Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):597-606
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the quality of mother-child bonding in three different contexts related to the labor, that is, vaginal delivery, elective cesarean section, and intrapartum cesarean section.
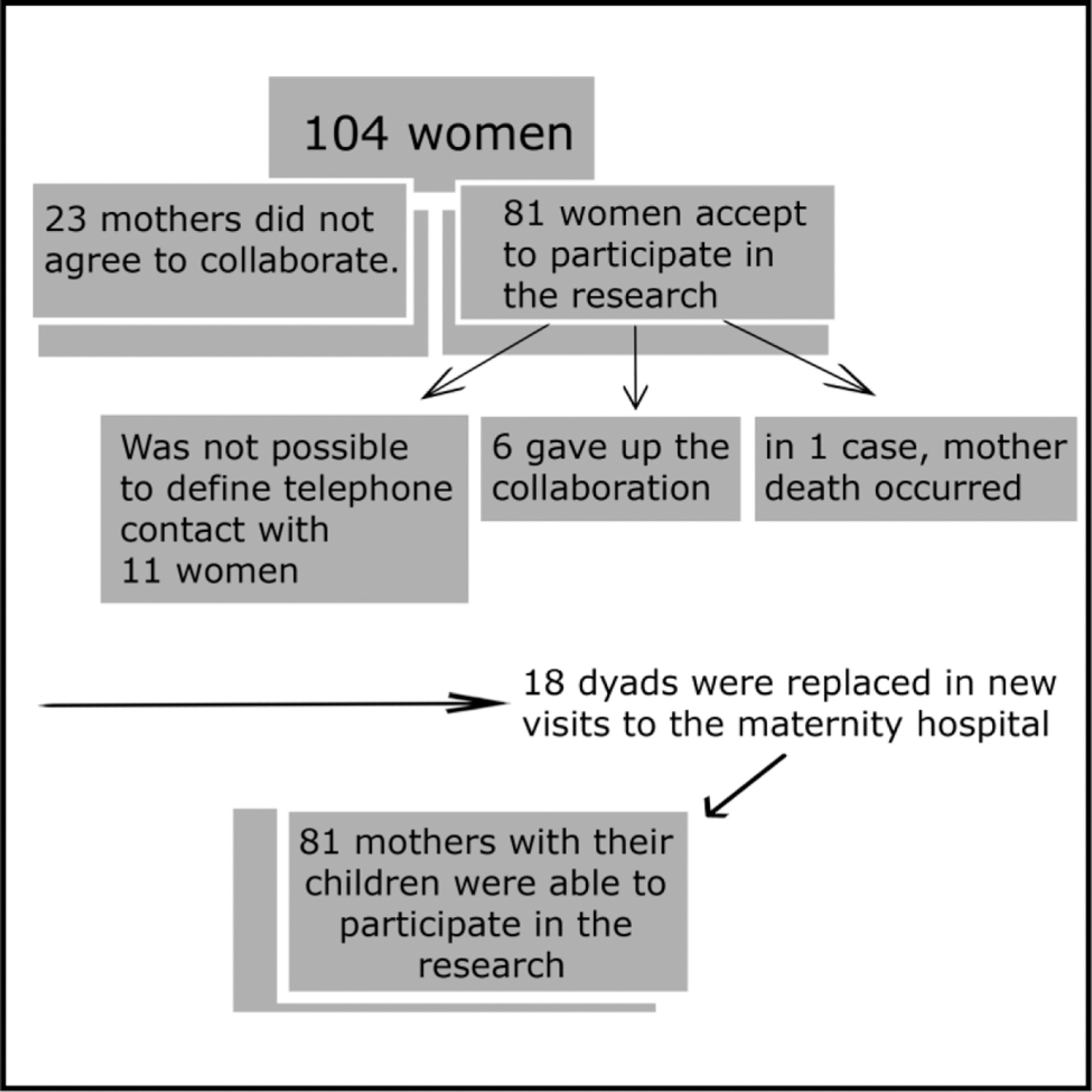
This was an observational, cross-sectional clinical study conducted in two cities within the state of São Paulo, Brazil. The study sample consisted of 81 babies born without any major complications during pregnancy and labor, aged 3 to 4 months, and their respective mothers, aged between 20 and 35 years old, primiparous, living in the cities of Palmital and Ourinhos, state of São Paulo, Brazil. The evaluation of the quality of the maternal-filial interaction was performed through video-image analysis, using the Mother-baby Interaction Observation Protocol from 0 to 6 months (POIMB 0-6, in the Portuguese acronym).
