Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 11-01-2018;40(11):686-692
The aim of the present study was to assess the anthropometric measures, food intake and food cravings during the menstrual cycle of undergraduate students of the faculty of nutrition.
A cross-sectional study was performed with 27 students from a public university in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, who had their food intake evaluated through a 24-hour food recall, their nutritional status evaluated based on anthropometric measures, and food cravings evaluated using the Food Desire Questionnaire. Data were collected during an evaluation in the follicular phase (between the 5th and the 9th day of the menstrual cycle) and another in the luteal phase (LP) (between the 20th and the 25th day of the menstrual cycle). For food intake variables, the analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was used, followed by the Tukey test. The Mann-Whitney test was used for the analysis of food cravings, considering a significance level of 5% (p< 0.05).
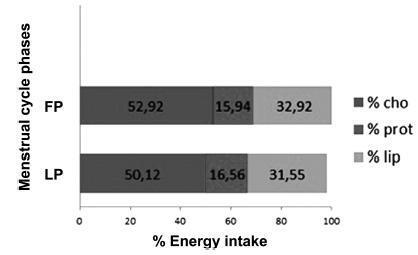
The desire for foods rich in sugar, salt, and fat, such as chocolate, pastries, snacks and desserts were higher (p< 0.05) during the premenstrual period, although it did not reflect neither a higher energy intake nor an alteration in the distribution of macronutrients. A higher intake of carbohydrates, proteins, fibers, and calcium was observed during the LP; however, without statistical difference between the groups. There were no differences either in the intake of any food group or in the anthropometric measurements (p> 0.05).
Food cravings of nutrition students differed between the phases of the menstrual cycle; however, with no difference in food intake and in anthropometric measures.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 05-11-2012;34(4):175-183
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000400007
PURPOSE: To associate the quality of life with the nutritional status of climacteric women. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional study on a sample of 200 climacteric women aged 40 to 65 years who responded to a 24-hour food recall and to questions about socioeconomic factors and current, previous and family medical history. Body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC) and waist-hip ratio were used for anthropometric evaluation. To assess the quality of life, we applied the MRS-menopause rating scale. RESULTS: The average BMI and waist circumference were 30.1 kg/m² (obesity grade 1) and 99 cm (very increased risk for cardiovascular disease), respectively. Increased protein consumption and decreased fiber, calcium and vitamin D intake were detected. The most prevalent disease was hypertension, 48.5% of the women studied were taking medication for cardiovascular disease and 23% were taking antidepressant medications. Regarding quality of life, significant results related to BMI as well as blood pressure were found. CONCLUSIONS: A nutritional intervention aiming to correct or improve food consumption and anthropometric profile may result in health benefits for climacteric women. The prevalence of obesity, associated with a poorer quality of life, morbidity and mortality underscores the need for a feeding re-education program during the climacteric.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 01-09-2008;29(10):511-518
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007001000004
PURPOSE: to analyze the association between maternal pre-gestational nutritional status and maternal outcomes - hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, vitamin A deficiency, and anemia - and the newborn outcome - low birth weight. METHODS: cross-sectional study, with 433 adult puerperal women (> 20 years old) and their newborns, attending the Maternidade Escola of Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ). Data was collected through interviews and access to their medical records. Maternal pre-gestational nutritional status was established through pre-gestational body mass index according to the cut-offs for adult women defined by the World Health Organization (WHO), in 1995. The association between gestational outcomes and pre-gestational nutritional status was estimated through odds ratio (OR) and a 95% confidence interval (95%CI). RESULTS: frequency of pre-gestational weight deviation (low weight, overweight and obesity) was 31.6%. Considering the pre-gestational nutritional status, overweight and obese women presented a lower weight gain than eutrophic and low-weight women (p<0.05). Women with pre-gestational obesity presented a higher risk of developing hypertensive disordens of pregnancy (OR=6.3; 95%CI=1.9-20.5) and those with low pre-gestational weight were more likely to give birth to low birth weigh infants (OR=7.1; 95%CI=1.9-27.5). There was no evidence of the association between pre-gestational nutritional status and the development of anemia, vitamin A deficiency and gestational diabetes. The mean weight gain among overweight and obese pregnant women was significantly lower when compared to eutrophic and low-weight pregnant women (p=0.002, p=0.049, p=0.002, p=0.009). CONCLUSIONS: the high number of women with pre-gestational weight deviation reinforces the importance of a nutritional guidance that favors a good nutritional state and reduces the risks of maternal and newborn adverse outcomes.