-
Review Article
Low-level laser therapy for nipple trauma and pain during breastfeeding: systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo3
03-18-2025
Summary
Review ArticleLow-level laser therapy for nipple trauma and pain during breastfeeding: systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo3
03-18-2025Views58Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to investigate the effect of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) on nipple trauma and pain during breastfeeding through a systematic review with a meta-analysis of selected studies.
Source of the data:
A thorough search was conducted on March 22, 2022, using the databases PubMed, SciELO, LILACS, PEDro, CINAHL, EMBASE, ScienceDirect, Scopus, Google Scholar, MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library, Clinical Trials, Web of Science, TRIP, DARE, and ProQuest. The search terms included various combinations of low-level laser therapy, nipple pain, nipple trauma, and breastfeeding.
Studies selection:
Out of 107 articles identified, only three controlled and randomized clinical trials was included. The extracted data encompassed breast and trauma characteristics, treatment types, outcomes (pain and healing process), evaluation tools, LLLT usage, laser brand, and parameters.
Data collection:
Data extraction was performed using RAYYAN for systematic reviews. The risk of bias in the studies was evaluated.
Data synthesis:
Pain was measured using the visual analog scale (VAS). The included studies did not use validated tools for assessing physical conditions. All studies employed LLLT with a 660-nm wavelength, though there were variations in equipment power, energy dose, and application methods. The meta-analysis revealed an average difference of −0.60 points (95% CI: −1.52 to 0.31) in the VAS pain scores between the LLLT and control groups. No heterogeneity was observed among the studies (I2=0%), indicating no significant difference in pain relief between LLLT (red light) and control groups.
Conclusion:
LLLT may offer a promising option for managing breastfeeding-related complications, though further research is required.
Key-words Breast feedingLaser therapyLow level light therapyLow-level laserNipple painNipple traumaNipplesSee more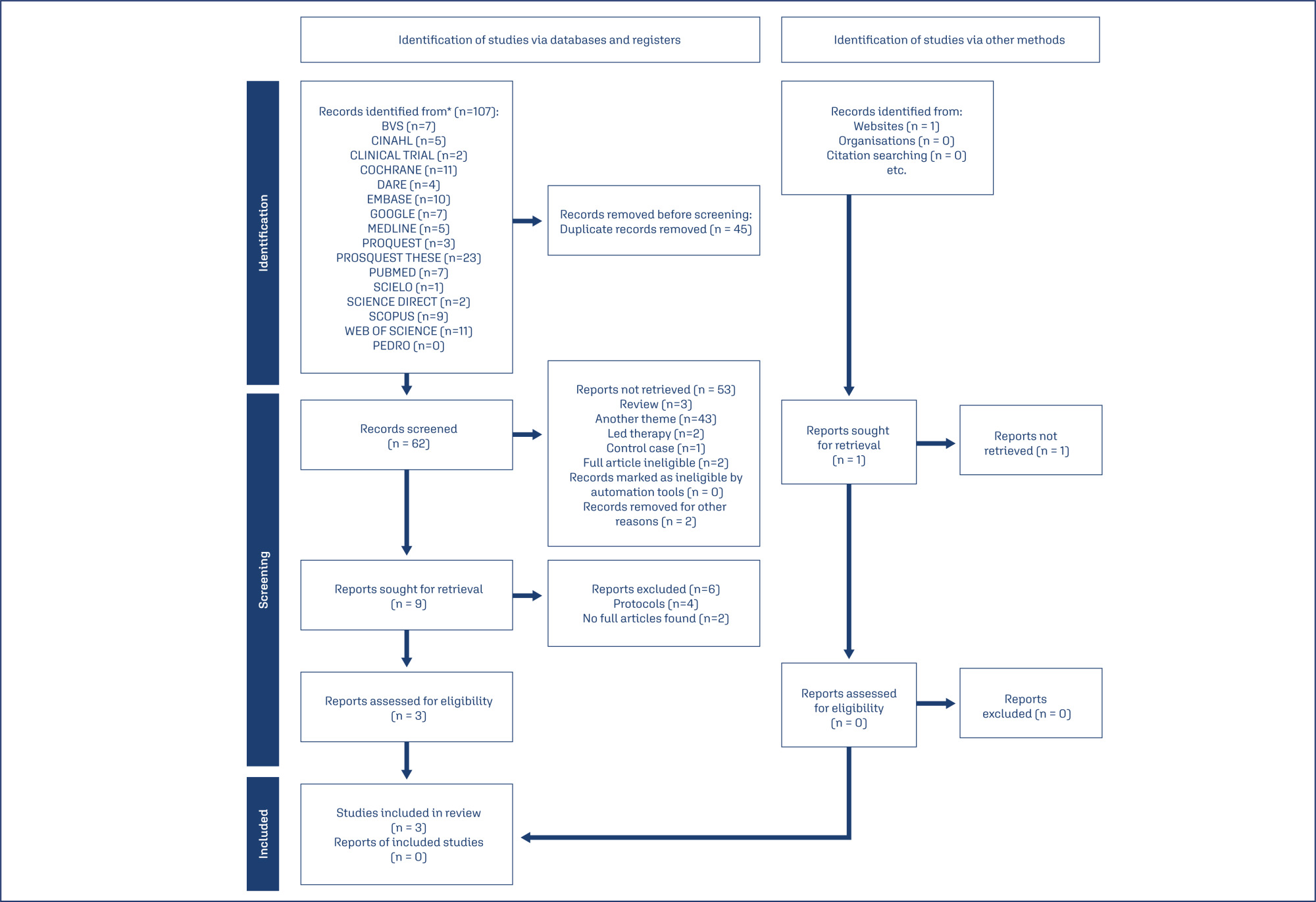
-
Original Article
Nipple-sparing mastectomy in young versus elderly patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo90
10-23-2024
Summary
Original ArticleNipple-sparing mastectomy in young versus elderly patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo90
10-23-2024Views121See moreAbstract
Objective:
In this study, we compared indications and outcomes of 115 young (< 40 years) versus 40 elderly (> 60 years) patients undergoing nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) as risk-reducing surgery or for breast cancer (BC) treatment.
