-
Original Article
Is there a Role for Antenatal Corticosteroids in Term Infants before Elective Cesarean Section?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):283-290
06-18-2021
Summary
Original ArticleIs there a Role for Antenatal Corticosteroids in Term Infants before Elective Cesarean Section?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):283-290
06-18-2021Views120See moreAbstract
Objective
Cesarean section (CS) delivery, especially without previous labor, is associated with worse neonatal respiratory outcomes. Some studies comparing neonatal outcomes between term infants exposed and not exposed to antenatal corticosteroids (ACS) before elective CS revealed that ACS appears to decrease the risk of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), transient tachypnea of the neonate (TTN), admission to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and the length of stay in the NICU.
Methods
The present retrospective cohort study aimed to compare neonatal outcomes in infants born trough term elective CS exposed and not exposed to ACS. Outcomes included neonatal morbidity at birth, neonatal respiratory morbidity, and general neonatal morbidity. Maternal demographic characteristics and obstetric data were analyzed as possible confounders.
Results
A total of 334 newborns met the inclusion criteria. One third of the population study (n=129; 38.6%) received ACS. The present study found that the likelihood for RDS (odds ratio [OR]=1.250; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.454-3.442), transient TTN (OR=1.,623; 95%CI: 0.556-4.739), and NIUC admission (OR=2.155; 95%CI: 0.474-9.788) was higher in the ACS exposed group, although with no statistical significance. When adjusting for gestational age and arterial hypertension, the likelihood for RDS (OR=0,732; 95%CI: 0.240-2.232), TTN (OR=0.959; 95%CI: 0.297--3.091), and NIUC admission (OR=0,852; 95%CI: 0.161-4.520) become lower in the ACS exposed group.
Conclusion
Our findings highlight the known association between CS-related respiratory morbidity and gestational age, supporting recent guidelines that advocate postponing elective CSs until 39 weeks of gestational age.
-
Original Article
The Influence of Preeclampsia, Advanced Maternal Age and Maternal Obesity in Neonatal Outcomes Among Women with Gestational Diabetes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):607-613
12-21-2020
Summary
Original ArticleThe Influence of Preeclampsia, Advanced Maternal Age and Maternal Obesity in Neonatal Outcomes Among Women with Gestational Diabetes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):607-613
12-21-2020Views241See moreAbstract
Objective
The present study aims to analyze adverse fetal or neonatal outcomes in women with gestational diabetes, including fetal death, preterm deliveries, birthweight, neonatal morbidity and mortality, as well as the synergic effect of concomitant pregnancy risk factors and poor obstetric outcomes, as advanced maternal age, maternal obesity and pre-eclampsia in their worsening.
Methods
The present cohort retrospective study included all pregnant women with gestational diabetes, with surveillance and childbirth at the Hospital da Senhora da Oliveira during the years of 2017 and 2018. The data were collected from the medical electronic records registered in health informatic programs Sclinico and Obscare, and statistical simple and multivariate analysis was done using IBM SPSS Statistics.
Results
The study participants included 301 pregnant women that contributed to 7.36% of the total institution childbirths of the same years, in a total of 300 live births. It was analyzed the influence of pre-eclampsia coexistence in neonatal morbidity (p = 0.004), in the occurrence of newborns of low and very low birthweight (p < 0.01) and in preterm deliveries (p < 0.01). The influence of maternal obesity (p = 0.270; p = 0.992; p = 0.684) and of advanced maternal age in these 3 outcomes was also analyzed (p = 0,806; p = 0.879; p = 0.985).Using a multivariate analysis, the only models with statistic significance to predict the three neonatal outcomes included only pre-eclampsia (p = 0.04; p < 0.01; p < 0.01).
Conclusion
Only coexistence of pre-eclampsia showed an association with adverse neonatal outcomes (neonatal morbidity, newborns of low and very low birthweight and preterm deliveries) and can be used as a predictor of them in women with gestational diabetes.
-
Original Articles
Obstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):673-679
11-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticlesObstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):673-679
11-01-2018Views133See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to analyze and compare obstetric and neonatal outcomes between Syrian refugees and ethnic Turkish women.
Methods
Retrospective, observational study. A total of 576 Syrian refugees and 576 ethnic Turkish women were included in this study, which was conducted between January 2015 and December 2015 at a tertiary maternity training hospital in Ankara, Turkey. The demographic characteristics, obstetric and neonatal outcomes were compared. The primary outcomes were pregnancy outcomes and cesarean rates between the groups
Results
The mean age was significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). Mean gravidity, proportion of adolescent pregnancies, proportion of pregnant women aged 12 to 19 years, and number of pregnancies at < 18 years were significantly higher among the refugee women (p< 0.001). Rates of antenatal follow-up, double testing, triple testing, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) screening, and iron replacement therapy were significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). The primary Cesarean section rate was significantly lower in the refugee group (p= 0.034). Pregnancies in the refugee group were more complicated, with higher rates of preterm delivery (< 37 weeks), preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), and low birth weight (< 2,500 g) when compared with the control group (4.2% versus 0.7%, p< 0.001; 1.6% versus 0.2%, p= 0.011; and 12% versus 5.8%, p< 0.001, respectively). Low education level (odds ratio [OR] = 1.7, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.5–0.1), and weight gain during pregnancy (OR = 1.7, 95% CI = 0.5–0.1) were found to be significant indicators for preterm birth/PPROM and low birthweight.
