Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):581-587
11-07-2019
To evaluate the association between the upright and supine maternal positions for birth and the incidence of obstetric anal sphincter injuries (OASIs).
Retrospective cohort study analyzed the data of 1,728 pregnant women who vaginally delivered live single cephalic newborns with a birth weight of 2,500 g. Multiple regression analyses were used to investigate the effect of the supine and upright positions on the incidence of OASIs after adjusting for risk factors and obstetric interventions.
In total, 239 (13.8%) births occurred in upright positions, and 1,489 (86.2%) in supine positions. Grade-III lacerations occurred in 43 (2.5%) patients, and grade-IV lacerations occurred in 3 (0.2%) women. Supine positions had a significant protective effect against severe lacerations, odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 0,47 [0.22- 0.99], adjusted for the use of forceps 4.80 [2.15-10.70], nulliparity 2.86 [1.44-5.69], and birth weight 3.30 [1.56-7.00]. Anesthesia (p<0.070), oxytocin augmentation (p<0.228), shoulder dystocia (p<0.670), and episiotomy (p<0.559) were not associated with the incidence of severe lacerations.
Upright birth positions were not associated with a lower rate of perineal tears. The interpretation of the findings regarding these positions raised doubts about perineal protection that are still unanswered.
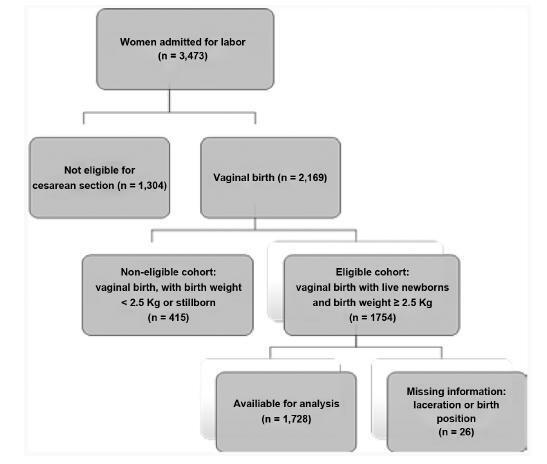
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):379-383
07-01-2018
Perineal trauma is a negative outcome during labor, and until now it is unclear if the maternal position during the second stage of labormay influence the risk of acquiring severe perineal trauma. We have aimed to determine the prevalence of perineal trauma and its risk factors in a low-risk maternity with a high incidence of upright position during the second stage of labor.
A retrospective cohort study of 264 singleton pregnancies during labor was performed at a low-risk pregnancymaternity during a 6-month period. Perineal trauma was classified according to the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (RCOG), and perineal integrity was divided into three categories: no tears; first/ second-degree tears + episiotomy; and third and fourth-degree tears. A multinomial analysis was performed to search for associated factors of perineal trauma.
From a total of 264 women, there were 2 cases (0.75%) of severe perineal trauma, which occurred in nulliparous women younger than 25 years old. Approximately 46% (121) of the women had no tears, and 7.95% (21) performed mediolateral episiotomies. Perineal trauma was not associated with maternal position (p = 0.285), health professional (obstetricians or midwives; p = 0.231), newborns with 4 kilos or more (p = 0.672), and labor analgesia (p = 0.319). The multinomial analysis showed that white and nulliparous presented, respectively, 3.90 and 2.90 times more risk of presenting perineal tears.
The incidence of severe perineal trauma was low. The prevalence of upright position during the second stage of labor was 42%. White and nulliparous women were more prone to develop perineal tears.