-
Original Articles
Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Brazilian Obstetricians Regarding Episiotomy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(11):636-646
12-20-2019
Summary
Original ArticlesKnowledge, Attitude and Practice of Brazilian Obstetricians Regarding Episiotomy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(11):636-646
12-20-2019Views106Abstract
Objective
To determine the prevalence of episiotomy and the factors associated with the knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP) of Brazilian obstetricians in relation to this procedure.
Methods
A KAP survey was conducted with obstetricians working in Brazil. An electronic form containing structured questions previously evaluated using the Delphi method was created in Google Docs and sent by e-mail. A multivariate logistic regression was performed to determine the principal factors associated with adequate KAP. For each dependent variable (knowledge, attitude and practice) coded as adequate (1 = yes; 0 = no), a multiple logistic regression model was developed. Binary codes (1 = yes and 0 = no) were assigned to every independent or predictor variables. Prevalence ratios (PRs) and their respective 95% confidence intervals (95%CIs) were calculated as measures of relative risk, at a significance level of 5%.
Results
Out of the 13 thousand physicians contacted, 1,163 replied, and 50 respondents were excluded. The mean episiotomy rate reported was of 42%. Knowledge was determined as adequate in 44.5% of the cases, attitude, in 10.9%, and practice, in 26.8% of the cases.
Conclusion
Most respondents had inadequate knowledge, attitudes and practices regarding episiotomy. Although some factors such as age, teaching, working in the public sector and attending congresses improved knowledge, attitude and practice, we must recognize that episiotomy rates remain well above what would be considered ideal. Adequate knowledge is more prevalent than adequate attitude or practice, indicating that improving knowledge is crucial but insufficient to change the outlook of episiotomies in Brazil.
Key-words attitudes in healthDeliveryEpisiotomyhealth knowledgeObstetricsPerineumpractices in healthSee more -
Original Article
Perineal Pain Management with Cryotherapy after Vaginal Delivery: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(7):325-332
07-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticlePerineal Pain Management with Cryotherapy after Vaginal Delivery: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(7):325-332
07-01-2016Views120See moreAbstract
Introduction
Systematic reviews that evaluate the perineal cryotherapy to reduce pain in the vaginal postpartum are inconclusive.
Purpose
To evaluate clinical effectiveness of cryotherapy in the management of humanized postpartum perineal pain and vaginal edema.
Methods
A double-bind randomized controlled clinical trial (UTN number: U1111- 1131-8433) was conducted in a hospital in Northeastern, Brazil.Women were included following humanized childbirth. All had vaginal deliveries of a single, full-term pregnancy with cephalic presentation. Exclusion criteria included previous perineal lesion, episiotomy during the current delivery, instrumental delivery, uterine curettage and postpartum hemorrhage. In the experimental group, an ice pack was applied six times on the perineum for 20 minutes, reducing the temperature between 10 and 15° C, then 60 minutes without exposure to cold. In the non-cryotherapy, a water bag unable to reduce the temperature to this extent was used, compliance with the same application protocol of the first group. Perineal temperature wasmonitored at zero, 10 and 20 minutes for application in both groups. Evaluations were made immediately before and after the applications and 24 hours after delivery spontaneous, to determine the association between variables.
Results
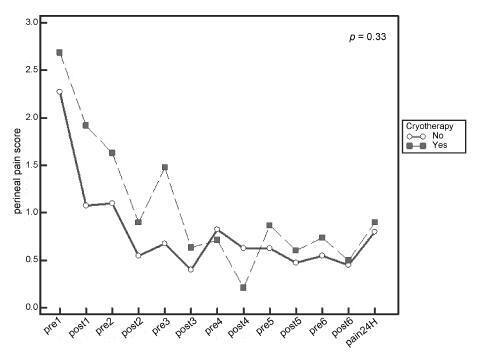
A total of 80 women were included in the study, 40 in each group. There was no significant difference in scores of perineal pain and edema between the groups with or without cryotherapy until 24 hours after childbirth. There was no difference between groups when accomplished repeated measures analysis over the 24 hours after delivery, considering the median perineal pain (p = 0.3) and edema (p = 0.9). Perineal cryotherapy did not influence the amount of analgesics used (p = 0.07) and no adverse effect was registered.
Conclusion
The use of cryotherapy following normal vaginal delivery within the concept of humanized minimally interventionist childbirth had no effect on perineal pain and edema, since it was already substantially lower, nor the need for pain medicaments.
