Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):780-789
01-11-2023
To compare the patterns of systemic inflammatory response in women with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) or no evidence of malignant disease, as well as to evaluate the profile of systemic inflammatory responses in type-1 and type-2 tumors. This is a non-invasive and indirect way to assess both tumor activity and the role of the inflammatory pattern during pro- and antitumor responses.
We performed a prospective evaluation of 56 patients: 30 women without evidence of malignant disease and 26 women with EOC. The plasma quantification of cytokines, chemokines, and microparticles (MPs) was performed using flow cytometry.
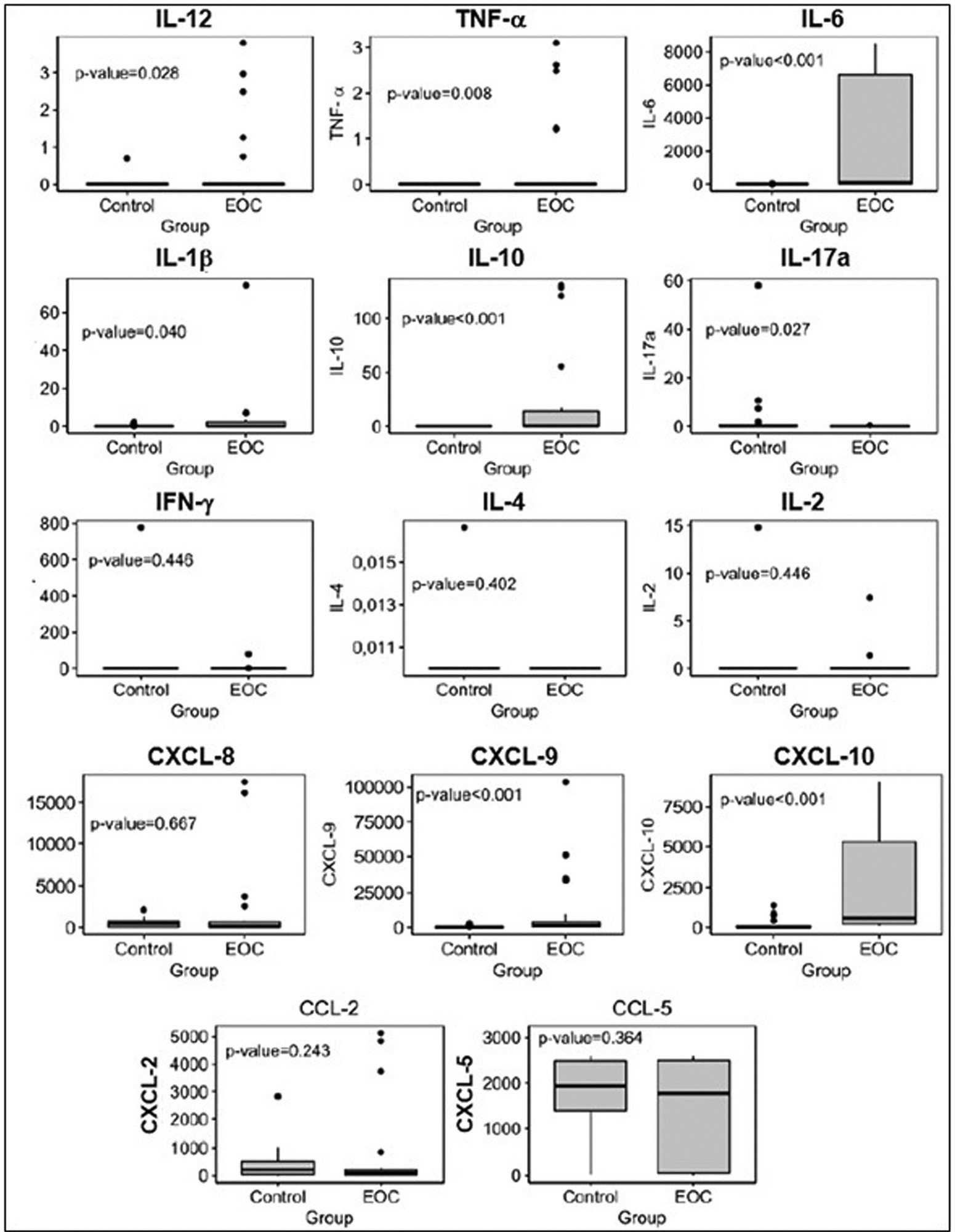
Plasma levels of proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-12 (IL12), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), and interleukin-10 (IL-10), and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9 (CXCL-9) and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL-10) were significantly higher in patients with EOC than in those in the control group. Plasma levels of cytokine interleukin-17A (IL-17A) and MPs derived from endothelial cells were lower in patients with EOC than in the control group. The frequency of leukocytes and MPs derived from endothelial cells was higher in type-2 tumors than in those without malignancy. We observed an expressive number of inflammatory/regulatory cytokines and chemokines in the cases of EOC, as well as negative and positive correlations involving them, which leads to a higher complexity of these networks.
