-
Original Article
Clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo91
12-04-2024
Summary
Original ArticleClinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo91
12-04-2024Views155See moreAbstract
Objective:
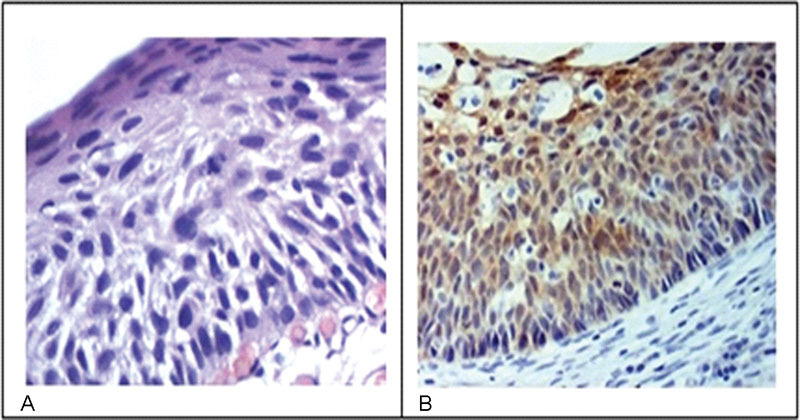
The average age of patients with vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) has been reported to have declined. Human papilloma virus (HPV)-related lesions have been shown to be associated with the expression of the immunohistochemical (IHC) marker p16. Non-HPV-related tumors have been characterized by p53 abnormal expression and PDL1 expression. We aimed to evaluate the correlation between these markers and vulvar SCC and to relate it to the clinical and pathological characteristics.
Methods:
Histopathologic assessments and IHC analyses of p16, p53, and PDL1 were performed in 41 samples of vulvar SCC collected between 2016 and 2021. The data were correlated with clinical and pathological characteristics of the patients.
Results:
The mean age of the patients was 72.1 years. Positive p16 and PDL1 staining was detected in 24.4% and 17.1% of the samples, respectively. p53 expression was negative in 19.5% of the samples, whereas it was overexpressed in 24.4%. p16-positive tumors showed a smaller depth of invasion (DOI) (p = 0.014), while tumors with p53 abnormal expression showed greater DOI (p = 0.041). PDL1 expression was correlated with increased number of inflammatory cells (p = 0.055). In addition, lesions with lymphovascular space invasion were p16-negative.
Conclusion:
In our sample, regarding to the SCC incidence the patients’ mean age did not change. The expression of p16 was inversely correlated with p53 results. Tumors with p53 abnormal expression and absence of p16 showed a greater DOI. Our data suggest an association between PDL1 expression and increased inflammatory infiltrates in vulvar SCC.
-
Original Articles
Expression of the Immunohistochemical Markers p16 and Ki-67 and Their Usefulness in the Diagnosis of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasms
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):82-87
02-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticlesExpression of the Immunohistochemical Markers p16 and Ki-67 and Their Usefulness in the Diagnosis of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasms
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):82-87
02-01-2016Views118See moreObjective
The aim of this study was to determine the expression of the immunohistochemical markers p16 and Ki-67 in cervical intraepithelial neoplasms and their influence on the level of agreement among different observers and for the same observer.
Methods
The study included 184 patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasms previously confirmed through biopsies performed between 2005 and 2006. Three pathologists reviewed the biopsies by using hematoxylin-eosin staining to reach a consensus on the diagnosis. Subsequently, an immunohistochemical study analyzed the expression of p16 and Ki-67 in such cases.
Results
The comparison among the reviewing pathologists revealed only moderate agreement (kappa = 0.44). The agreement improved when the differentiation of highgrade lesions (cervical intraepithelial neoplasm - CIN - 3) was analyzed (kappa = 0.59). p16 staining exhibited a high negative predictive value and sensitivity; however, the specificity was low. Overall, both qualitative and quantitative analyses of p16 and a quantitative analysis Ki-67 exhibited low accuracy. The agreement among diagnoses before immunohistochemistry was 0.47. The use of immunohistochemistry increased the agreement to 0.68.
Conclusion
Our study showed that the agreement among observers using traditional diagnostic criteria of cervical intraepithelial lesions can improve with the use of immunohistochemistry.