Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):535-539
To evaluate the obstetric outcomes of singleton high-risk pregnancies with a small size uterine fibroid.
This retrospective cohort study was conducted among 172 high-risk pregnant women who were followed-up by a single surgeon between 2016 and 2019. Pregnant women with preconceptionally diagnosed small size (< 5 cm) single uterine fibroids (n = 25) were compared with pregnant women without uterine fibroids (n = 147) in terms of obstetric outcomes.
There was no statistically significant difference between the groups in terms of adverse pregnancy outcomes. The size of the fibroids was increased in 60% of the cases, and the growth percentage of the fibroids was 25% during pregnancy. Intrapartum and short-term complication was not observed in women who underwent cesarean myomectomy.
Small size uterine fibroids seem to have no adverse effect on pregnancy outcomes even in high-risk pregnancies, and cesarean myomectomy may be safelyperformed in properly selected cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):476-485
To evaluate the factors associated with complete myomectomy in a single surgical procedure and the aspects related to the early complications.
A cross-sectional study with women with submucous myomas. The dependent variables were the complete myomectomy performed in a single hysteroscopic procedure, and the presence of early complications related to the procedure.
We identified 338 women who underwent hysteroscopic myomectomy. In 89.05% of the cases, there was a single fibroid to be treated. According to the classification of the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d’Obstétrique, FIGO, in French),most fibroids were of grade 0 (66.96%), followed by grade 1 (20.54%), and grade 2 (12.50%). The myomectomies were complete in 63.31% of the cases, and the factors independently associated with complete myomectomy were the diameter of the largest fibroid (prevalence ratio [PR]: 0.97; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 0.96-0.98) and the classification 0 of the fibroid according to the FIGO (PR: 2.04; 95%CI: 1.18-3.52). We observed early complications in 13.01% of the hysteroscopic procedures (4.44% presented excessive bleeding during the procedure, 4.14%, uterine perforation, 2.66%, false route, 1.78%, fluid overload, 0.59%, exploratory laparotomy, and 0.3%, postoperative infection). The only independent factor associated with the occurrence of early complications was incomplete myomectomy (PR: 2.77; 95%CI: 1.43-5.38).
Our results show that hysteroscopic myomectomy may result in up to 13% of complications, and the chance of complete resection is greater in small and completely intracavitary fibroids; women with larger fibroids and with a high degree of myometrial penetration have a greater chance of developing complications from hysteroscopic myomectomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(4):198-201
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000400008
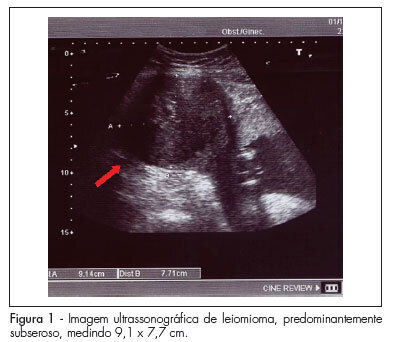
Uterine leiomyomas are characterized as a benign disease and are observed in 2 to 3% of all normal pregnancies. Out of these, about 10% may present complications during pregnancy. We present a case of a pregnant patient sought emergency obstetric care at the 17th week, complaining of severe pain, presenting with painful abdominal palpation and sudden positive decompression. Ultrasonography revealed a myoma nodule measuring 9.1 x 7.7 cm; the patient was hospitalized and medicated, being also submitted to laparotomy and myomectomy due to worsening of her condition. Prenatal care revealed no further abnormalities, with resolution of gestation at 39 weeks. The newborn weighed 3,315 g, with Apgar scores of 9 and 10. In such cases, clinical treatment should always be attempted and surgery should be considered only in selected cases, mainly in the impossibility of conservative treatment or when the patient's clinical features require immediate intervention. In this case, myomectomy was effective against maternal-fetal obstetric complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(6):324-328
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000600008
Leiomyomas are benign tumors. They appear in the myometrium and present a variable amount of fibrous conjunctive tissue. About 75% of the cases are not symptomatic and are usually found during abdominal, bimanual pelvic examination or during ultrasonography. The symptoms are directly related to the size, number and localization of the myomas. In the present review, the current clinical therapeutic procedures (oral anti-conceptive drugs, progestins and anti-progestins, analogues of the gonadothrophins’ releasing hormone (GnRH), and non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs), and also the surgical procedures (hysterectomy, myomectomy, embolization) are presented for the treatment of leiomyomas.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(3):167-169
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000300008
Uterine torsion is an unusual pathology of difficult diagnosis and it is generally associated with an enlargement of uterine volume combined with other alterations of the pelvic organs. This report presents a case of a malnourished elderly woman with acute abdomen and intraoperative diagnosis of myoma and uterine torsion of 360 degrees to the right. The uterus showed signs of severe ischemia.
