Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):165-171
05-24-2021
To describe the obstetric outcomes of patients withmultiple sclerosis (MS) and the impact of pregnancy and the postpartum period on the progression of the disease.
A case series study performed between December 2019 and February 2020, reporting pregnancies occurred between 1996 and 2019. The subjects included were women with MS undergoing follow-up at an MS referral center in Northeastern Brazil, and who had at least one pregnancy after the onset of MS symptoms, or who had their first relapse in the first year after delivery.
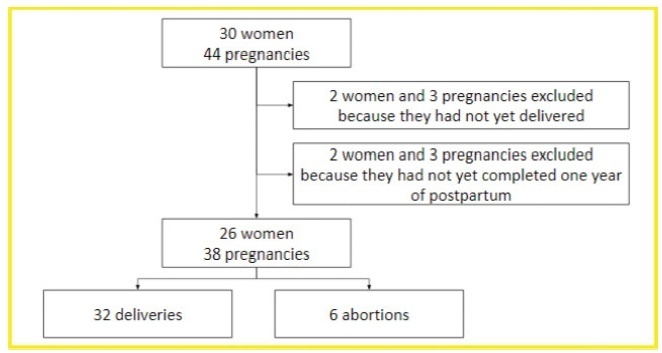
In total, 26 women and 38 pregnancies were analyzed - 32 of them resulted in delivery, and the remaining 6, in miscarriages. There was a significant increase in the prevalence of relapse during the postpartum period when compared with the gestational period. In 16 (42.1%) of the pregnancies, there was exposure to diseasemodifying therapies (DMTs) - 14 (36.8%), to interferon β, and 2 (5.3%), to fingolimod. Higher rates of abortion, prematurity and low birth weight were reported in the group was exposed to DMT when compared with the one who was not.
In the sample of the present study, there was a significant increase in the rate of MS relapse during the postpartum period when compared with the gestational period. Additionally, it seems that exposure to DMTs during pregnancy may affect the obstetric outcomes of the patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(12):544-549
01-11-2012
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001200003
PURPOSE: To describe the epidemiological cases and microbiological profile of Streptococcus agalactiae serotypes isolated from infected newborns of a Women's Health Reference Centre of Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil. METHODS: Cross-sectional laboratory survey conducted from January 2007 to December 2011. The newborns' strains, isolated from blood and cerebrospinal fluid samples, were screened by hemolysis on blood ágar plates, Gram stain, catalase test, CAMP test, hippurate hydrolysis or by microbiological automation: Vitek 2 BioMerieux®. They were typed by PCR, successively using specific primers for species and nine serotypes of S. agalactiae. RESULTS: Seven blood samples, one cerebrospinal fluid sample and an ocular sample, were isolated from nine newborns with infections caused by S. agalactiae, including seven cases of early onset and two of late onset. Only one of these cases was positive for paired mother-child samples. Considering that 13,749 deliveries were performed during the study period, the incidence was 0.5 cases of GBS infections of early onset per 1 thousand live births (or 0.6 per 1 thousand, including two cases of late onset) with 1, 3, 2, zero and 3 cases (one early and two late onset cases), respectively, for the years from 2007 to 2011. It was possible to apply PCR to seven of nine samples, two each of serotypes Ia and V and three of serotype III, one from a newborn and the other two from a paired mother-child sample. CONCLUSIONS: Although the sample was limited, the serotypes found are the most prevalent in the literature, but different from the other few Brazilian studies available, except for type Ia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(9):240-245
12-20-2011
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000900004
PURPOSE: To determine the accuracy of ultrasound in fetal weight estimation and to evaluate maternal and/or fetal factors that could interfere in the result. METHODS: This was a transverse prospective study, involving 106 patients, with 212 fetal weight evaluations, by two observers, within 24 h to delivery. The following parameters were measured: biparietal diameter, head circumference, abdominal circumference, and femoral length. Fetal weight was estimated using the Hadlock formula and the results were compared to birth weight. The maternal factors examined were: weight, BMI, and skin to uterus distance measured by ultrasound, and the fetal factors were: presentation, position, placental localization and thickness, fetal weight, and amniotic fluid index (AFI). RESULTS: There was good correlation between estimated fetal weight and birth weight (R=0.97). In 79.2% and in 92.4% of cases the estimated fetal weight was within 10% and 15% of birth weight, respectively. The only maternal factor that presented a positive correlation with percent error in the estimate of fetal weight was the skin to uterus distance (R³0.56). Fetal weight showed negative correlation with percent error (R>-0.36; p<0.001), with a significant tendency to overestimate fetal weight in the group of very low weight - <1000 g (p<0.05). The AFI showed a low negative correlation with percent error (R=-0.21; p<0.001) with no difference between AFI groups (p=0.516). CONCLUSION: Ultrasound presented good accuracy in the estimation of fetal weight. The error of weight estimate was directly proportional to the skin to uterus distance and inversely proportional to fetal weight. AFI did not interfere significantly in the ultrasound prediction of fetal weight.