Methods:
Between January 2004 and December 2018, young and elderly patients undergoing NSM with complete data from at least 6 months of follow-up were included.
Results:
BC treatment was the main indication for NSM, observed in 85(73.9%) young versus 33(82.5%) elderly patients, followed by risk-reducing surgery in 30(26.1%) young versus 7(17.5%) elderly patients. Complication rates did not differ between the age groups. At a median follow-up of 43 months, the overall recurrence rate was higher in the younger cohort (p = 0.04). However, when stratified into local, locoregional, contralateral, and distant metastasis, no statistical difference was observed. During the follow-up, only 2(1.7%) young patients died.
Conclusion:
Our findings elucidate a higher recurrence rate of breast cancer in younger patients undergoing NSM, which may correlate with the fact that age is an independent prognostic factor. High overall survival and low complication rates were evidenced in the two groups showing the safety of NSM for young and elderly patients.
-
Original Article
Immediate prepectoral versus submuscular breast reconstruction in nipple-sparing mastectomy: a retrospective cohort analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo76
09-06-2024
Summary
Original ArticleImmediate prepectoral versus submuscular breast reconstruction in nipple-sparing mastectomy: a retrospective cohort analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo76
09-06-2024Views165Abstract
Objective
To evaluate early complications in prepectoral breast reconstruction.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study including 180 consecutive cases of nipple-sparing mastectomy, comparing immediate breast reconstruction with subpectoral to prepectoral mammary implants in 2012-2022. Clinical and demographic characteristics and complications in the first three months following surgery were compared between the two techniques.
Results
The prepectoral technique was used in 22 cases (12.2%) and the subpectoral in 158 (87.8%). Median age was higher in the prepectoral group (47 versus 43.8 years; p=0.038), as was body mass index (25.1 versus 23.8; p=0.002) and implant volume (447.5 versus 409 cc; p=0.001). The prepectoral technique was more associated with an inframammary fold (IMF) incision (19 cases, 86.4% versus 85, 53.8%) than with periareolar incisions (3 cases, 13.6% versus 73, 46.2%); (p=0.004). All cases in the prepectoral group underwent direct-to-implant reconstruction compared to 54 cases (34.2%) in the subpectoral group. Thirty-eight complications were recorded: 36 (22.8%) in the subpectoral group and 2 (9.1%) in the prepectoral group (p=0.24). Necrosis of the nipple-areola complex/skin flap occurred in 27 patients (17.1%) in the subpectoral group (prepectoral group: no cases; p=0.04). The groups were comparable regarding dehiscence, seroma, infection, and hematoma. Reconstruction failed in one case per group (p=0.230). In the multivariate analysis, IMF incision was associated with the prepectoral group (aOR: 34.72; 95%CI: 2.84-424.63).
Conclusion
The incidence of early complications was comparable between the two techniques and compatible with previous reports. The clinical and demographic characteristics differed between the techniques. Randomized clinical trials are required.
Key-words Breast implantationBreast implantsBreast neoplasmsMammaplastyMastectomyNipplesPectoralis musclesSurgical procedures, operativeSee more -
Artigos Originais
Assessment of pain sensitivity and factors involved in the quality of the sample fluid cytologic papillary: preliminary results from the use of automated collection
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(10):491-496
02-01-2010
Summary
Artigos OriginaisAssessment of pain sensitivity and factors involved in the quality of the sample fluid cytologic papillary: preliminary results from the use of automated collection
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(10):491-496
02-01-2010DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001000004
Views59See morePURPOSE: to evaluate painful sensitivity and factors involved in producing papillary fluid suitable for cytological analysis by means of automated collection. METHODS: we selected 50 asymptomatic women without a personal or family history of breast cancer, outside the pregnancy and childbirth cycle in order to collect papillary fluid by the automated system. We recorded and related to the production of papillary fluid patient age, smoking habit, previous breast surgery, parity, breastfeeding, menopausal status and age at menarche. All material collected was fixed in appropriate place, and sent separately for cytological analysis. The painful sensitivity of the collection procedure was assessed using the Borg Category-Ratio Scale (CR10 Scale). RESULTS: patient age ranged from 22 to 59 years, mean 41.6±8.6 years. Of the 50 patients, 20 (40%) showed no papillary fluid suitable for analysis in the breasts. In those patients from whom appropriate fluid was obtained for analysis of papillary cytology, parity was inversely related to the ability to obtain suitable cell samples with a level of statistical significance of p=0.035, OR=0.0032 (95%CI=0.0001-0.1388). Regarding soreness, the exam was well tolerated. CONCLUSIONS: the automated method of fluid collection for analysis of papillary cytology was well tolerated by the women; thus producing analyzable material in 60% of cases, a rate was inversely related to parity.