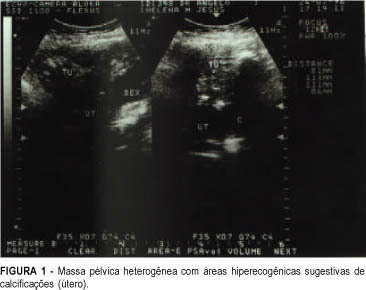
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(10):590-595
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001000004
Uterine myomas are common benign tumors of the female genital tract. The expression of growth factor signal transduction cascade components including the protooncogenes c-myc, c-fos, and c-jun seem to be involved in the development of myomas. PURPOSE: To compare the gene (mRNA) and protein expression of the protooncogenes c-fos, c-myc, and c-jun in human normal myometrium and leiomyoma. METHOD: A case-control study was performed. Samples were collected from 12 patients submitted to hysterectomy at the Hospital de Clínicas at Porto Alegre. The expression of the specific mRNA for c-myc, c-fos, c-jun, and beta-microglobulin was assessed through the RT-PCR technique, using specific primers to each gene. The protein expression of these protooncogenes was evaluated through the Western blot technique with specific antibodies. RESULTS: No statistically significant difference was observed in the gene expression for these protooncogenes between normal myometrium and leiomyoma (c-myc: 0,87 ± 0,08 vs 0,87 ± 0,08, p = 0,952; c-fos: 1,10 ± 0,17 vs 1,01 ± 0,11, p = 0,21; c-jun: 1,03 ± 0,12 vs 0,96 ± 0,09, p = 0,168, respectively). No statiscally significant difference was observed for the protein expression of these protooncogenes between normal myometrium and leiomyoma (c-myc: 1,36 ± 0,48 vs 1,53 ± 0,29, p = 0,569; c-fos: 8,85 ± 5,5 vs 6,56 ± 4,22, p = 0,434; e c-jun: 6,47 ± 3,04 vs 5,42 ± 2,03, p = 0,266, respectively). CONCLUSION: No difference was observed in the gene expression (transcription) nor in the protein expression (translation) of the protooncogenes c-myc, c-fos, and c-jun between leiomyoma and myometrium.
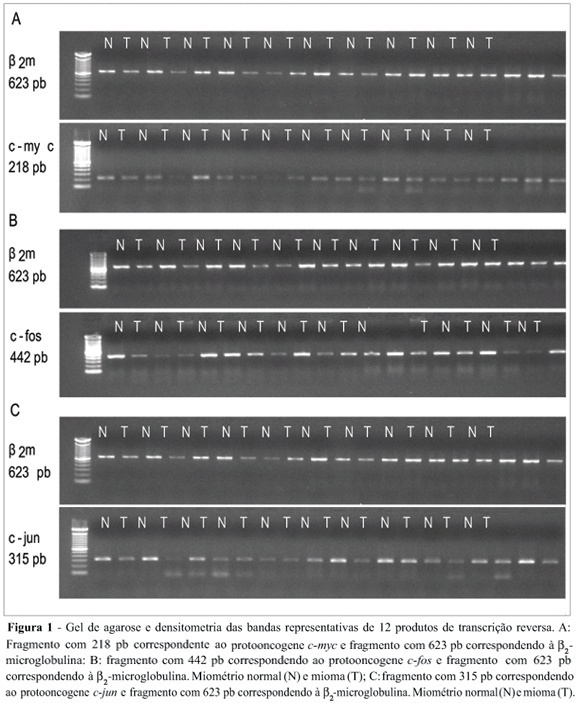
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(10):596-600
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001000005
PURPOSE: To analyze gestation evolution and deliveries after myoma treatment by embolization of the uterine arteries. METHODS: In the initial evaluation, 112 patients submitted to embolization of uterine arteries were included for treatment of myoma. From those, only nine wanted to be submitted to conservative treatment in order to keep their reproductive capacity. This procedure was indicated to the nine patients, since they were not susceptible to a conservative surgical treatment. They were submitted to embolization of the uterine arteries with particles of polyvinyl alcohol or embospheres with diameters ranging from 500 to 700 µm, and they have evolved without intercurrence. RESULTS: During the follow-up of these patients, there was a good clinical response with significant reduction in the uterus and myoma volumes. Four of them got pregnant, two had an early abortion and two evolved normally till the end of gestation with a term delivery. One of these had twins. CONCLUSION: Embolization of the uterine arteries is an option for the treatment of uterine myoma, and presents good clinical and anatomical results, allowing patients to preserve their reproductive capacity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):305-309
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400007
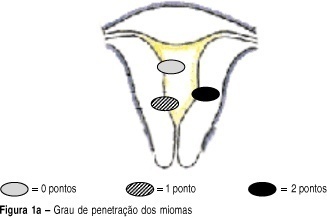
OBJECTIVE: to develop a new preoperative classification of submucous myomas to evaluate the viability and the degree of difficulty of hysteroscopic myomectomy. METHODS: forty-four patients were submitted to hysteroscopic resection of submucous myomas. The possibility of total resection of the myoma, the surgery duration, the fluid deficit, and the incidence of complications were evaluated. The myomas were classified by the Classification of the European Society of Endoscopic Surgery (CESES) and by the classification proposed (CP) by our group, that besides the degree of penetration of the myoma in the myometrium, adds the parameters: extent of the base of the myoma as related to the uterine wall, the size of the myoma in centimeters and its topography at the uterine cavity. For statistical analysis the Fisher test, the Student t test and the analysis of variance were used. Statistic significance was considered when the p-value was smaller than 0.05 in the bicaudal test. RESULTS: in 47 myomas the hysteroscopic surgery was considered complete. There was no significant difference among the three levels (0, 1 and 2) by CESES. By CP, the difference among the number of complete surgeries was significant (p=0.001) between the two levels (groups I and II). The difference between the surgery duration was significant when the two classifications were compared. In relation to the fluid deficit, just CP presented significant differences among the levels (p=0,02). CONCLUSIONS: the proposed classification includes more clues about the difficulties of the hysteroscopic myomectomy than the standard classification. It should be noted that the number of hysteroscopic myomectomies used for that analysis was modest, being interesting to evaluate the performance of the proposed classification in larger series of cases.