Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):596-601
To investigate the clinical and sonographic parameters associated with adverse fetal outcomes in patients with congenital parvovirus B19 infection managed by intrauterine transfusion.
This was a single-center retrospective study conducted from January 2005 to December 2016 that assessed patients with singleton pregnancies with fetal parvovirus infection confirmed by a polymerase chain reaction of the amniotic fluid or fetal blood samples who underwent at least one intrauterine transfusion. The maternal characteristics, sonographic findings and parameters related to intrauterine transfusion were compared between the two groups (recovery/non-recovery), who were categorized based on fetal response after in-utero transfusions. Progression to fetal death or delivery without fetal recovery after the transfusions was considered nonrecovery and categorized as an adverse outcome.
The final analysis included ten singleton pregnancies: seven of which were categorized into the recovery group and three of which into the non-recovery group. The baseline characteristics were similar between the groups. All fetuses were hydropic at the time of diagnosis. No significant differences related to sonographic or intrauterine transfusion parameters were identified between the groups; however, the nonrecovery group tended to have an increased number of sonographic markers and lower fetal hemoglobin and platelet levels before the transfusion.
We were unable to firmly establish the clinical or sonographic parameters associated with adverse fetal outcomes in patients with parvovirus infection managed with intrauterine transfusions; however, edema, placental thickening and oligohydramnios may indicate greater fetal compromise and, subsequently, adverse outcomes. However, further studies are necessary, mainly due to the small number of cases analyzed in the present study.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):47-49
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000100008
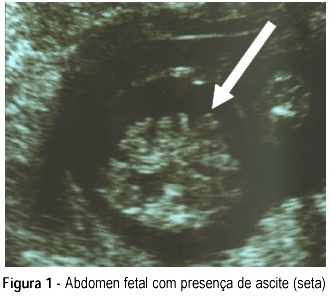
We report a case in which there was spontaneous regression of hydrops fetalis. Hydrops was probably caused by fetal infection with parvovirus B19. Anemia and hypokinesia of the heart were also observed. Diagnosis was accomplished by the ultrasound, virus detection in maternal serum, complete fetal blood count, and analysis of hepatic enzymes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(5):317-321
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000500003
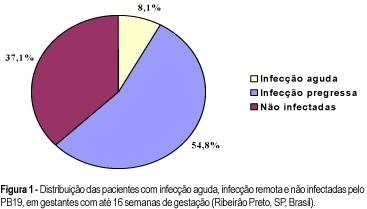
PURPOSE: to evaluate the rate of seropositivity for parvovirus B19 (PB19) among pregnant women and the rate of seroconversion against this infection during pregnancy. METHODS: prospective study carried out in the Hospital of the Medical School of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo. In the first stage of the present study, we evaluated 245 pregnant women with gestational age less than 16 weeks to determine the seroprevalence of PB19 infection by ELISA. According to the serological results we determined if the PB19 infection was an acute infection (IgM positive and IgG negative or positive), or a former infection (IgM negative and IgG positive). In the second stage of this study, 73 previously seronegative pregnant women were tested again when they came to the hospital for delivery (IgM and IgG), to detect the seroconversion rate during pregnancy. RESULTS: the seroprevalence of the PB19 infection until 16 weeks of gestation was 62.9% (95% IC: 56.8-68.9), divided into acute infection (8.1%), or former infection (54.8%). Of the 73 patients, seronegative in the first stage of this investigation, seven (9.6%) showed seroconversion during pregnancy (95% IC: 2.8-16.3), two (2.7%) showed acute serological infection and five (6.9%) presented markers of past infection. The final seroprevalence of PB19 infection during pregnancy was 72.5%. CONCLUSIONS: considering that only the acute PB19 infection is associated with risk for vertical transmission, the high seroprevalence of this infection observed in this study would be protecting these fetuses against this form of infection. Despite the relatively high rate of seroconversion against PB19 infection during the pregnancy period, we did not observe any symptomatic neonate in this group.