The present study showed that, through the development of networks consisting of cytokines, chemokines, and MPs, there is a greater systemic inflammatory response in patients with EOC and a more complex correlation of these biomarkers in type-2 tumors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(9):866-870
08-29-2022
Female sterilization is a surgical procedure that aims women to permanently stop the use of conception. The benefits, risks and cost-effectiveness are important issues. The purpose of this study was comparing the applicability, complications and efficacy of salpingectomy versus electrocoagulation and tubal occlusion by laparoscopy in the Ambulatory Surgery Unit.
We performed a retrospective and observational study that included women undergoing laparoscopic sterilization procedures at our Ambulatory Surgery Unit, during three years. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS, applying the Fisher exact test, the Mann-Whitney test, and Linear Regression.
Two hundred and twenty-one laparoscopic surgical procedures were performed, including 79 (35.7%) bilateral total salpingectomies and 142 (64.3%) electrocoagulation and bilateral tubal occlusion procedures. The majority of the procedures were performed by a resident (n = 162; 73.3%), with 40% (n = 33) of salpingectomies. The surgical time, independently the type of surgeon, was significantly shorter in the tubal occlusion (42.2 vs. 52.7 min, p < 0.001). Safety and efficacy endpoints were not significantly different between the two groups, with a case of pregnancy in tubal occlusion group.
Salpingectomy is a safe and effective alternative comparing with electrocoagulation and tubal occlusion.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):225-231
01-19-2021
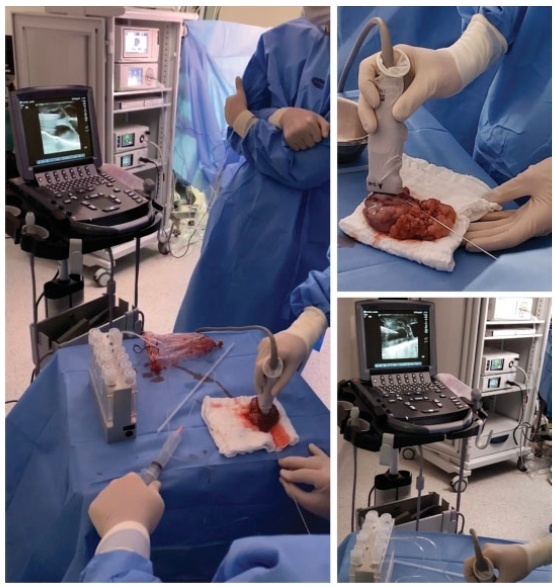
We report a case of ultrasound-guided ex vivo oocyte retrieval for fertility preservation in a woman with bilateral borderline ovarian tumor, for whom conventional transvaginal oocyte retrieval was deemed unsafe because of the increased risk of malignant cell spillage. Ovarian stimulation with gonadotropins was performed. Surgery was scheduled according to the ovarian response to exogenous gonadotropic stimulation; oophorectomized specimens were obtained by laparoscopy, and oocyte retrieval was performed ~ 37 hours after the ovulatory trigger. The sum of 20 ovarian follicles were aspirated, and 16 oocytes were obtained.We performed vitrification of 12 metaphase II oocytes and 3 oocytes matured in vitro. Our result emphasizes the viability of ex vivo mature oocyte retrieval after controlled ovarian stimulation for those with high risk of malignant dissemination by conventional approach.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):555-561
10-23-2020
To evaluate the role of clinical features and preoperativemeasurement of cancer antigen 125 (CA125), human epididymis protein(HE4), and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) serum levels in women with benign and malignant non-epithelial ovarian tumors.
One hundred and nineteen consecutive women with germ cell, sex cordstromal, and ovarian leiomyomas were included in this study. The preoperative levels of biomarkers were measured, and then surgery and histopathological analysis were performed. Information about the treatment and disease recurrence were obtained from the medical files of patients.
Our sample included 71 women with germ cell tumors (64 benign and 7 malignant), 46 with sex cord-stromal tumors (32 benign and 14 malignant), and 2 with ovarian leiomyomas. Among benign germ cell tumors, 63 were mature teratomas, and, amongmalignant, fourwere immatureteratomas. Themost common tumors in the sex cordstromal group were fibromas (benign) and granulosa cell tumor (malignant). The biomarker serum levels were not different among benign andmalignant non-epithelial ovarian tumors. Fertility-sparing surgeries were performed in 5 (71.4%) women with malignant germ cell tumor. Eleven (78.6%) patients with malignant sex cord-stromal tumors were treated with fertility-sparing surgeries. Five women (71.4%) with germ cell tumors and only 1 (7.1%) with sex cord-stromal tumor were treated with chemotherapy. One woman with germ cell tumor recurred and died of the disease and one woman with sex cord-stromal tumor recurred.
