-
Original Article00-00-2024
Prevalence of colorectal symptoms and anal incontinence in patients with pelvic organ prolapse attended at an outpatient urogynecology service
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo10
Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of colorectal symptoms and anal incontinence in patients with pelvic organ prolapse attended at an outpatient urogynecology service
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo10
Views392See moreAbstract
Objective:
To analyze data of patients with symptomatic pelvic organ prolapse evaluated with PFDI20 and its subscales to report the prevalence of lower gastrointestinal symptoms and anal incontinence in the population of a public hospital and analyze its impact on quality of life.
Methods:
Cross-sectional study of patients with symptomatic POP. Patients were evaluated with demographic data, POP-Q, pelvic floor ultrasonography, urological parameters, and pelvic floor symptoms (PFDI-20), and quality of life (P-QoL) surveys. Patients were classified as CRADI-8 "positive" for colorectal symptoms, with responses "moderate" in at least 3 and/or "severe" in at least 2 of the items in the CRADI-8 questionnaires.
Results:
One hundred thirteen patients were included. 42.5% (48) were considered positive for colorectal symptoms on CRADI-8. 53.4% presented anal incontinence. No significant differences were found in sociodemographic variables, POP-Q stage, ultrasound parameters, or urological parameters. Positive patients had a significantly worse result in PFDI-20, POPDI (48 vs 28; p<0.001), UDI6 (51 vs 24; p<0.001), and in the areas of social limitation (44.4 vs 22.2; p = 0.045), sleep- energy (61.5 vs 44.4; p = 0.08), and severity (56.8 vs 43.7, p=0.015) according to P-QoL.
Conclusion:
Moderate or severe colorectal symptoms are seen in 40% of patients with symptomatic POP in our unit. Full evaluation of pelvic floor dysfunction symptoms should be performed routinely in urogynecology units.
-
Original Article12-11-2023
Efficacy of Sacrospinous Fixation or Uterosacral Ligament Suspension for Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Stages III and IV: Randomized Clinical Trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(10):584-593
Abstract
Original ArticleEfficacy of Sacrospinous Fixation or Uterosacral Ligament Suspension for Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Stages III and IV: Randomized Clinical Trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(10):584-593
Views169Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy and outcomes of the surgical treatment for pelvic organ prolapse (POP) in stages III and IV by sacrospinous ligament fixation (SSLF) or uterosacral ligament suspension (USLS) by comparing anatomical and subjective cure rates and quality-of-life parameters (through the version validated for the Portuguese language of the Prolapse Quality of Life [P-QoL] questionnaire) under two definitions: genital prolapse Ba, Bp, and C< −1 (stage I) and Ba, Bp, and C ≤ 0 (stage II).
Materials and Methods
After we obtained approval from the Ethics Committee (under CAAE 0833/06) and registered the study in ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT 01347021), 51 patients were randomized into two groups: the USLS group (N = 26) and the SSLF group (N = 25), with follow-up 6 and 12 months after the procedures.
Results
There was a significant improvement in the P-QoL score and anatomical measurements of all compartments in both groups after 12 months (p< 0.001). The anatomical cure rates in the USLS and SSLF groups, considering stage 1, were of 34.6% and 40% (anterior) respectively; of 100% both for groups (apical); and of 73.1% and 92% (posterior) respectively. The rates of adverse outcomes were of 42% (N = 11) and 36% (N = 11) for the USLS and SSLF groups respectively (p = 0.654), and those outcomes were excessive bleeding, bladder perforation (intraoperative) or gluteal pain, and urinary infection (postoperative), among others, without differences between the groups.
Conclusion
High cure rates in all compartments were observed according to the anatomical criterion (stage I), without differences in P-QoL scores and complications either with USLS or SSLF for the surgical treatment of accentuated POP.
