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes significantly correlated with NT-proBNP levels in all newborns (Spearman's r = 0.23 ; p = 0.03 and Spearman's r = 0.24; p = 0.02, respectively). The umbilical venous NTproBNP levels did not differ between newborns who needed mechanical ventilation and those who didn't (p = 0.595).
Conclusions
NT-proBNP is a biomolecule that may provide insights into the pathogenesis of fetal circulatory problems and subsequent renal failure. Further investigations are warranted.
-
Relato de Caso
Recurrent polyhydramnios management in an HIV-1 infected pregnant woman: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(3):241-245
07-05-2004
Summary
Relato de CasoRecurrent polyhydramnios management in an HIV-1 infected pregnant woman: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(3):241-245
07-05-2004DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000300011
Views87See moreThe reduction of mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) of the HIV-1 using zidovudine (ZDV) represents a cornerstone in the prenatal and obstetrical care to these patients. The invasive fetal and obstetric procedures are proscribed in HIV-1 infected pregnant patients, to avoid the increased risk of MTCT of this virus. The authors present a case of an HIV-1 infected woman with recurrent polyhydramnios. Four ultrasound-guided amniotic punctures were performed in the 23rd, 26th, 27th and 29th weeks of gestation, each one draining the respective volumes of 1,800, 1,450, 1,700 and 1,960 ml of clear amniotic fluid. The patient started preterm labor with 30 weeks and 5 days resulting in vaginal delivery of a male neonate weighing 1,690g and measuring 43cm. The baby presented a post natal diagnosis of a sodium-losing nephropathy and was submitted to three negative polymerase chain reaction tests for HIV-1. The authors point out that the option to manage cases of HIV-1 infected pregnancies that could need invasive obstetric procedures should be to give the patient 2 mg//kg of ZDV endovenously before the procedure, in order to avoid MTCT of HIV-1, as it has demonstrated good results in this case.


