-
Original Article04-30-2025
An assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
Abstract
Original ArticleAn assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
Views221Abstract
Objective:
In vitro, fertilization is the primary treatment method for infertility. Follicular fluid analysis is an approach used to optimize the results of assisted reproductive techniques. Oxidative stress represents the imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and their detoxification. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative Stress Index levels are the main oxidative stress markers. This study investigated the effects of oxidative stress markers on infertility etiology, embryo quality, and success of In vitro fertilization.
Methods:
Before enrolling in the ICSI-ET cycle, participants had their FSH and LH levels assessed on the second day of the cycle. The ovarian degrees of the participants were evaluated by transvaginal ultrasonography. Participants underwent controlled ovarian stimulation using the GnRH antagonist protocol. TV-USG and serial E2 measurements were performed at appropriate intervals to follow follicular development. Follicle sizes, quantity, and endometrial thickness were recorded. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative analyses were conducted using Rel Assay Diagnostics Assay Kits.
Results:
The average number of total oocytes in the participants was 10.25±6.66, and the average of mature M2 stage oocytes was 6.71±3.72. The average number of fertilized oocytes was 4.65±2.81. Fertilization rates were calculated as approximately 54.75±25.58%. A statistically significant positive correlation was found between embryo quality and serum Total Antioxidant Status levels (p=0.004). Similarly, a significant positive correlation was observed between embryo quality and follicular Total Antioxidant Status values (r = 0.42, p = 0.01).
Conclusion:
This study concluded that oxidative stress markers affect certain stages of the IVF treatment process.
Key-words AntioxidantsFertilization in vitroFollicular fluidInfertilityOocytesOxidantsOxidative stressSee more
-
Review Article07-27-2021
Morphology and Biochemistry of Ovulation Morfologia e bioquímica da ovulação
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):480-486
Abstract
Review ArticleMorphology and Biochemistry of Ovulation Morfologia e bioquímica da ovulação
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):480-486
Views336See moreAbstract
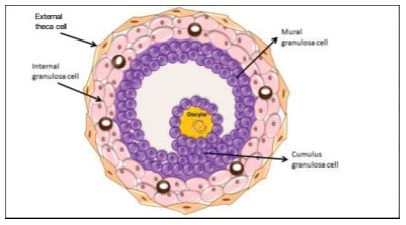
The process of ovulation involves multiple and iterrelated genetic, biochemical, and morphological events: cessation of the proliferation of granulosa cells, resumption of oocyte meiosis, expansion of cumulus cell-oocyte complexes, digestion of the follicle wall, and extrusion of the metaphase-II oocyte. The present narrative review examines these interrelated steps in detail. The combined or isolated roles of the folliclestimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) are highlighted. Genes indiced by the FSH genes are relevant in the cumulus expansion, and LH-induced genes are critical for the resumption ofmeiosis and digestion of the follicle wall. A nonhuman model for follicle-wall digestion and oocyte release was provided.
-
Original Article06-09-2009
Spontaneous pregnancies after ovarian puncture for in vitro maturation in women with the polycystic ovary syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(3):138-141
Abstract
Original ArticleSpontaneous pregnancies after ovarian puncture for in vitro maturation in women with the polycystic ovary syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(3):138-141
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000300006
Views136See morePURPOSE: to report three cases of spontaneous gestation in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), that occurred in the months subsequent to transvaginal oocyte retrieval for in vitro maturation (IVM). METHODS: three infertile patients with PCOS, submitted to oocytes' IVM without previous ovarian stimulation, were included in the study. During the procedure of oocytes' collection, each ovary was drilled from four to eight times. RESULTS: none of the patients got pregnant with the IVM technique. Evaluating the cases' follow-up, in seven months after the procedure, the three patients got pregnant without the help of techniques of assisted reproduction, which resulted in three births. CONCLUSIONS: the multiple drillings in the ovary of these patients with PCOS, during the process to collect oocytes, may have contributed to their pregnancy in the months following the procedure.
-
Original Article02-03-2008
First polar body morphology and fertilization rate, cleavage rate, and embryo quality
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(7):360-365
Abstract
Original ArticleFirst polar body morphology and fertilization rate, cleavage rate, and embryo quality
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(7):360-365
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000700007
Views190PURPOSE: to determine the relationship between the morphology of the first spindle pole of human oocytes and rates of fertilization, fragmentation and embryo quality in procedures of Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI). METHODS: retrospective study of 582 consecutive ICSI cycles, from July 2003 to July 2005. The morphology of the first spindle pole (SP) was assessed through the analysis of 3,177 oocytes in metaphase II, immediately before the ICSI procedure, always by the same observer. SP has been classified in the following categories: normal size intact, fragmented or augmented SP. Fertilization rate and fragmentation, and the number and rate of good quality embryos in each one of the three groups studied have been evaluated, 48 hours after ICSI (D2). Embryos with four cells, without fragmentation and with symmetric blastomeres in D2 were considered as of good quality. RESULTS: rates of fertilization, fragmentation and of good quality embryo formation, resulting from oocyte insemination, with augmented SP (20.7, 16.7 and 5% respectively) were significantly lower than the ones from intact and normal size SP (70.8, 62.5 and 19%, respectively) or from fragmented SP oocytes (69.7, 60.5 and 17.1%, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: it has been observed that the presence of augmented first spindle pole is related to worse rates of fertilization, fragmentation and bad quality embryo formation. Nevertheless, fragmentation in the first spindle pole of the oocyte does not seem to affect ICSI results.