Key-words patient health questionnairepatient-reported outcome measurespelvic floor disorderspelvic organ prolapsereconstructive surgical proceduresSee more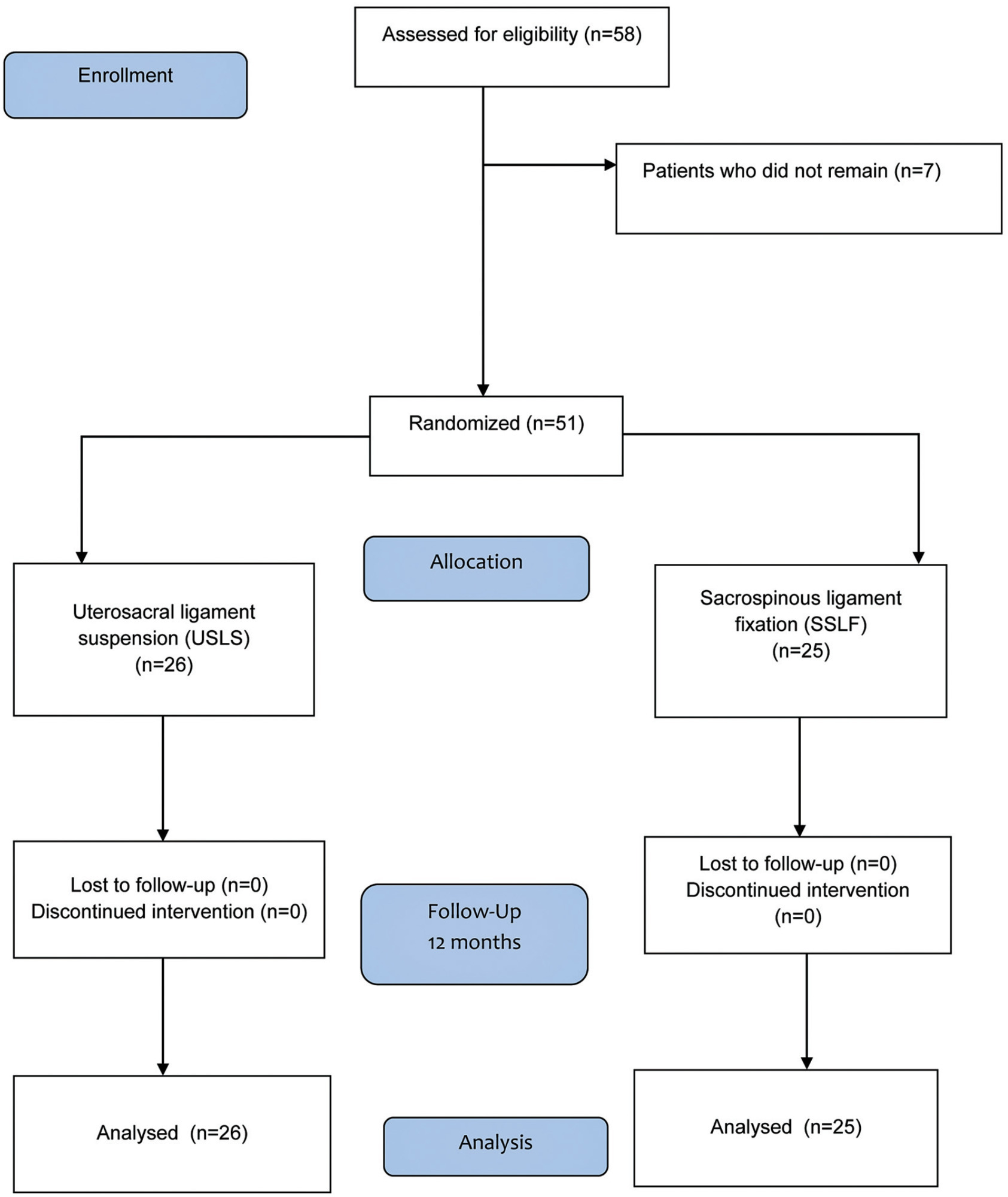
-
Case Report10-18-2021
Conservative Management of Spondylodiscitis after Laparoscopic Sacral Colpopexy: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):570-577
Abstract
Case ReportConservative Management of Spondylodiscitis after Laparoscopic Sacral Colpopexy: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):570-577
Views220See moreAbstract
Sacral colpopexy is one of the standard procedures to treat apical pelvic organ prolapse. In most cases, a synthetic mesh is used to facilitate the colposuspension. Spondylodiscitis is a rare but potentially serious complication that must be promptly diagnosed and treated, despite the lack of consensus in the management of this complication.We report one case of spondylodiscitis after a laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy and sacral colpopexy treated conservatively. We also present a literature review regarding this rare complication. A conservative approach without mesh removal may be possible in selected patients (stable, with no vaginal lesions, mesh exposure or severe neurologic compromise). Hemocultures and culture of imageguided biopsies should be performed to direct antibiotic therapy. Conservative versus surgical treatment should be regularly weighted depending on clinical and analytical progression. A multidisciplinary team is of paramount importance in the follow-up of these patients.
