-
Case Report
Limb Body Wall Complex Associated with Placenta Accreta: A Mere Coincidence or a Sign of an Etiopathogenic Link?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):142-146
03-01-2017
Summary
Case ReportLimb Body Wall Complex Associated with Placenta Accreta: A Mere Coincidence or a Sign of an Etiopathogenic Link?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(3):142-146
03-01-2017Views153See moreAbstract
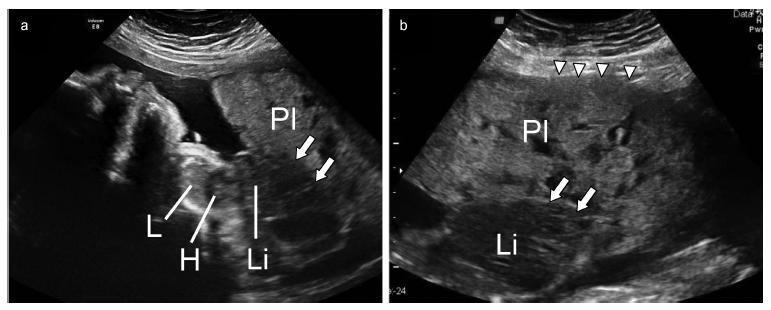
A case was reported of a fetus with the anomaly of limb body wall complex associated with placenta accreta. To date, only one account of this condition has been published in the world literature. Due to the low frequency of both complications, the hypothesis has been raised that this association may have happened not by mere coincidence, but rather by a possible common etiopathogenic mechanism. For the first time, a study proposes the existence of a possible etiopathogenic connection between the anomaly of limb body wall complex and hypoxic disorders caused by inadequate placentation in previous uterine scarring.
-
Artigos Originais
Value of magnetic resonance imaging in prenatal diagnosis of placental accretism
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(12):700-707
03-19-2006
Summary
Artigos OriginaisValue of magnetic resonance imaging in prenatal diagnosis of placental accretism
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(12):700-707
03-19-2006DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001200003
Views34See morePURPOSE: to establish the main signs of placental accretism in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in patients with clinical suspicion and to estimate the benefit of this method. METHODS: prospective transversal study with 15 patients suspected of placental accretism, referred between March 2003 and February 2006. Gestational age varied from 20 to 31 weeks. All patients underwent MRI to study the placenta and had previously done an ultrasonography. Material was sent to histological study. MRI was done on Magnetom Impact and Sonata Maestro Class Siemens®, with acquired sequences HASTE, TURBO SPIN in axial, sagittal, coronal planes and echo gradient (GE®), pre- and post-dynamic contrast in the best plan for acquisition. Images were analyzed by a team of two radiologists. RESULTS: mean gestational age was 24.3 weeks. We studied seven placenta previa (47%), six anterior placentas (40%) and two posterior placentas (13%). Ultrasonography was positive in 80% of the palcentas and MRI in 53%. However, echography had a low concordance with anatomic pathological studies by Kappa test (11%), revealing 75% of sensitivity, 14% of specificity, 50% as positive predictive value (PPV) and 33% as negative predictive value (NPV). MRI had an excellent concordance with anatomic pathological studies (0.86), showing 100% of sensitivity, 86% of specificity, 89% as PPV and 100% as NPV. CONCLUSIONS: MRI is useful for placental accretism diagnosis. The principal findings are transmural hyper-signal, the loss of continuity in myometrial wall in fast sequences and the identification of vessels invading myometrial layer in dynamic sequences.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Placenta Previa: Risk Factors for Accretion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(7):417-422
06-24-2001
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisPlacenta Previa: Risk Factors for Accretion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(7):417-422
06-24-2001DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000700002
Views67See morePurpose: to investigate risk factors associated with accretion in placenta previa (PP) patients. Methods: this was a retrospective case-control study of all the records of patients who delivered between 1986-1998 at Maternidade Escola de Vila Nova Cachoeirinha (São Paulo) with a diagnosis of placenta previa. The groups with and without accretion were compared regarding age, parity, previous history of miscarriage, curettage and cesarean section, type of PP and predominant area of placental attachment. Possible associations between the dependent (accretion) and independent (maternal and placental characteristics) variables were evaluated using the chi² test, univariate and multivariate analyses. Results: reviewing 245 cases of PP, two risk factors were significantly associated with accretion: central placenta previa (odds ratio (OR): 2.93) and two or more previous cesarean sections(OR: 2.54). Based on these data, a predictive model was constructed, according to which a patient with central PP and two more previous cesarean sections has a 44.4% risk for accretion. Conclusions: results of the current study may help obstetricians in the classification of their patients with PP in different risk categories for accretion. This could be useful in preparing for possible delivery complications in those patients considered at a higher risk for accretion.