Non-epithelial ovarian tumors were benign in the majority of cases, and the malignant caseswere diagnosed at initial stages with good prognosis. Themeasurements of CA125, HE4, and CEA serum levels were not useful in the preoperative diagnosis of these tumors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):397-403
08-26-2020
To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of cancer antigen 125 (CA125) and complete blood count (CBC) parameters, such as the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), the platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and thrombocytosis in patients with ovarian masses.
The present is a retrospective study conducted at a single tertiary hospital from January 2010 to November 2016. We included consecutive women referred due to suspicious adnexal masses. The CBC and CA125 were measured in the serum of 528 women with ovarian masses before surgery or biopsy. We evaluated the diagnostic performance of the NLR, PLR, platelets (PLTs), CA125, and the associations between them. We tested the clinical utility of the CBC parameters and CA125 in the discrimination of ovarian masses through decision curve analysis (DCA).
The best balance between sensitivity and specificity was obtained by the associations of CA125 or PLTs ≥ 350/nL, with 70.14% and 71.66%, CA125 or PLTs ≥ 400/ nL, with 67.30% and 81.79%, CA125 or PLR, with 76.3% and 64.87%, and CA125 or NLR, with 71.09% and 73.89% respectively. In the DCA, no isolated CBC parameter presented a higher clinical utility than CA125 alone.
We showed that no CBC parameter was superior to CA125 in the prediction of the malignancy of ovarian tumors in the preoperative scenario.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):513-515
09-01-2017
Acute abdomen secondary to epithelial ovarian cancer rupture during pregnancy is a rare event. Our aim is to present how the work of a coordinated multidisciplinary team in a case of ruptured epithelial ovarian cancer during pregnancy is feasible to obtain the best results possible. A 34-year-old woman during the 37th week of her first gestation presented with an acute abdomen. During laparotomy, a ruptured 16.5-cm left ovarian tumor was detected; the tumor was extirpated and sent to pathologic evaluation. In the meantime, a Kerr cesarean section was performed, and a healthy female neonate was born. The tumor was diagnosed as a cystadenocarcinoma; therefore, the family and the combined surgical team (obstetricians and a surgical oncologist) decided to complete a definitive radical ovarian cancer surgery: hysterectomy, right salpingooophorectomy, lymphadenectomy, omentectomy and appendectomy. The patient’s postoperative evolution was uneventful, and she was sent to adjuvant chemotherapy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(5):411-416
08-04-2004
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000500011
OBJECTIVE: to evaluate the incidence of non-gynecological surgical procedures used in the treatment of ovarian cancer, as well to describe their complications. METHODS: eighty-two patients with ages from 22 to 89 (mean = 54.1 ± 15.1 years), submitted to laparotomy for surgical treatment of ovarian cancer from February 1999 to October 2003 were retrospectively evaluated. This study included only patients with epithelial ovary carcinoma. The patients were divided into 2 groups, patients submitted exclusively to gynecological procedures and patients submitted to non-gynecological procedures. Statistical analysis was made with the Student's t-test or the chi-square test. RESULTS: 5 patients (6.1%) were in stage (FIGO) I, 18 (21.9%) in stage II, 40 (48.8%) in stage III, and 19 (23.2%) in stage IV. Non-gynecological procedures were done in 35 cases (42.7%), including: 17 colostomies, 16 enterectomies, 8 peritonectomies, 7 colectomies, 5 partial diaphragm resections, 4 partial cystectomies, 4 splenectomies, 2 ileostomies, and 1 hepatectomy. All patients submitted to non-gynecological procedures were included in stages III and IV. This group of patients underwent longer-lasting surgeries (5.3 ± 1.4 versus 3.1 + 0,0 h; p < 0.001). There was no significant difference between these two groups regarding hemotransfusion requirement (42,2 versus 40%; p = 0.512) and hospitalization time (11.5 ± 7.2 versus 10 ± 9.9 days; p = 0.454). Patients submitted to non-gynecological surgeries developed higher rates of postoperative complications (37 versus 17.1%; p = 0.042), and two of them (2.4%) died. CONCLUSION: non-gynecological surgical procedures are frequently used in the treatment of patients with ovarian cancer. These procedures are associated with a longer-lasting surgery and higher rates of postoperative complications.