-
Original Article03-08-2021
Mid- to Long-Term Magnetic Resonance Imaging Results of Two Prolapse Surgeries for Apical Defect: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):46-53
Abstract
Original ArticleMid- to Long-Term Magnetic Resonance Imaging Results of Two Prolapse Surgeries for Apical Defect: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):46-53
Views181See moreAbstract
Objective
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been considered another tool for use during the pre- and postoperative periods of the management of pelvic-organ prolapse (POP). However, there is little consensus regarding its practical use for POP and the association betweenMRI lines of reference and physical examination.We aimedto evaluate the mid- to long-term results of two surgical techniques for apical prolapse.
Methods
In total, 40 women with apical POP randomized from 2014 to 2016 underwent abdominal sacrocolpopexy (ASC group; n = 20) or bilateral vaginal sacrospinous fixation with an anterior mesh (VSF-AM group; n = 20). A physical examination using the POP Quantification System (POP-Q) for staging (objective cure) and the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire-Vaginal Symptoms (ICIQ-VS: subjective cure), were applied and analyzed before and one year after surgery respectively. All MRI variables (pubococcigeous line [PCL], bladder base [BB], anorectal junction [ARJ], and the estimated levator ani subtended volume [eLASV]) were investigated one year after surgery. Significance was established at p < 0.05.
Results
After a mean 27-month follow-up, according to the MRI criteria, 60% of the women were cured in the VSF-AM group versus 45% in ASC group (p= 0.52). The POP-Q and objective cure rates by MRI were correlated in the anterior vaginal wall (p= 0.007), but no correlationwas foundwith the subjective cure. The eLASVwas largeramongthe patients with surgical failure, and a cutoff of ≥ 33.5mm3 was associated with postoperative failure (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve [ROC]: 0.813; p= 0.002).
Conclusion
Both surgeries for prolapse were similar regarding theobjective variables (POP-Q measurements and MRI cure rates). Larger eLASV areas were associated with surgical failure.
-
Original Article04-15-2019
Association between col1a2 Polymorphism and the Occurrence of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(1):31-36
Abstract
Original ArticleAssociation between col1a2 Polymorphism and the Occurrence of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(1):31-36
Views189See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the rs42524 polymorphism of the procollagen type I alpha (α) 2 (COL1A2) gene as a factor related to the development of pelvic organ prolapse (POP) in Brazilian women.
Methods
The present study involved 112 women with POP stages III and IV (case group) and 180 women with POP stages zero and I (control group). Other clinical data were obtained by interviewing the patients about their medical history, and blood was also collected from the volunteers for the extraction of genomic DNA. The promoter region of the COL1A2 gene containing the rs42524 polymorphism was amplified, and the discrimination between the G and C variants was performed by digestion of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products with the MspA1I enzyme followed by agarose gel electrophoresis analysis.
Results
A total of 292 women were analyzed. In the case group, 71 had the G/G genotype, 33 had the G/C genotype, and 7 had the C/C genotype. In turn, the ratio in the control group was 117 G/G, 51 G/C, and 11 C/C. There were no significant differences between the groups.
Conclusion
Our data did not show an association between the COL1A2 polymorphism and the occurrence of POP.
-
Original Article04-01-2017
Can the Pessary Use Modify the Vaginal Microbiological Flora? A Cross-sectional Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):169-174
Abstract
Original ArticleCan the Pessary Use Modify the Vaginal Microbiological Flora? A Cross-sectional Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):169-174
Views255See moreAbstract
Introduction
Vaginal pessary is used as a conservative treatment for pelvic organ prolapse (POP). Some studies have shown that common complaints of its use may include vaginal discomfort and increased vaginal discharge. Scant information is available about the microflora status after using this device.
Objective
To determine if the usage of vaginal pessary can interfere with the vaginal environment.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was performed from March of 2014 to July of 2015 including 90 women with POP. The study group was composed of 45 women users of vaginal pessary and 45 nom-users. All enrolled women answered a standardized questionnaire and were subjected to a gynecological exam to collect vaginal samples for microbiological evaluation under optic microscopy. Clinical and microbiological data were compared between study and control groups.
Results
Vaginal discharge was confirmed in 84% of the study group versus 62.2% in the control group (p< 0.01); itching was reported in 20 and 2.2%, respectively (p< .05); genital ulcers were only found in the pessary group (20%). There was no difference with regard to the type of vaginal flora. Bacterial vaginosis was prevalent in the study group (31.1% study group versus 22.2% control group), (p=.34).
Conclusion
Women using vaginal pessaries for POP treatment presented more vaginal discharge, itching and genital ulcers than non-users.