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):460-466
12-05-2006
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800004
PURPOSE: to assess the performance of lamellar body count compared to the shake (Clements) test in the prediction of fetal lung maturity in diabetics. METHODS: prospective study of 62 patients who underwent amniocentesis between the 26th and 39th week of pregnancy. Immediately after collection, the amniotic fluid sample was submitted to the shake test and lamellar body count. Deliveries occurred within three days of amniocentesis. Immature test results (absence of a complete bubble ring in the third tube for the shake test and less than 50,000 lamellar bodies) were confronted with the occurrence of pulmonary immaturity in the neonate (respiratory distress syndrome). The performance of both tests was compared using the chi2 test and p<0.05 was considered to be significant. RESULTS: seven infants had respiratory distress syndrome (11.3%). The lamellar body count and shake test were similar regarding sensitivity (100 vs 71.4%, respectively) and negative predictive value (100 vs 93.5%). Lamellar body count was superior as regards specificity (87.3 vs 52.7%, p=0.0001), positive predictive value (50 vs 16.1%, p=0.017), and accuracy (88.7 vs 54.8%, p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: lamellar body count is a simple and accurate method of assessing fetal lung maturity. It performs slightly better than the shake test in terms of specificity, positive predictive value and accuracy, with the advantage of not requiring manipulation or reagents. Similar to the shake test, lamellar body count has a high-negative predictive value: mature results (50,000 or more) indicate thar the infant will not have hyaline membrane.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(10):655-661
03-18-2002
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002001000004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of antenatal corticosteroid treatment on the incidence of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), neonatal morbidities, and mortality in preterm babies assisted at IMIP, a teaching hospital in Brazil. METHODS: this was an observational, analytical, cohort study which included 155 newborns from women who delivered prematurely. The study was conducted between February and November 2001 and included 78 women in the corticosteroid-treated group and 77 in the nontreated group. The study design included the incidence of RDS, assessment of morbidities related to prematurity and tabulation of neonatal mortality. The risk ratio and its 95% confidence interval were determined for estimation of the relative risk for RDS and neonatal outcome (dependent variables) according to antenatal corticoid therapy administration (independent variable). RESULTS: corticosteroid treatment was administered to 50.3% of the patients (64% of the women received the full treatment course, while 36% of the same group received a partial course of treatment). The incidence of RDS was significantly lower in the corticosteroid treated group (37.2%) compared with the nontreated group (63.6%). There was no observable decrease in the risk for morbidities associated with prematurity. There was a decrease in mortality and in the frequency of supplemental oxygen therapy in the corticosteroid group (37%). On multiple logical regression analysis, there was a 72% reduction in the risk for RDS in the corticosteroid group, and approximately a seven times greater risk for RDS in babies of gestational age below 32 weeks. CONCLUSIONS: a favorable impact of antenatal corticosteroid administration was observed, with significant reduction of the risk for RDS in patients with gestational age between 26 and 35 weeks. Although no effect on the other morbidities was observed, this can be explained by the small size of the sample.