-
Review Article
Morphology and Biochemistry of Ovulation Morfologia e bioquímica da ovulação
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):480-486
07-27-2021
Summary
Review ArticleMorphology and Biochemistry of Ovulation Morfologia e bioquímica da ovulação
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):480-486
07-27-2021Views240See moreAbstract
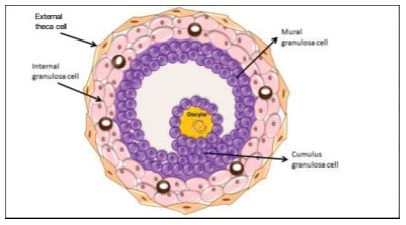
The process of ovulation involves multiple and iterrelated genetic, biochemical, and morphological events: cessation of the proliferation of granulosa cells, resumption of oocyte meiosis, expansion of cumulus cell-oocyte complexes, digestion of the follicle wall, and extrusion of the metaphase-II oocyte. The present narrative review examines these interrelated steps in detail. The combined or isolated roles of the folliclestimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) are highlighted. Genes indiced by the FSH genes are relevant in the cumulus expansion, and LH-induced genes are critical for the resumption ofmeiosis and digestion of the follicle wall. A nonhuman model for follicle-wall digestion and oocyte release was provided.
-
Original Articles
Variability of Three-dimensional Automatic Ovarian Follicle Count in Menstrual Cycle
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):35-40
01-01-2016
Summary
Original ArticlesVariability of Three-dimensional Automatic Ovarian Follicle Count in Menstrual Cycle
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):35-40
01-01-2016Views136See moreObjective
To evaluate the variability of three-dimensional automatic counts of ovarian follicles measuring 2-6 to 2-10 mm during the menstrual cycle and to determine if this test can be applied outside the early follicular phase of the menstrual cycle.
Methods
in a prospective observational study, serial transvaginal ultrasound scans were performed from April 20, 2013, to October 30, 2014, on infertile patients. Inclusion criteria: age between 18 and 35 years, BMI 18-25 kg/m2, regular menstrual cycles, no history of ovarian surgery and no hormonal changes in TSH, prolactin, fasting insulin or glucose. We excluded patients with ovarian cysts or who did not complete one or more days of the serial transvaginal ultrasound scans. The follicle count was performed in 3D mode ultrasound with a Sono AVC system. Visits were scheduled for the early follicular, mid-follicular, periovulatory and luteal phases of the menstrual cycle.
Results
Forty-five women were included. The Friedman test showed that the total number of follicles measuring 2-6 mmvaried significantly (p = 0.001) across the four periods of the menstrual cycle. The Paired Student t-test showed a significant increase in 2-6 mm follicle count from the mid-follicular and periovulatory phase to the luteal phase. We found no significant intra-cycle variation between the small follicles (2-6 mm) in the early follicular, mid-follicular and periovulatory phases. The Friedman test showed that the total number of follicles measuring 2-10 mm varied significantly (p = 0.003) across the menstrual cycle.
Conclusions
The variation of three-dimensional automatic counts of 2-6 mm follicles in the early follicular, mid-follicular and periovulatory phases was not statistically significant. The significant variability in the counts of follicles measuring 2-10 mm across the menstrual cycle does not permit this examination to be performed side the early follicular phase.
-
Artigos Originais
Number of antral follicles and the success of in vitro fertilization: a multivariate analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):473-479
09-23-2014
Summary
Artigos OriginaisNumber of antral follicles and the success of in vitro fertilization: a multivariate analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):473-479
09-23-2014DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005046
Views85See morePURPOSE:
To determine whether the antral follicle count can predict the number of retrieved oocytes in patients undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) and to correlate it with maternal age and pregnancy rate.
METHODS:
This was a retrospective observational study based on a review of medical records from 193 patients who underwent assisted reproduction techniques between September 2010 and September 2012 in a Clinic for Human Reproduction. The study included women indicated for IVF who had follicle-stimulating hormone levels below 10 mIU/mL on third day of the menstrual cycle, with oocyte recipients being excluded. The patients were divided into three groups according to the number of antral follicle (up to 10 follicles, 11–22 follicles, and 23 or more follicles). To compare these three groups with the group of patients who became pregnant, patients who had not developed oocytes and had not undergone embryo transfer were also excluded. Spearman's correlation coefficient was used to measure the level of association between the numerical variables, and χ2 test was used to compare pregnancy rates with antral follicle count. To assess the likelihood of pregnancy, we used multivariate logistic regression, with the level of significance set at 5%.
RESULTS:
The pregnancy rate of the sample was 35.6%. There was a positive significant correlation (sc) between antral follicle count and number of retrieved oocytes (sc=0.5; p<0.05) and a negative correlation between antral follicle count and age (sc= -0.5; p<0.05). There was no significant difference (p=0.16) when groups with different numbers of follicles were compared to the positive pregnancy test group; however, a cutoff of 27 antral follicles was observed in multivariate analysis, after which the probability of successful gestation tended to remain constant.
CONCLUSIONS:
The antral follicle count decreases over the years, is a predictor of the number of retrieved oocytes and can predict the likelihood of the success of in vitro fertilization.
