Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(8):439-446
10-09-2023
To evaluate the fetal and maternal effects of the severe acute respiratory syndrome virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in women with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
Patients with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction (PCR) positivity (n = 55) were compared with cases with similar characteristics and PCR negativity (n = 53). The study group was further divided into two groups as severe (n = 11) and nonsevere (n = 44) coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The groups were compared in terms of clinical characteristics and perinatal outcomes.
The study and control groups were similar in terms of maternal age, parity, gestational age at diagnosis, type of hypertensive disorders, magnesium sulfate administration rate, gestational age at birth, birth weight, Apgar scores, and maternal complications. However, all cases of fetal loss (n = 6) were observed in the SARS-CoV-2 positive group (p = 0.027). From the 6 cases, there were 5 in the nonsevere group and 1 patient in the severe SARS-CoV-2 positive group. Moreover, higher rates of maternal complications, lower oxygen saturation values, and intensive care unit admissions were observed in the severe COVID-19 group.
Physicians should be cautious about the management of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy cases with SARS-CoV-2 positivity. Fetal loss seems to be more common in cases with SARS-CoV-2 positivity and severe COVID-19 seems to be associated with higher rates of maternal complications. Close follow-up for fetal wellbeing and active management of severe cases in terms of maternal complications seem to be favorable.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1094-1101
03-24-2022
To assess maternal and neonatal outcomes in women with chronic kidney disease (CKD) at a referral center for high-risk pregnancy.
A retrospective cohort of pregnant women with CKD was followed at the Women's Hospital of Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Brazil, between 2012 and 2020. Variables related to disease etiology, treatment duration, sociodemographic variables, lifestyle, other associated diseases, obstetric history, and perinatal outcomes were assessed. The causes of CKD were grouped into 10 subgroups. Subsequently, we divided the sample according to gestational age at childbirth, as preterm and term births, comparing maternal and neonatal outcomes, and baseline characteristics as well as outcomes among such groups.
A total of 84 pregnancies were included, in 67 women with CKD. Among them, six pregnancies evolved to fetal death, five to miscarriage, and one was a twin pregnancy. We further analyzed 72 single pregnancies with live births; the mean gestational age at birth was 35 weeks and 3 days, with a mean birth weight of 2,444 g. Around half of the sample (51.39%) presented previous hypertension, and 27.7% developed preeclampsia. Among the preterm births, we observed a higher frequency of hypertensive syndromes, longer maternal intensive care unit (ICU) stay in the postpartum period, higher incidence of admission to the neonatal ICU, higher neonatal death, lower 5-minute Apgar score, and lower birth weight.
This study demonstrates increased adverse outcomes among pregnancies complicated by CKD and expands the knowledge on obstetric care among such women in an attempt to reduce maternal risks and identify factors related to prematurity in this population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):336-342
02-09-2022
To evaluate clinical characteristics, maternal and fetal outcomes in pregnant women who underwent surgery for adnexal torsion (AT).
All patients, who underwent surgical operation due to AT during pregnancy at the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, School of Medicine, Ege University between 2005 and 2020 were retrospectively investigated. Main clinical and perioperative outcomes were evaluated.
A total of 21 patients who underwent surgery due to AT during pregnancy were included. Of all patients, 61.9% underwent laparoscopy and the remaining 38.1% underwent laparotomy. The most common surgical procedure was adnexal detorsion in both groups (48%). Mean gestational age at the time of diagnosis, duration of surgery and hospitalization were significantly lower in the laparoscopy group, when compared with the laparotomy group (p=0.006, p=0.001, and p=0.001, respectively.) One of the patients had an infection during the postoperative period. Spontaneous abortion was only observed in one case.
It can be concluded that the surgical intervention implemented for the exact diagnosis and treatment of AT (laparotomy or laparoscopy) did not have an unfavorable effect on pregnancy outcomes such as abortion, preterm delivery, and fetal anomaly. However, laparoscopy may be superior to laparotomy in terms of advantages.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):811-819
01-12-2021
To investigate the characteristics of women who had preterm birth (PTB) and related outcomes according to ethnicity.