Key-words Embryo implantationFertilizationFertilization in vitroOcytesOocytesQuality controlSperm injections, intracytoplasmicSee more -
Original Article10-16-2008
Meiotic abnormalities of oocytes from patients with endometriosis submitted to ovarian stimulation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(8):413-419
Abstract
Original ArticleMeiotic abnormalities of oocytes from patients with endometriosis submitted to ovarian stimulation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(8):413-419
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000800007
Views161See morePURPOSE: to evaluate the meiotic spindle and the chromosome distribution of in vitro mature oocytes from stimulated cycles of infertile women with endometriosis, and with male and/or tubal infertility factors (Control Group), comparing the rates of in vitro maturation (IVM) between the two groups evaluated. METHODS: fourteen patients with endometriosis and eight with male and/or tubal infertility factors, submitted to ovarian stimulation for intracytoplasmatic sperm injection have been prospectively and consecutively selected, and formed a Study and Control Group, respectively. Immature oocytes (46 and 22, respectively, from the Endometriosis and Control Groups) were submitted to IVM. Oocytes presenting extrusion of the first polar corpuscle were fixed and stained for microtubules and chromatin evaluation through immunofluorescence technique. Statistical analysis has been done by the Fisher's exact test, with statistical significance at p<0.05. RESULTS: there was no significant difference in the IVM rates between the two groups evaluated (45.6 and 54.5% for the Endometriosis and Control Groups, respectively). The chromosome and meiotic spindle organization was observed in 18 and 11 oocytes from the Endometriosis and Control Groups, respectively. In the Endometriosis Group, eight oocytes (44.4%) presented themselves as normal metaphase II (MII), three (16.7%) as abnormal MII, five (27.8%) were in telophase stage I and two (11.1%) underwent parthenogenetic activation. In the Control Group, five oocytes (45.4%) presented themselves as normal MII, three (27.3%) as abnormal MII, one (9.1%) was in telophase stage I and two (18.2%) underwent parthenogenetic activation. There was no significant difference in meiotic anomaly rate between the oocytes in MII from both groups. CONCLUSIONS: the present study data did not show significant differences in the IVM or in the meiotic anomalies rate between the IVM oocytes from stimulated cycles of patients with endometriosis, as compared with controls. Nevertheless, they have suggested a delay in the outcome of oocyte meiosis I from patients with endometriosis, shown by the higher proportion of oocytes in telophase I observed in this group.
-
Original Article08-15-2008
Evaluation of meiotic abnormalities of oocytes from polycystic ovary syndrome patients submitted to ovarian stimulation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(5):241-247
Abstract
Original ArticleEvaluation of meiotic abnormalities of oocytes from polycystic ovary syndrome patients submitted to ovarian stimulation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(5):241-247
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000500006
Views160PURPOSE: to evaluate the meiotic spindle and the chromosome distribution of in vitro matured oocytes obtained from stimulated cycles of infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and with male factor and/or tubal infertility (Control Group) and compare in vitro maturation (IVM) rates between the groups analyzed. METHODS: five infertile patients with PCOS and eight controls, submitted to stimulated cycles for intracytoplasmic sperm injection, were selected prospectively and consecutively, and respectively assigned to the study group and the Control Group. Immature oocytes (21 and 29, respectively, from PCOS and Control Group) were submitted to IVM. After IVM, oocytes with first polar body extruded were fixed and submitted to immunostaining and fluorescence microscopy for morphological evaluation of the spindle and of chromosome distribution. Statistical analysis was performed by the Fisher test with significance, when p<0.05. RESULTS: IVM rates were similar between groups (47.6 e 44.8%, respectively, for PCOS and Control Group). Six of the ten oocytes (60%) from the study group and four of the 12 oocytes (33.3%) from the Control Group presented meiotic anomalies of the spindle and/or anomalous chromosome distribution, without statistical difference between groups. CONCLUSIONS: data from the present study did not demonstrate significant difference neither in IVM rates nor in the proportions of meiotic anomalies between in vitro matured oocytes obtained from stimulated cycles from PCOS patients and control ones.
Key-words Infertility, femaleInfertility, maleOocytesOvulation InductionPolycystic ovary syndromeSperm injections, intracytoplasmicSee more -
Original Article12-05-2007
Oocyte reception: patients’ profile in a waiting list of the program of Hospital Regional da Asa Sul, Brasília, Distrito Federal
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(9):459-464
Abstract
Original ArticleOocyte reception: patients’ profile in a waiting list of the program of Hospital Regional da Asa Sul, Brasília, Distrito Federal
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(9):459-464
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000900004
Views116PURPOSE: describe epidemiologic profile of patients enrolled in the oocyte reception program at Hospital Regional da Asa Sul (HRAS) in Brasília, Distrito Federal, Brazil, and its main indications. METHODS: prospective descriptive study, in which 330 patients enrolled in the waiting list program were studied. Sixty-seven women, irrespective of their infertility factor and that had not been contemplated by the treatment were included. Thirty women who lived in other cities, 50 patients over 50 years old, 24 patients that didn't want to take part in the study, nine patients that asked to be left out of the program and 150 women that couldn't be found by phone calls were excluded. The 67 patients included were interviewed in order to answer a questionnaire. Their medical handbook was recovered to confirm that the investigation required to establish the cause of infertility had been done. The data was registered and analyzed by SPSS version 12.0 software. RESULTS: the patients' epidemiologic profile is age range 40 to 49 years old (82%), non-white skinned (77,6%), catholic (71,6%), married (59,7%), in high school (76,1%), secondary infertility (53,6%) from which due to tubal sterilization (40,3%) and those ones who started trying to conceive before 35 years old (91%). The main indication to enroll in this oocyte reception program was age and low ovarian reserve. CONCLUSION: the results demonstrated the indiscriminate tubal sterilization. The oocyte reception program benefits women with reserved reproductive prognostic.
Key-words Fertilization in vitroInfertility, femaleOocyte donationOocytesReproductive, techniques,assistedSterilization, tubalSee more