-
Artigos Originais
Morphology of the interstitial cells of rat polycystic ovaries: an experimental study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(7):323-328
08-28-2012
Summary
Artigos OriginaisMorphology of the interstitial cells of rat polycystic ovaries: an experimental study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(7):323-328
08-28-2012DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000700006
Views138See morePURPOSES: To evaluate the histomorphometry of ovarian interstitial cells, as well as the blood sex steroid concentrations of female rats with polycystic ovaries induced by continuous light. METHODS: Twenty female rats were divided into two groups: Control Group - in the estrous phase (CtrlG), and a group of rats with polycystic ovaries induced by continuous illumination (POG). CtrlG animals were maintained on a light period from 07:00 a.m. to 07:00 p.m., and POG animals with continuous illumination (400 Lux) for 60 days. After this period all animals were anesthetized and blood was collected for the determination of serum estradiol (E2), progesterone (P4), and testosterone (T), followed by removal of the ovaries that were fixed in 10% formalin and processed for paraffin embedding. Five-µm histological sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and used for histomorphometric analysis. Morphological analyses, cyst count, determination of concentration and of the nuclear volume of interstitial cells were performed with the aid of a light microscope adapted to a high resolution camera (AxioCam), whose images were transmitted to and analyzed by the computer using AxioVision Rel 4.8 software (Carl Zeiss). Data were analyzed statistically by the Student's t-test (p<0.05). RESULTS: Morphological analysis showed the presence of ovarian cysts in POG animals and corpora lutea in CtrlG animals, as well as evidence of the origin of interstitial cells from the internal theca of these cysts. POG animals presented increased serum estradiol levels (pg/mL) compared to CtrlG animals (POG=124.9±4.2>CtrlG=73.2±6.5, p<0.05), the same occurring with testosterone levels (pg/mL) (POG=116.9±4.6>CtrlG=80.6±3.9, p<0.05). However, progesterone levels (ng/mL) were higher in CtrlG than in POG animals (CtrlG=16.3±2.0>POG=4.2±1.5, p<0.05). Morphometry showed a significant increase in nuclear volume in POG animals (POG=102.1±5.2>CtrlG=63.6±16.5, p<0.05), as well as in the area occupied (%) by interstitial cells (POG=24.4±6.9>CtrlG=6.9±3.2, p<0.05) compared to CtrlG animals. CONCLUSION: The interstitial cells of the rat polycystic ovary probably originate from ovarian cysts due to the degeneration of granulosa cells and differentiation of the internal theca cells. The elevations of serum testosterone and estradiol were probably due to the significant increase in cell activity and in the area occupied by interstitial cells.
-
Artigos Originais
Correlation between age and antral follicles count in infertile women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(4):184-188
05-11-2012
Summary
Artigos OriginaisCorrelation between age and antral follicles count in infertile women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(4):184-188
05-11-2012DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000400008
Views120PURPOSE: To produce age-related nomograms for ovarian antral follicle count (AFC) in infertile women. METHODS: It was done a cross-sectional study of patients attended in the center of assisted reproduction Fêmina, from March 2010 to October 2011. The patients were submitted to transvaginal ultrasonography from day 2 to day 4 of their menstrual period. Patients included were between 21 to 45 years old, with regular menses, two healthy ovaries, without any evidence of endocrinopathies and who gave written informed consent. Patients excluded were smokers, with galactosemia or ovarian cysts, with antecedents of liver disease, ovarian surgeries or who were treated with chemotherapy or radiotherapy. In order to check the evolution of the AFC in relation to patient age, we used the 5th, 25th, 50th, 75th and 95th percentiles. Linear regression was carried out using these percentiles, permitting us to determine the effect of age on the CFA. RESULTS: A total of 172 patients with a mean age of 32.7 years were included in the trial. The male and tubal factors were the main causes of infertility, accounting for 65% of cases. The age-related nomogram for the 5th, 25th, 50th, 75th and 95th percentiles of AFC revealed that changes were best fitted by a linear function. The percentiles that showed the highest correlations were 25 (r=-0.9; p<0.001), 50 (r=-0.9; p<0.001) and 75 (r=-0.9; p<0.001). CONCLUSION: A nomogram was constructed correlating age with the different AFC percentiles in infertile women without endocrinopathies. This showed a linear pattern of decline in AFC with age in all percentiles. These nomograms could provide a reference guide for the clinician. However, future validation, with longitudinal data, still is needed.