Mothers who had vaginal delivery had higher amount of visual contact or attempted visual contact (p = 0.034), better response to the social behavior of the child (p = 0.001) and greater sensitivity (p = 0.007) than the others. Their children also showed more interaction with them, as they looked more frequently at the mother's face (p ≤ 0.008) and responded more frequently to the mother's communicative stimulus (p < 0.001).
Considering the occurrence of vaginal delivery, it is concluded that the interaction between the mother-child dyad is quantitatively larger and qualitatively better when compared with intrapartum or elective cesarean section.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):522-528
To obtain cesarean-section (CS) rates according to the Robson Group Classification in five different regions of Brazil.
A descriptive epidemiological study using data from secondary birth records fromthe Computer Science Department of the Brazilian Unified Health System (Datasus, in Portuguese) between January 1st, 2014, and December 31st, 2016, including all live births in Brazil.
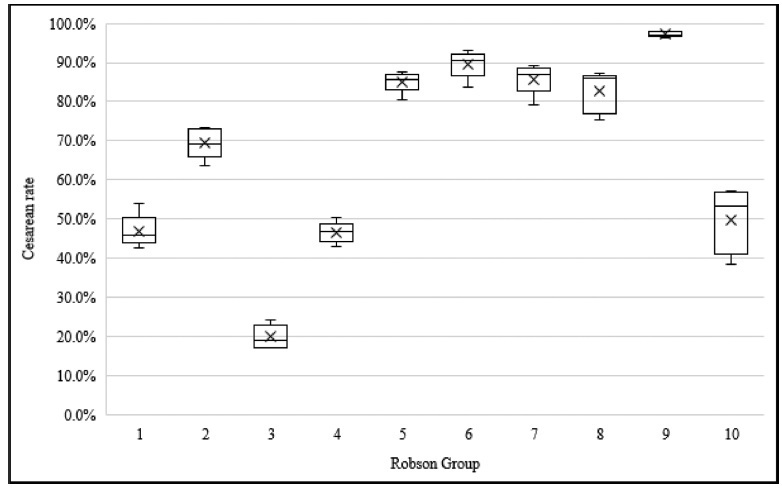
The overall rate of CSwas of 56%. The sample was divided into 11 groups, and vaginal births were more frequent in groups 1 (53.6%), 3 (80.0%) and 4 (55.1%). The highest CS rates were found in groups 5 (85.7%), 6 (89.5%), 7 (85.2%) and 9 (97.0%). The overall CS rate per region varied from 46.2% in the North to 62.1% in the Midwest. Group 5 was the largest obstetric population in the South, Southeast and Midwest, and group 3 was the largest in the North and Northeast. Group 5 contributed the most to the overall CS rate, accounting for 30.8% of CSs.
Over half of the births in Brazil were cesarean sections. The Midwest had the highestCS rates,while theNorth had the lowest. The largestobstetric population in the North and in the Northeast was composed of women in group 3, while in the South, Southeast and Midwest it was group 5. Among all regions, the largest contribution to the overall CS rate was from group 5.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):476-484
Labor induction does not always result in vaginal delivery, and can expose both the mother and the fetus to the risks inherent to the induction procedure or a possible cesarean section. Transvaginal sonography (TVS) of the cervix is a useful tool to predict prematurity; in the present study, this tool was used to evaluate postterm induction.
We evaluated the ultrasound characteristics of the cervix (cervical length, cervical funneling, internal os dilation, the presence or absence of the cervical gland area [CGA], and the morphological changes of the cervix as a result of applying fundal pressure) before the onset of labor induction among women with postterm pregnancy to identify the possible predictors of failed labor induction. The Bishop score (BS) was used for comparison purposes. Three groups were evaluated: successful versus unsuccessful induction; vaginal delivery versus cesarean delivery (excluding cases of acute fetal distress [AFD]); and vaginal delivery versus cesarean delivery (including cases of AFD). A fourth group including only the primiparous women from the three previous groups was also evaluated.
Based on the studied characteristics and combinations of variables, a cervical length ≥ 3.0 cm and a BS ≤ 2 were the best predictors of induction failure.
Although TVS is useful for screening for induction failure, this tool should not be used as an indication for cesarean section.