A secondary analysis of a multicenter cross-sectional study conducted in Brazil. Women who had PTB were classified by self-report as white and non-white. Clinical, pregnancy, and maternal data were collected through postpartum interviews and reviews of medical charts. The sociodemographic, obstetric and clinical characteristics of the women, as well as the mode of delivery and the neonatal outcomes among different ethnic groups were compared through a bivariate analysis.
Of the 4,150 women who had PTB, 2,317 (55.8%) were non-white, who were more likely: to be younger than 19 years of age (prevalence ratio [PR]: 1.05; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.01-1.09); to be without a partner; to live on low income; to have lower levels of schooling; to have ≥ 2 children; to perform strenuous work; to be fromthe Northeastern region of Brazil rather than the from Southern region; to have a history of ≥ 3 deliveries; to have an interpregnancy interval<12 months; to have pregnancy complications such as abortion, PTB, preterm premature rupture of membranes (pPROM), and low birth weight; to initiate antenatal care (ANC) visits in the second or third trimesters; to have have an inadequate number of ANC visits; to be under continuous overexertion; to smoke in the first and second or third trimesters; and to have anemia and gestational hypertension. The maternal and neonatal outcomes did not differ between the groups, except for the higher rate of low birth weight (73.7% versus 69.0%) in infants born to non-white women, and the higher rate of seizures (4.05% versus 6.29%) in infants born to white women.
Unfavorable conditions weremore common in non-whites than inwhites. Proper policies are required to decrease inequalities, especially in the context of prematurity, when women and their neonates have specific needs.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):820-825
01-12-2021
To compare maternal and perinatal risk factors associated with complete uterine rupture and uterine dehiscence.
Cross-sectional study of patients with uterine rupture/dehiscence from January 1998 to December 2017 (30 years) admitted at the Labor and Delivery Unit of a tertiary teaching hospital in Canada.
There were 174 (0.1%) cases of uterine disruption (29 ruptures and 145 cases of dehiscence) out of 169,356 deliveries. There were associations between dehiscence and multiparity (odds ratio [OR]: 3.2; p=0.02), elevated maternal body mass index (BMI; OR: 3.4; p=0.02), attempt of vaginal birth after a cesarian section (OR: 2.9; p=0.05) and 5-minute low Apgar score (OR: 5.9; p<0.001). Uterine rupture was associated with preterm deliveries (36.5 ± 4.9 versus 38.2 ± 2.9; p=0.006), postpartum hemorrhage (OR: 13.9; p<0.001), hysterectomy (OR: 23.0; p=0.002), and stillbirth (OR: 8.2; p<0.001). There were no associations between uterine rupture and maternal age, gestational age, onset of labor, spontaneous or artificial rupture of membranes, use of oxytocin, type of uterine incision, and birthweight.
This large cohort demonstrated that there are different risk factors associated with either uterine rupture or dehiscence. Uterine rupture still represents a great threat to fetal-maternal health and, differently from the common belief, uterine dehiscence can also compromise perinatal outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):736-742
12-17-2021
Thyroid diseases are the second most common endocrine disorders in the reproductive period of women. They can be associated with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), preterm delivery, low Apgar score, low birthweight (LBW) or fetal death. The aim of the present study is to explore thyroid dysfunction and its relationship with some poor perinatal outcomes (Apgar Score, low birthweight, and preterm delivery).
Dried blood spot samples from 358 healthy pregnant women were analyzed for thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), total thyroxine (TT4), and thyroglobulin (Tg). Neonatal data were collected upon delivery. Four groups were formed based on thyroid function tests (TFTs).
Of the 358 tested women, 218 (60.72%) were euthyroid. Isolated hypo thyroxinemia was present in 132 women (36.76%), subclinical hyperthyroidism in 7 women (1.94%), and overt hypothyroidism in 1 (0.28%). The perinatal outcomes IUGR (p = 0.028) and Apgar score 1 minute (p = 0.015) were significantly different between thyroid function test [TFT]-distinct groups. In the multiple regression analysis, TT4 showed a statistically significant inverse predictive impact on LBW (p < 0.0001), but a positive impact of Tg on LBW (p = 0.0351).