Conclusion
Syrian refugees had increased risks of certain adverse obstetric outcomes, including preterm delivery, PPROM, lower birth weight, and anemia. Several factors may influence these findings; thus, refugee women would benefit from more targeted care during pregnancy and childbirth.
-
Original Article
Tocolysis among Women with Preterm Birth: Associated Factors and Outcomes from a Multicenter Study in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):171-179
04-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleTocolysis among Women with Preterm Birth: Associated Factors and Outcomes from a Multicenter Study in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):171-179
04-01-2018Views176See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the use of tocolysis in cases of preterm birth due to spontaneous preterm labor in a Brazilian sample.
Methods
A sample of 1,491 women with preterm birth due to spontaneous preterm labor were assessed, considering treatment with tocolysis or expectant management, according to gestational age at birth (< 34 weeks and 34 to 36 þ 6 weeks) and drugs prescribed. The study took place in 20 Brazilian hospitals from April 2011 to July 2012. Bivariate analyses were conducted to evaluate associations with sociodemographic and obstetric characteristics and odds ratios with their respective 95% confidence intervals were estimated for maternal and neonatal outcomes.
Results
A total of 1,491 cases of preterm birth were considered. Tocolysis was performed in 342 cases (23%), 233 of which (68.1%) were delivered before 34 weeks. Within the expectant management group, 73% was late preterm and with more advanced labor at the time of admission. The most used drugs were calcium channel blockers (62.3%), followed by betamimetics (33%). Among the subjects in the tocolysis group, there were more neonatal and maternal complications (majority non-severe) and an occurrence of corticosteroid use that was 29 higher than in the expectant management group.
Conclusion
Tocolysis is favored in cases of earlier labor and also among thosewith less than 34 weeks of gestation, using preferably calcium channel blockers, with success in achieving increased corticosteroid use. Tocolysis, in general, was related to higher maternal and neonatal complication rates, which may be due to the baseline difference between cases at admission. However, these results should raise awareness to tocolysis use.
-
Original Article
Effect of Obesity on Gestational and Perinatal Outcomes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):330-336
07-01-2017
Summary
Original ArticleEffect of Obesity on Gestational and Perinatal Outcomes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):330-336
07-01-2017Views97See moreAbstract
Purpose
To assess the impact of pre-pregnancy obesity (body mass index [BMI] ≥30 kg/m2) on the gestational and perinatal outcomes.
Methods
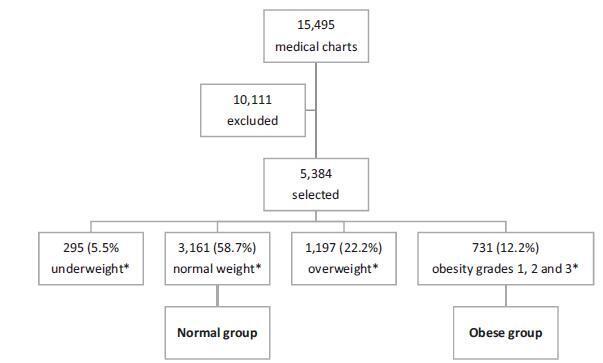
Retrospective cohort study of 731 pregnant women with a BMI ≥30 kg/m2 at the first prenatal care visit, comparing them with 3,161 women with a BMI between 18.5 kg/m2 and 24.9 kg/m2. Maternal and neonatal variables were assessed. Statistical analyses reporting the demographic features of the pregnant women (obese and normal) were performed with descriptive statistics followed by two-sided independent Student’s t tests for the continuous variables, and the chi-squared (χ2) test, or Fisher’s exact test, for the categorical variables. We performed a multiple linear regression analysis of newborn body weight based on the mother’s BMI, adjusted by maternal age, hyperglycemic disorders, hypertensive disorders, and cesarean deliveries to analyze the relationships among these variables. All analyses were performed with the R (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) for Windows software, version 3.1.0. A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Obesity was associated with older age [OR 9.8 (7.8-12.2); p < 0.01], hyperglycemic disorders [OR 6.5 (4.8-8.9); p < 0.01], hypertensive disorders [OR 7.6 (6.1-9.5); p < 0.01], caesarean deliveries [OR 2.5 (2.1-3.0); p < 0.01], fetal macrosomia [OR 2.9 (2.3-3.6); p < 0.01] and umbilical cord pH [OR 2.1 (1.4-2.9); p < 0.01). Conversely, no association was observed with the duration of labor, bleeding during labor, Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes after birth, gestational age, stillbirth and early neonatal mortality, congenital malformations, and maternal and fetal injury.
Conclusion
We observed that pre-pregnancy obesity was associated with maternal age, hyperglycemic disorders, hypertension syndrome, cesarean deliveries, fetal macrosomia, and fetal acidosis.