-
Artigos Originais
Topographic modifications of the urethrovesical junction and proximal urethra after combined Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz and Burch surgery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(8):391-396
10-09-2009
Summary
Artigos OriginaisTopographic modifications of the urethrovesical junction and proximal urethra after combined Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz and Burch surgery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(8):391-396
10-09-2009DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000800004
Views119See morePURPOSE: to study the changes in the urethrovesical junction (UVJ) and in the proximal urethra (PU) caused by the Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz-Burch (MMK-B) combined surgery through perineal ultrasonography. METHODS: an interventional, longitudinal and prospective study has been conducted. Thirty-two women with stress urinary incontinence were submitted to perineal ultrasonography before and 30 days after surgery to evaluate the pubo-urethral distance (PUD), the proximal urethra length, the UVJ horizontal distance (UVJHD) and the UVJ vertical distance (UVJVD), the patient being at rest, and in effort during the Valsava manoeuvre. Results have been expressed in mean and standard deviation. The Student's t-test has been used to compare pre and postoperative results whenever the variables fulfilled the normality test criterion; otherwise, the Wilcoxon's paired test has been used. RESULTS: as compared with the preoperative measures, the Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz-Burch surgery has reduced the PUD at rest (14 mm x 4.3 mm) and during effort (20.8 mm x 6.4 mm); has reduced the UVJHD at rest (14 mm x 4.3 mm) and during effort (20.8 mm x 6.4 mm); has increased the PU length at rest (16.7 mm x 19.7 mm) and during effort (1.6 mm x 15.4 mm); and has increased UVJVD during effort (-5.4 mm x 14.8 mm), but has not changed it at rest (16.2 mm x 18.7 mm, p = 0.085). CONCLUSIONS: the Marshall-Marchetti-Krantz-Burch surgery has significantly reduced the urethrovesical junction vertical and horizontal mobility without raising the urethrovesical junction.
-
Artigos Originais
Relationship between perineal muscular force in the puerperal period and the type of delivery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(9):523-529
01-18-2006
Summary
Artigos OriginaisRelationship between perineal muscular force in the puerperal period and the type of delivery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(9):523-529
01-18-2006DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000900004
Views48See morePURPOSE: to determine the values of perineal muscular force (PMF) in the lying and seated positions and to identify the values of PMF between first pregnancy, according to type and the characteristics of the vaginal delivery and cesarean section. METHODS: study of the transversal type, performed in a maternity of Brazilian Public the Health System (SUS) in the city of São Paulo. The sample consisted of 95 primiparae at term. Evaluation occurred between the 40th and 45 th, day with an interview, physical examination and measurement of PMF using a perineometer of the Kegel type. The measurement was carried out in the lying and seated positions, muscular status (at rest and in maximum contraction), and the average of three measures for each position and muscular state were considered. RESULTS: 76.8% (73) of the women had vaginal delivery and 23.2% (22) cesarean section. After vaginal delivery, intact perineum in 18.9%, (18), perineal rupture in 24.2% (23), and episiotomy in 33.7% (32) were observed. Obtained values of the PMF were: lying position muscular rest 18. 9 mmHg, lying position maximum contraction: 30,7 mmHg, seated position muscular rest: 34.5 mmHg, seated positions maximum muscular contraction: 46.5 mmHg. CONCLUSION: there was association between the type and the characteristics of the delivery and PMF.
-
Artigos Originais
Evaluation of the synergy of the abdomino-pelvic musculature in nulliparouswomen with eletromyography and perineal biofeedback
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(4):210-215
07-30-2005
Summary
Artigos OriginaisEvaluation of the synergy of the abdomino-pelvic musculature in nulliparouswomen with eletromyography and perineal biofeedback
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(4):210-215
07-30-2005DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000400008
Views56See morePURPOSE: to verify the behavior of the abdominal and perineal musculature in respiratory changes induced in 15 nulliparous women without previous history of perineal or respiratory failures, with age ranging from 20 to 26 years (22.9±1.83). METHODS: the electrical abdominal and perineal activities were analyzed simultaneously through surface electromyography and perineal pressure (PP) obtained through digital biofeedback. The volunteers were told to accomplish three types of respiratory maneuvers: maximum inspiration (PImax), maximum expiration (PEmax) and Valsalva (VM), at random. The electromyographic signs were collected by the AqDados® (4.4) software for binary language ASCII, being processed later using the Matlab® (6.5.1) software. The statistical analysis of the envoltory (EN) of the signal was accomplished through Spearman correlation and Kruskal-Wallis test, and the level of significance was set at 5% (p<0.05). RESULTS: it was observed that PP was larger in PImax (2.98±2,38), followed by VM (29.10±10.68), both being overcome by PEmax (38.22±9,98) (p<0.01). A positive correlation between PEmax and PP (p<0.01), as well as between EN of the perineal and abdominal musculature in PEmax and PImax (p<0.05 and p=0,03, respectively) could be shown. The results regarding VM were not significant, when PP and EN were analyzed. CONCLUSION: it was possible to identify the presence of abdomino-pelvic synergy during the execution of breathing maneuvers, especially in relation to PEmax.