Thyroid hormones alone do not have a direct impact on neonatal outcomes, but the percentage of their participation in the total process cannot be neglected. Based on the regression analysis, we can conclude that TT4 and Tg can be used as predictors of neonatal outcome, expressed through birthweight and Apgar score. The present study aims to contribute to determine whether a test for thyroid status should become routine screening during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):207-215
05-24-2021
The evaluation of the available evidence on vertical transmission by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV)-2.
An electronic search was performed on June 13, 2020 on the Embase, PubMed and Scopus databases using the following search terms: (Coronavirus OR COVID-19 OR COVID19 OR SARS-CoV-2 OR SARS-CoV2 OR SARSCoV2) AND (vertical OR pregnancy OR fetal).
The electronic search resulted in a total of 2,073 records. Titles and abstracts were reviewed by two authors (WPM, IDESB), who checked for duplicates using the pre-established criteria for screening (studies published in English without limitation regarding the date or the status of the publication).
Data extraction was performed in a standardized way, and the final eligibility was assessed by reading the full text of the articles. We retrieved data regarding the delivery of the potential cases of vertical transmission, as well as themain findings and conclusions of systematic reviews.
The 2,073 records were reviewed; 1,000 duplicates and 896 clearly not eligible records were excluded. We evaluated the full text of 177 records, and identified only 9 suspected cases of possible vertical transmission. The only case with sufficient evidence of vertical transmission was reported in France.
The risk of vertical transmission by SARS-CoV-2 is probably very low. Despite several thousands of affected pregnant women, we have identified only one case that has fulfilled sufficient criteria to be confirmed as a case of vertical transmission. Well-designed observational studies evaluating large samples are still necessary to determine the risk of vertical transmission depending on the gestational age at infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(6):309-314
06-01-2017
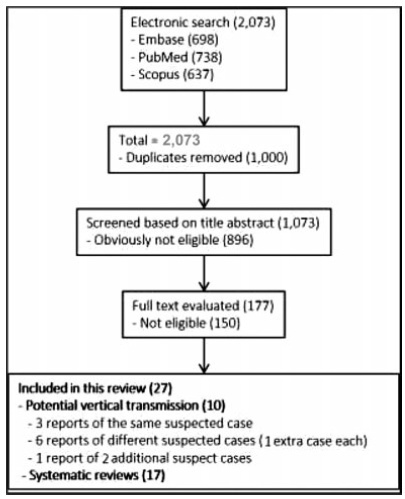
To describe the prenatal diagnosis of Galen vein aneurysm (GVA) based on ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in a series of cases, as well as its postnatal outcomes and follow-up until 4 years of age.
A retrospective longitudinal study was performed, analyzing a database comprising seven cases of prenatal diagnosis of GVA at two Brazilian institutions from February of 2000 to May of 2012. The following data were evaluated: gestational age at diagnosis, GVA dimensions on ultrasonography, associated fetal changes, findings on fetal echocardiography, gestational age at delivery, type of delivery, birth weight, Apgar score at the 1st and 5th minutes, neonatal outcomes, and survival with follow-up until 4 years of age.
The mean gestational age ± standard deviation on the prenatal diagnosis of GVA based on ultrasonography was 25±4.9 weeks. The mean length of GVA was 3.2±0.4 cm. The mean gestational age at birth was 37.5±0.7 weeks, and a cesarean section was performed in 85.7% of the cases (6/7). The mean birth weight was 3,070±240.4 g. The total survival rate was 42.8% (4/7), with three neonatal deaths. Of the four survivors, three presented with normal neuropsychomotor development until 4 years of age and only one showed serious neurological sequelae. Ultrasonography and MRI showed similar findings for all seven cases.
Galen Vein Aneurysm is associated with a high neonatal death rate. Therefore, its prenatal diagnosis is essential for parent counseling and follow-up at tertiary care institutions.