Key-words Age factorsfemaleFollicle stimulating hormoneInfertilityNomogramsOvarian follicleUltrasonographySee more -
Artigos Originais
Evidence of follicle responsiveness to FSH by antimüllerian hormone in ovulating women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(3):142-147
06-08-2009
Summary
Artigos OriginaisEvidence of follicle responsiveness to FSH by antimüllerian hormone in ovulating women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(3):142-147
06-08-2009DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000300007
Views62See morePURPOSE: to test the hypothesis that the anti-müllerian hormone (AMH) serum level reflects the antral follicles' response to the administration of FSH. METHODS: prospective study, including 116 normo-ovulatory infertile patients submitted to controlled ovarian hyperstimulation with GnRH and FSH agonists. The AMH serum level was measured after reaching the pituitary suppression and before the FSH administration (basal day). The number of antral follicles was determined by ultrasonography at the basal day (precocious antral follicles; 2 to 8 mm) and at the day of hCG administration (dhCG; pre-ovulatory follicles; >16 mm). The follicle response to FSH was determined by the percentage of precocious antral follicles which reached pre-ovulatory stage in response to FSH (maturation rate). The correlation of AMH with the patients' age, the total number of precocious antral and pre-ovulatory follicles, collected oocytes, total dose of FHS in the controlled ovarian stimulation and the rate of follicular maturation was studied. For the statistical analysis, it simple regression analysis and the Spearman's test were used, at a 5% significance level. RESULTS: The serum level of AMH was positively correlated with the number of precocious antral follicles at the basal day (r=0.64; p<0.0001) and pre-ovulatory follicles in dhCG (r=0.23; p=0.01). Exceptionally, the serum level of AMH was negatively correlated with the maturation ratio (r=-0.24; p<0.008). CONCLUSIONS: AMH attenuates the follicular development caused by FSH administration.
-
Artigos Originais
Use of antral follicle count to predict the response pattern in controlled ovarian hyperstimulation cycles with GnRH antagonist
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):36-41
04-08-2008
Summary
Artigos OriginaisUse of antral follicle count to predict the response pattern in controlled ovarian hyperstimulation cycles with GnRH antagonist
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(1):36-41
04-08-2008DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000100007
Views134PURPOSE: to establish whether there is a predictive relationship between the antral follicle count (AFC) on the second day of the cycle and the response pattern in controlled ovarian hyperstimulation cycles for intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). METHODS: a prospective study developed from May 2004 to May 2005, in which 51 patients aged <37 years old were submitted to assisted reproduction/ICSI in ovarian hyperstimulation protocol with gonadotropin recombinant and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist. A transvaginal ultrasonography was performed on the second day of the cycle, to count the number of follicles measuring 2 to 10 mm, at the beginning of stimulus, data compared with the number of follicles with >15 mm on the day of ovulation triggering, the total number of oocytes retrieved and in metaphases II, the number of good quality embryos transferred and pregnancy rate. The statistical analysis was performed by the t-Student test and the Mann-Whitney test, with statistical significance of 5% (p<0.05). RESULTS: the mean age in the study group was 32.4 years. The AFC average was 7.1, minimum of 1 and maximum of 16. Considering AFC as a main variable, a significant direct correlation was observed with the number of follicles >15 mm on the day of ovulation triggering (p=0.0001), the total number of oocytes retrieved (p=0.0001) and those in metaphases II (p=0.0001). Such correlation between AFC and pregnancy was not observed (p=0.43). There was no significant correlation between AFC and the number of good quality embryos transferred (p=0.081). CONCLUSIONS: AFC on the second day of the stimulated cycle can be used to predict the quality of ovarian stimulation, the number of oocytes retrieved and the number of mature oocytes in in vitro fertilization cycles using GnRH antagonist.
Key-words Gonadotropin-releasing formoneOvarian follicleOvulation InductionSperm injections, intracytoplasmicSee more -
Artigos Originais
Follicular density evaluation in ovaries of human fetuses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):614-618
03-13-2007
Summary
Artigos OriginaisFollicular density evaluation in ovaries of human fetuses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(12):614-618
03-13-2007DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001200003
Views90See morePURPOSE: to determine the variation of the number of ovarian follicles during fetal life. METHODS: twelve ovaries donated for research were included in our study, nine from fetuses and three from newborn babies who died in the first hour after being delivered with 39 weeks of pregnancy. Fetal age was confirmed both by the last menstrual period of the woman and by ultrasonography. Ovaries were fixed in formaldehyde, included in paraffin and serially sliced at 7 mm. At every 50 cuts, the obtained material was haematoxilin-eosin stained and evaluated with an optical microscope (400 X). The follicles were counted in ten different regions of the ovarian cortex, each region with an area of 625 mm². The presence of a nucleus was considered the parameter for counting. Follicular density, per 1 mm³ was calculated using the formula Nt=(No x St x t)/do, where Nt is the number of follicles; No is the mean number of follicles in 1 mm²; St is the total number of slices in 1 mm³; t is the slice thickness and do is the nuclei mean diameter. RESULTS: the gestational age of fetuses ranged from 24 to 39 weeks. The number of follicles per 0.25 mm² ranged from 10.9 ± 4.8 in a newborn to 34.7 ± 10.6 in another newborn. Among the fetuses, the least value was obtained in a 36 week-old fetus (11.1 ± 6.2) and the highest in a 28 week-old fetus (25.3 ± 9.6). The total number of slices per ovary ranged from six to 13, corresponding to follicles counted in areas from 15 to 32.5 mm². The total number of follicles ranged from 500,000 at the age of 22 weeks to > 1,000,000 at the age of 39 weeks. CONCLUSIONS: our results demonstrate different (increasing) densities of ovarian follicles along the gestational period, providing more knowledge about this still not well-known subject.


